Blog
ARE BATTERY-POWERED INFUSION PUMPS SAFE? A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF MODERN MEDICAL DEVICE TECHNOLOGY
Battery-powered infusion pumps have revolutionized healthcare delivery by providing portable, precise medication administration capabilities that enhance patient mobility and improve quality of life. These sophisticated medical devices, ranging from large-volume pumps to ambulatory syringe drivers, play a critical role in modern healthcare settings including hospitals, hospices, and home care environments. Understanding their safety profile is essential for healthcare providers, patients, and families who rely on these life-sustaining technologies.

Understanding Battery-Powered Infusion Pump Technology
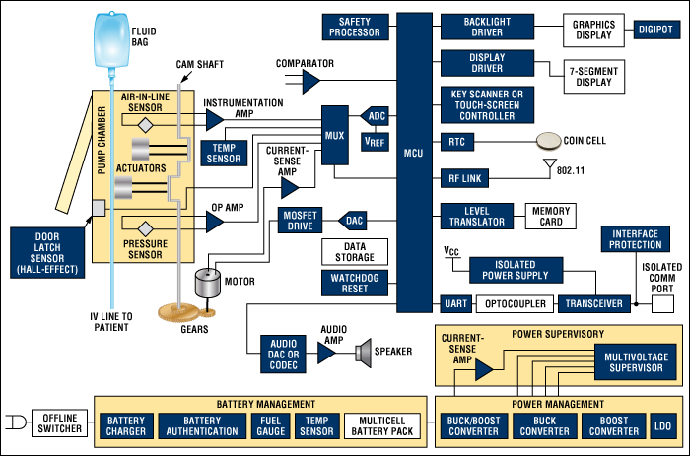
Battery-powered infusion pumps are medical devices designed to deliver fluids, medications, and nutrients into a patient’s body in precisely controlled amounts. Unlike their predecessors that required constant electrical connection, modern battery-powered units provide unprecedented flexibility and mobility for patients while maintaining accuracy and reliability in medication delivery.
These devices utilize advanced lithium-ion battery technology, sophisticated microprocessor controls, and multiple safety systems to ensure consistent performance. The integration of smart pump technology with dose error reduction systems (DERS) has significantly enhanced safety profiles compared to earlier generations of infusion equipment.
FDA Approval and Regulatory Framework
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies infusion pumps as Class II medical devices, requiring 510(k) premarket clearance to demonstrate safety and effectiveness. As of 2024, portable infusion pumps are FDA approved, though the agency emphasizes caution when operating without direct medical professional supervision FDA Infusion Pumps.
The regulatory framework encompasses comprehensive requirements for:
- Design Controls: Rigorous testing of hardware and software components
- Biocompatibility Testing: Ensuring materials are safe for patient contact
- Electrical Safety Standards: Compliance with IEC 60601 medical electrical equipment standards
- Battery Performance Requirements: Specific standards for battery life, charging, and failure modes
- Software Validation: Extensive testing of programming algorithms and user interfaces
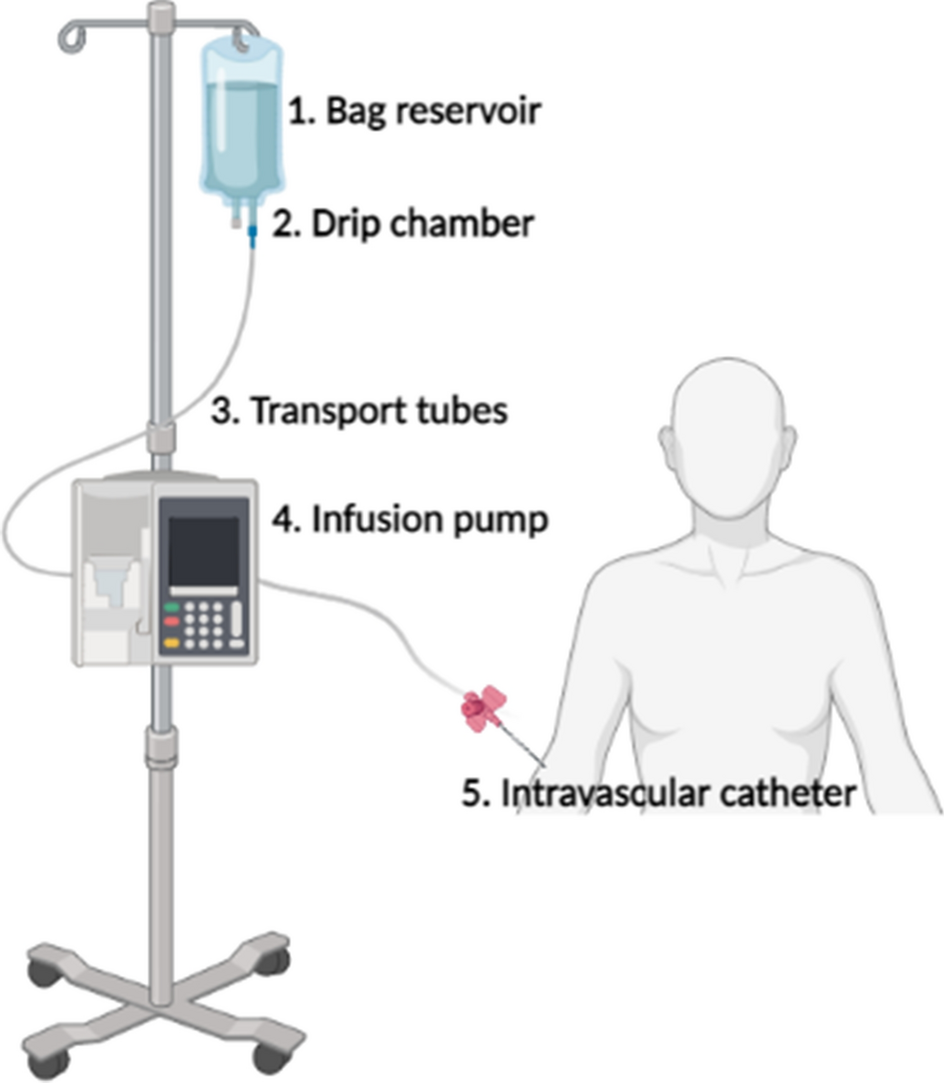
Advanced Safety Features and Risk Mitigation
Modern battery-powered infusion pumps incorporate multiple layers of safety features designed to prevent medication errors and ensure reliable operation:
Intelligent Alarm Systems
Contemporary infusion pumps feature sophisticated alarm systems that provide audible and visual alerts for various conditions including:
- Low Battery Warnings: Multiple-level alerts beginning well before battery depletion
- Occlusion Detection: Immediate notification of flow restrictions or blockages
- Air-in-Line Detection: Advanced sensors that identify air bubbles in the delivery system
- Dose Limit Alerts: Programming safeguards that prevent potentially dangerous dosing errors

