HOW CLINICS CAN START USING TELEMEDICINE DEVICES: A COMPREHENSIVE IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE
The healthcare landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years, with telemedicine emerging as a critical component of modern medical practice. For clinics looking to expand their reach, improve patient outcomes, and remain competitive in today’s digital healthcare environment, implementing telemedicine devices represents both an opportunity and a necessity. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about starting your telemedicine journey, from understanding the technology to successful implementation and ongoing management.
UNDERSTANDING THE TELEMEDICINE REVOLUTION
Telemedicine has evolved far beyond simple video consultations. Today’s telemedicine ecosystem encompasses sophisticated diagnostic devices, remote monitoring systems, and integrated healthcare platforms that enable clinics to provide comprehensive care regardless of geographical barriers. The technology allows healthcare providers to conduct thorough examinations, monitor chronic conditions, and deliver specialized care to patients in remote locations or those with mobility constraints.
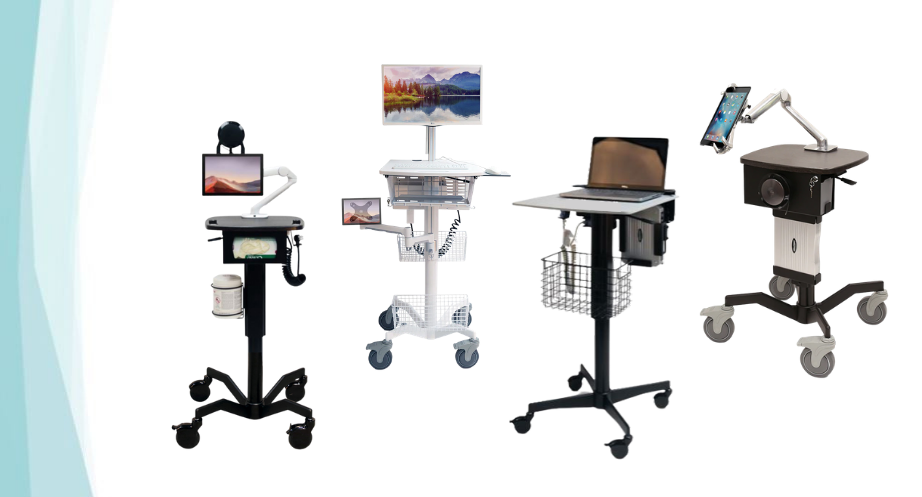

The integration of telemedicine devices into clinical practice has proven particularly valuable for improving healthcare access in underserved areas, reducing patient travel time and costs, and enabling more frequent monitoring of chronic conditions. According to recent studies, healthcare providers implementing telemedicine solutions have seen significant improvements in patient satisfaction rates and clinical outcomes while reducing operational costs.
Essential Telemedicine Devices for Modern Clinics
Primary Diagnostic Equipment
The foundation of any successful telemedicine program lies in having the right diagnostic equipment. Modern telemedicine kits typically include several essential devices that enable comprehensive remote examinations:
Digital Stethoscopes represent one of the most crucial components of telemedicine equipment. These advanced devices capture heart and lung sounds with exceptional clarity and can transmit audio data in real-time to remote physicians. Modern digital stethoscopes offer noise cancellation features, amplification capabilities, and the ability to record and store heart sounds for later analysis or consultation with specialists.

Digital Otoscopes enable detailed examination of the ear canal and tympanic membrane. These devices feature high-resolution cameras with specialized lighting systems that can capture clear images and videos of the ear’s interior. Many modern digital otoscopes can magnify images up to 50x, allowing for precise diagnosis of ear infections, wax buildup, and other auditory conditions.
Portable Ultrasound Devices have revolutionized remote diagnostic capabilities. These compact units can perform various imaging studies, from cardiac assessments to abdominal examinations. Modern portable ultrasound devices offer image quality comparable to traditional machines while being small enough to fit in a briefcase.
