WHAT ARE THE STEPS TO CREATE A MEDICAL DEVICE AI BUILT IN
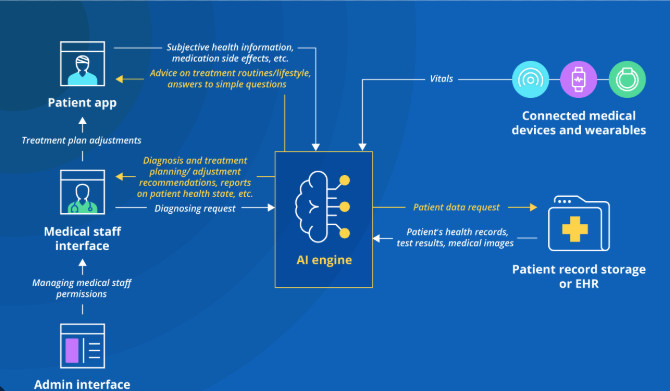
Creating a medical device with AI built in is a complex but rewarding journey that requires a multidisciplinary approach. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved:
1. IDENTIFY A CLINICAL NEED AND DEFINE THE PROBLEM:
- Start with a clear clinical need: What problem are you trying to solve? What are the current limitations of existing solutions?
- Define the specific task for AI: What will the AI do? How will it improve patient care or outcomes? Will it analyze images, predict risks, assist with diagnosis, or personalize treatment?
- Consider the target user: Who will use the device? What are their needs and expectations? Doctors, nurses, patients, or at-home users?
2. DATA ACQUISITION AND PREPARATION :
- Gather high-quality data: AI algorithms need vast amounts of data to learn and make accurate predictions. This data can come from various sources, such as:
- Electronic health records
- Clinical trials
- Medical images
- Sensor data
- Ensure data quality: The data must be accurate, relevant, and representative of the target population.
- Data preprocessing: Clean, normalize, and annotate the data to prepare it for AI training. This may involve removing errors, handling missing values, and labeling data for supervised learning.
3. AI MODEL DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION:
- Choose the right AI model: Select an appropriate AI model based on the specific task and data characteristics. This could include:
- Machine learning algorithms (e.g., support vector machines, random forests)
- Deep learning models (e.g., convolutional neural networks for image analysis, recurrent neural networks for time-series data)
- Natural language processing techniques (for text analysis)
- Train and validate the AI model: Train the AI model on the prepared data and validate its performance on a separate dataset. This helps ensure the model generalizes well to new, unseen data.
- Optimize the AI model: Fine-tune the model to achieve the desired accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and performance. This may involve adjusting hyperparameters, trying different architectures, or using techniques like transfer learning.
4. DEVICE DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT :
- Integrate the AI model into the device: This may involve embedding the AI model on the device itself (edge AI) or using a cloud-based approach where the AI processing happens on a remote server.
- Design the user interface: Create a user-friendly interface that allows users to interact with the device and interpret the AI’s output. Consider factors like ease of use, accessibility, and clear presentation of results.
- Develop the hardware and software: Build the physical device and develop the software that will run the AI model and user interface. This involves selecting appropriate sensors, microcontrollers, and communication protocols.
5. REGULATORY COMPLIANCE AND APPROVAL :
- Meet regulatory requirements: Medical devices must meet stringent regulatory requirements to ensure safety and effectiveness. This includes complying with standards such as:
- ISO 13485 (quality management system)
- IEC 62304 (medical device software)
- GDPR (data privacy)
- Obtain regulatory approval: Obtain regulatory approval from agencies like the FDA (in the US) or obtain the CE marking (in Europe) before marketing the device.
- Clinical validation: Conduct clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of the AI-powered medical device in a real-world setting.
6. DEPLOYMENT AND MONITORING:
- Deploy the device: Make the device available to healthcare providers and patients. This may involve manufacturing, distribution, and training.
- Monitor performance: Continuously monitor the device’s performance and collect feedback from users to identify areas for improvement. This helps ensure the AI model remains accurate and effective over time.
KEY CONSIDERATIONS:
- Explainability and transparency: It’s important to understand how the AI model makes decisions and to be able to explain its output to users, especially in healthcare where trust and transparency are crucial.
- Data privacy and security: Protect patient data and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Ethical considerations: Address ethical concerns related to AI, such as bias, fairness, and accountability. Ensure the AI model is not biased against certain patient groups and that its decisions are explainable and justifiable.
Creating a medical device with AI built in is a challenging but transformative process. By following these steps and considering the key considerations, you can develop innovative solutions that improve patient care and advance the field of medicine.