Battery Technology and Power Management
Modern infusion pumps utilize high-performance lithium-ion batteries with advanced management systems:
Battery Specifications:
- Extended operational life (typically 8-12 hours of continuous use)
- Rapid charging capabilities (often 2-3 hour full charge times)
- Temperature monitoring and protection
- Multiple power backup systems
Power Management Features:
- Real-time battery monitoring with precise remaining time calculations
- Automatic power conservation modes
- Graceful shutdown procedures to protect patient safety
- Battery health monitoring and replacement alerts

Clinical Safety Evidence and Performance Data
Extensive clinical evidence supports the safety and efficacy of battery-powered infusion pumps when used according to manufacturer guidelines and proper clinical protocols.
Adverse Event Analysis
From 2005 to 2009, the FDA received approximately 56,000 reports of adverse events associated with infusion pump use. However, analysis revealed that many issues were related to user error, inadequate training, or older pump technologies rather than inherent safety problems with modern battery-powered systems FDA Infusion Pump Safety.
Most Common Historical Issues:
- Software defects in older systems
- User interface complications
- Mechanical or electrical failures
- Inadequate alarm systems
Modern Improvements:
- Enhanced software validation processes
- Intuitive user interfaces with error prevention
- Robust mechanical design with redundant safety systems
- Advanced alarm management with customizable settings