Remote Monitoring Equipment
Pulse Oximeters measure blood oxygen saturation and pulse rate, providing critical vital sign data that can be transmitted instantly to healthcare providers. These devices are particularly valuable for monitoring patients with respiratory conditions, cardiac issues, or those recovering from surgery.
Digital Blood Pressure Monitors equipped with Bluetooth connectivity can automatically transmit readings to electronic health records, enabling continuous monitoring of hypertensive patients without requiring office visits.
Portable ECG Devices can capture single-lead or multi-lead electrocardiograms, allowing for cardiac monitoring and arrhythmia detection. These devices are particularly valuable for patients with known cardiac conditions or those experiencing chest pain.

Advanced Examination Tools
Dermatoscopes enable detailed skin examinations and are essential for teledermatology applications. These devices can capture high-resolution images of skin lesions, moles, and other dermatological conditions, enabling remote diagnosis and monitoring of skin conditions.
Examination Cameras provide high-definition video and still image capabilities for general examination purposes. These cameras often feature specialized lighting and magnification capabilities to capture detailed images of wounds, rashes, and other visible symptoms.
SETTING UP YOUR TELEMEDICINE INFRASTRUCTURE
TECHNOLOGY REQUIREMENTS
Implementing telemedicine devices requires robust technological infrastructure to ensure seamless operation and patient safety. The foundation begins with reliable, high-speed internet connectivity. Clinics should have broadband internet with upload and download speeds of at least 25 Mbps to handle multiple simultaneous video consultations and data transmission from various medical devices.
Network Security is paramount when dealing with protected health information. Clinics must implement enterprise-grade security measures including firewalls, VPN connections, and encrypted data transmission protocols. All telemedicine devices should connect to secure networks separate from general office internet access.
Hardware Integration involves connecting various medical devices to a centralized platform that can manage data collection, storage, and transmission. This typically requires compatible software platforms that can interface with multiple device types and integrate with existing electronic health record systems.
Physical Space Considerations
Creating an effective telemedicine consultation room requires careful attention to lighting, acoustics, and equipment positioning. The consultation space should have consistent, natural lighting supplemented by professional lighting equipment to ensure clear video quality. Sound management is equally important, with acoustic treatments to minimize echo and background noise interference.
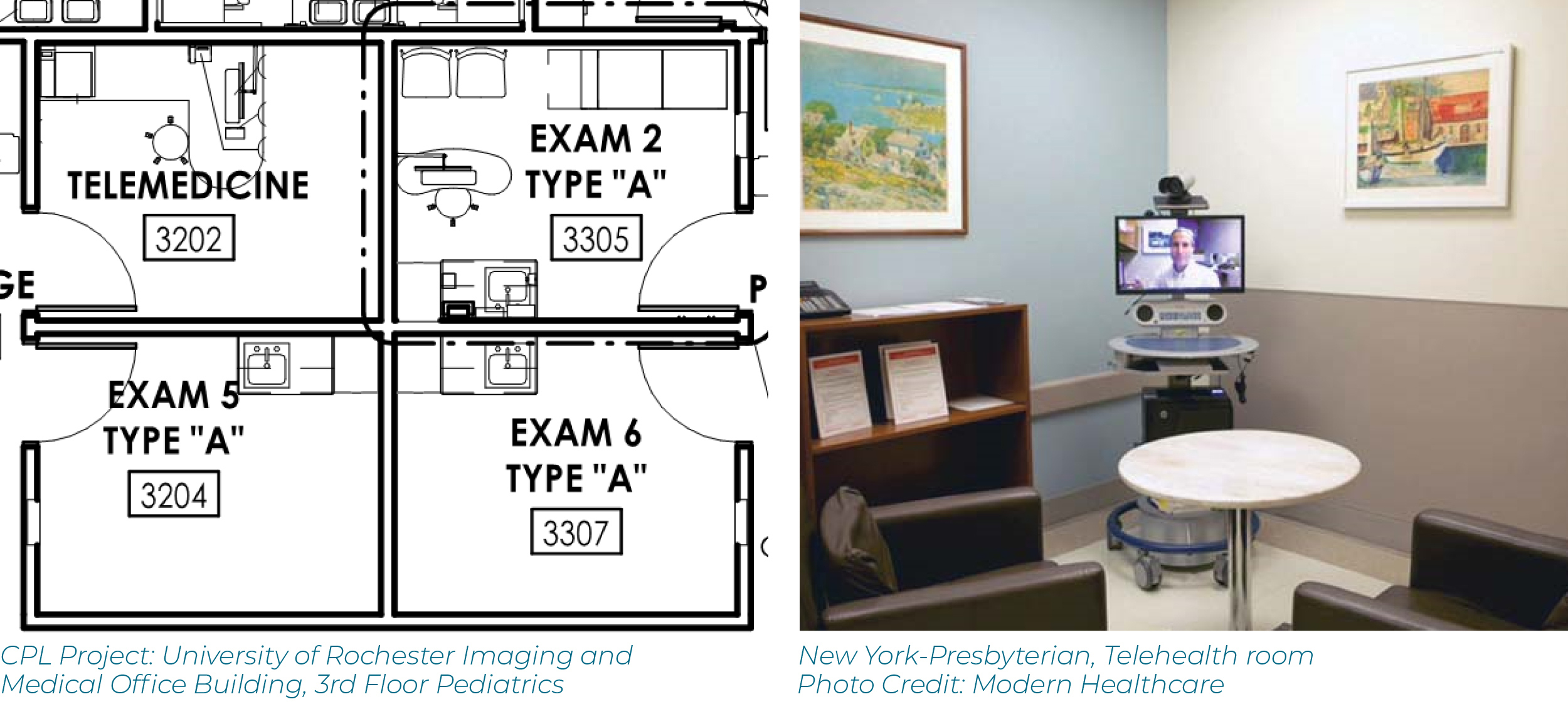
Equipment placement should follow ergonomic principles, allowing healthcare providers to easily access and operate devices while maintaining natural interaction with patients on screen. Consider installing ceiling-mounted or wall-mounted equipment arms to keep devices organized and easily accessible.
Implementation Costs and Budget Planning
Initial Investment Requirements
The cost of implementing telemedicine devices varies significantly based on the scope of services and quality of equipment selected. Basic telemedicine setups for primary care clinics typically range from $15,000 to $50,000, while comprehensive systems with advanced diagnostic capabilities can exceed $100,000.
Equipment Costs for a standard telemedicine kit including digital stethoscope, otoscope, pulse oximeter, blood pressure monitor, and basic examination camera typically range from $5,000 to $15,000. High-end professional-grade equipment can cost significantly more but offers superior diagnostic capabilities and durability.
Software and Platform Costs vary depending on whether clinics choose cloud-based solutions or on-premise systems. Subscription-based platforms typically cost between $200 to $500 per provider per month, while comprehensive enterprise solutions may require substantial upfront licensing fees.
Infrastructure Upgrades may be necessary to support telemedicine operations, including network improvements, security enhancements, and physical space modifications. These costs can range from $10,000 to $30,000 depending on existing infrastructure quality.
Ongoing Operational Expenses
Beyond initial setup costs, clinics must budget for ongoing operational expenses including software licensing, equipment maintenance, staff training, and technical support. Monthly operational costs typically range from $1,000 to $5,000 depending on the scale of the telemedicine program.
Maintenance and Support contracts are essential for ensuring device reliability and minimizing downtime. Most medical device manufacturers offer comprehensive service agreements that include regular maintenance, software updates, and technical support for approximately 10-15% of the initial equipment cost annually.
REGULATORY COMPLIANCE AND HIPAA REQUIREMENTS
HIPAA COMPLIANCE FRAMEWORK
All telemedicine implementations must comply with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requirements for protecting patient health information. This includes ensuring that all video conferencing platforms, data storage systems, and communication channels are HIPAA-compliant and include appropriate business associate agreements with technology vendors.
Data Encryption is mandatory for all patient information transmitted through telemedicine systems. This includes both data in transit during video calls and device data transmission, as well as data at rest in storage systems. Clinics must implement end-to-end encryption using industry-standard protocols.
Access Controls must be implemented to ensure that only authorized personnel can access patient information through telemedicine systems. This includes multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, and comprehensive audit logging of all system access and activities.
State Licensing and Credentialing
Healthcare providers must ensure they maintain appropriate licensing for telemedicine practice in all states where they provide services. Many states have specific telemedicine licensing requirements and may require additional certifications for remote practice.
Interstate Practice regulations continue to evolve, with some states participating in interstate medical licensure compacts that facilitate cross-state practice. Clinics should consult with legal counsel to ensure compliance with all applicable state regulations.
STAFF TRAINING AND WORKFLOW INTEGRATION
COMPREHENSIVE TRAINING PROGRAMS
Successful telemedicine implementation requires comprehensive staff training that goes beyond basic technology operation. Training programs should be modular and role-specific, addressing the unique needs of different staff members from clinical providers to administrative support.
Clinical Training focuses on adapting examination techniques for remote practice, learning to use diagnostic devices effectively, and developing communication skills specific to telemedicine consultations. Providers must learn to conduct thorough examinations using available technology while maintaining patient rapport through video interaction.
Technical Training ensures that all staff members can operate telemedicine equipment effectively, troubleshoot common technical issues, and manage patient data securely. This includes training on device operation, software navigation, and emergency backup procedures.

Workflow Optimization
Integrating telemedicine into existing clinical workflows requires careful planning and gradual implementation. Successful integration involves mapping current patient flow processes and identifying optimal points for telemedicine intervention.
Appointment Scheduling systems must be adapted to accommodate both in-person and virtual visits, with clear protocols for determining appropriate visit types based on patient needs and clinical requirements.
Documentation Processes should be standardized to ensure consistent record-keeping across all visit types. Electronic health record systems should be configured to capture telemedicine-specific data while maintaining compatibility with traditional documentation requirements.
ELECTRONIC HEALTH RECORD INTEGRATION
SEAMLESS DATA INTEGRATION
Modern telemedicine platforms must integrate seamlessly with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems to maintain continuity of care and ensure comprehensive patient documentation. This integration allows providers to access complete patient histories during telemedicine consultations while automatically recording visit notes and diagnostic data.
Interoperability Standards such as HL7 FHIR enable different healthcare systems to communicate effectively, allowing telemedicine devices to share data directly with EHR platforms. This reduces manual data entry requirements and minimizes the risk of transcription errors.
Real-Time Data Synchronization ensures that information collected during telemedicine encounters is immediately available to other healthcare providers, enabling coordinated care and reducing the risk of medication interactions or duplicate testing.
Data Management Strategies
Effective telemedicine implementations require robust data management strategies that address storage, backup, and retrieval requirements. Cloud-based storage solutions offer scalability and accessibility advantages but must be carefully evaluated for security and compliance requirements.
Backup and Recovery procedures are essential for protecting patient data and ensuring system availability. Clinics should implement automated backup systems with regular testing to ensure data can be recovered quickly in the event of system failures.
RETURN ON INVESTMENT AND BUSINESS BENEFITS
FINANCIAL BENEFITS
Telemedicine implementations typically demonstrate positive return on investment within 12-24 months of deployment. The primary financial benefits include reduced overhead costs, increased patient capacity, improved no-show rates, and the ability to serve patients in broader geographic areas.
Revenue Enhancement comes from the ability to see more patients per day, reduced cancellation rates, and access to new patient populations. Many telemedicine visits can be conducted more efficiently than traditional in-person appointments, allowing providers to increase their daily patient volume.
Cost Reduction is achieved through decreased facility overhead, reduced administrative costs, and improved staff efficiency. Telemedicine can also reduce the need for expensive emergency department visits and hospital readmissions through better chronic disease management.
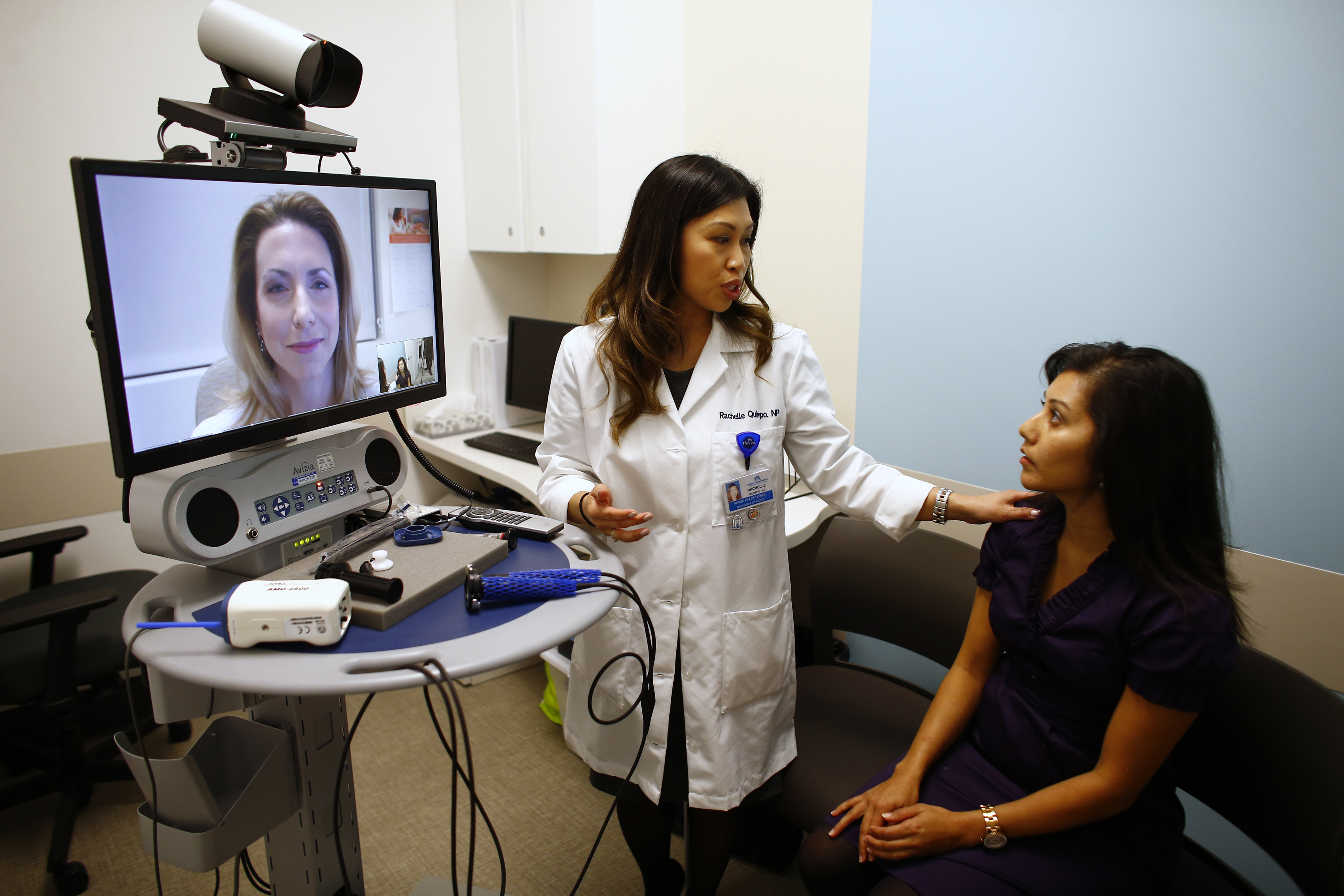
Quality of Care Improvements
Studies have consistently shown that telemedicine can improve patient outcomes through increased access to care, more frequent monitoring of chronic conditions, and reduced barriers to specialist consultation. Patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart failure show improved clinical indicators when managed through telemedicine programs.
Patient Satisfaction rates are typically higher for telemedicine services due to increased convenience, reduced travel time, and improved access to care. Many patients appreciate the ability to receive medical attention without leaving their homes or workplaces.
BEST PRACTICES FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION
PHASED IMPLEMENTATION APPROACH
The most successful telemedicine implementations follow a phased approach that begins with pilot programs and gradually expands to full-scale deployment. This approach allows clinics to identify and resolve technical issues, refine workflows, and train staff incrementally.
Phase 1 typically involves implementing basic video consultation capabilities for existing patients with established relationships. This allows staff to become comfortable with the technology while serving patients who are already familiar with the clinic’s care approach.
Phase 2 expands services to include remote monitoring capabilities and basic diagnostic devices. This phase focuses on developing efficient workflows for data collection, analysis, and follow-up care coordination.
Phase 3 introduces advanced diagnostic capabilities and expands patient populations to include new patients and those requiring specialized care. This phase may also include integration with other healthcare systems and providers.
Quality Assurance and Monitoring
Continuous quality improvement is essential for maintaining high standards of care in telemedicine practice. This involves regular monitoring of clinical outcomes, patient satisfaction, and technical performance metrics.
Clinical Quality Metrics should include diagnostic accuracy, patient outcomes, medication adherence rates, and follow-up compliance. These metrics help identify areas for improvement and ensure that telemedicine care meets or exceeds traditional care standards.
Technical Performance Monitoring includes tracking system uptime, connection quality, device reliability, and user experience metrics. Regular monitoring helps identify potential issues before they impact patient care.
FUTURE CONSIDERATIONS AND TECHNOLOGY EVOLUTION
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
The telemedicine field continues to evolve rapidly, with new technologies promising even greater capabilities for remote care delivery. Artificial intelligence integration is beginning to enhance diagnostic accuracy and automate routine tasks, while virtual and augmented reality technologies offer new possibilities for remote medical training and patient education.
Artificial Intelligence applications in telemedicine include automated image analysis, predictive analytics for chronic disease management, and clinical decision support systems. These technologies can enhance provider capabilities and improve diagnostic accuracy.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices are expanding the possibilities for continuous patient monitoring and automated data collection. Smart medical devices can provide real-time health data and alert providers to changes in patient condition.
REGULATORY EVOLUTION
Healthcare regulations continue to evolve to accommodate the growing role of telemedicine in healthcare delivery. Clinics should stay informed about changing regulations and prepare for ongoing compliance requirements as the regulatory landscape continues to develop.
Reimbursement Policies are expanding to cover more telemedicine services, making these programs increasingly financially viable. However, reimbursement rules vary by state and insurance provider, requiring careful attention to billing and documentation requirements.
CONCLUSION
Implementing telemedicine devices in clinical practice represents a significant opportunity to improve patient care, expand service reach, and enhance operational efficiency. Success requires careful planning, appropriate technology selection, comprehensive staff training, and ongoing commitment to quality improvement.
The initial investment in telemedicine technology and infrastructure is substantial, but the long-term benefits in terms of improved patient outcomes, increased revenue, and operational efficiency make it a worthwhile investment for most clinics. As healthcare continues to evolve toward more patient-centered, technology-enabled delivery models, telemedicine will become increasingly essential for maintaining competitive advantage and meeting patient expectations.
Clinics considering telemedicine implementation should begin with a thorough assessment of their current capabilities, patient needs, and strategic objectives. Working with experienced telemedicine consultants and technology partners can help ensure successful implementation and maximize the benefits of this transformative technology.
The future of healthcare is increasingly digital, and telemedicine devices are at the forefront of this transformation. Clinics that embrace these technologies now will be well-positioned to thrive in the evolving healthcare landscape while providing their patients with the convenient, high-quality care they expect and deserve.
This comprehensive guide provides clinics with the essential information needed to successfully implement telemedicine devices and transform their practice for the digital age. For specific implementation support and technology recommendations, consult with qualified telemedicine specialists and technology vendors who can provide customized solutions based on your clinic’s unique needs and requirements.