Smart Pump Technology and Error Prevention
The evolution toward “smart” infusion pumps represents a significant advancement in patient safety. These devices incorporate drug libraries, dose calculation assistance, and clinical decision support systems that dramatically reduce the risk of medication errors.
Dose Error Reduction Systems (DERS)
Smart pumps feature comprehensive drug libraries containing:
- Maximum and minimum dose limits for specific medications
- Age-based dosing recommendations
- Weight-based calculation assistance
- Drug interaction warnings
- Clinical unit-specific protocols
Integration Capabilities
Modern battery-powered infusion pumps increasingly integrate with:
- Electronic health records (EHRs)
- Barcode medication administration systems
- Pharmacy information systems
- Remote monitoring platforms
- Clinical decision support tools
Home Use Safety Considerations
The extension of infusion pump therapy to home settings has introduced new safety considerations and requirements for patient and caregiver education.
Patient Training Requirements
Comprehensive training programs must address:
- Device Operation: Proper startup, programming, and shutdown procedures
- Battery Management: Charging schedules, low battery recognition, and backup procedures
- Problem Recognition: Understanding alarm conditions and appropriate responses
- Emergency Procedures: When to contact healthcare providers and emergency services
- Maintenance: Basic cleaning and care requirements
Safety Protocols for Home Use
Essential safety protocols include:
- Regular medication verification and expiration date checking
- Proper hand hygiene before device handling
- Maintenance of clean workspace areas
- Appropriate storage of medications and supplies
- 24-hour emergency contact access
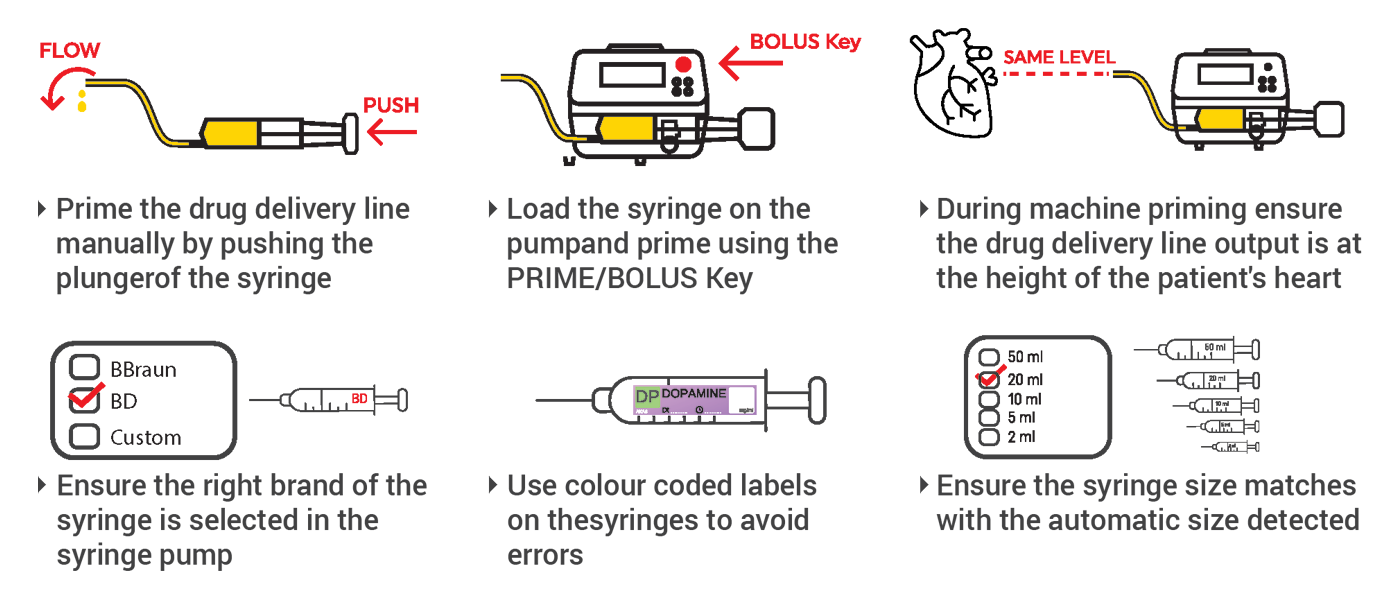
Ambulatory Infusion Pump Safety Profile
Ambulatory infusion pumps, designed for maximum patient mobility, present unique safety considerations that have been extensively studied by healthcare safety organizations.
Recent Safety Investigations
The UK Health Services Safety Investigations Body (HSSIB) conducted a comprehensive investigation into ambulatory infusion pump safety, revealing important insights:
Key Findings:
- Current alarm systems may not effectively notify staff in all clinical environments
- Environmental factors significantly impact staff ability to respond to alarms
- Patient education about device interaction is often insufficient
- Standardized checking protocols are essential for safe operation
Safety Recommendations:
- Enhanced staff training on device-specific protocols
- Improved alarm notification systems
- Standardized safety protocols across healthcare settings
- Better integration with hospital monitoring systems

Battery Safety and Reliability Standards
Battery safety represents a critical component of infusion pump safety, with specific standards governing design, testing, and performance requirements.
Battery Safety Standards
Modern infusion pump batteries must comply with:
- IEC 62133: Secondary cells and batteries for portable applications
- UN 38.3: Transportation testing for lithium batteries
- UL 2089: Health/medical electrical equipment safety standards
- ISO 14971: Risk management for medical devices
Performance Requirements
Battery systems must demonstrate:
- Consistent performance across temperature ranges
- Resistance to physical impact and vibration
- Protection against overcharging and deep discharge
- Fail-safe operation during battery replacement
- Accurate remaining capacity indication

Risk Management and Mitigation Strategies
Comprehensive risk management approaches address potential safety concerns through multiple layers of protection and monitoring.
Clinical Risk Mitigation
Healthcare organizations implement various strategies to minimize risks:
Equipment Management:
- Regular preventive maintenance schedules
- Battery performance monitoring and replacement protocols
- Software update management
- Inventory tracking and expiration monitoring
Staff Training and Competency:
- Initial device-specific training programs
- Annual competency assessments
- Ongoing education about software updates and new safety features
- Error reporting and learning systems
Environmental Considerations:
- Noise level assessments in patient care areas
- Lighting adequacy for visual alarm recognition
- Space planning for optimal device placement
- Communication system integration
Technological Advances and Future Safety Improvements
Ongoing technological developments continue to enhance infusion pump safety through innovative features and capabilities.
Emerging Technologies
Wireless Connectivity:
- Real-time monitoring and alert notification
- Remote programming capabilities
- Integration with wearable health monitors
- Cloud-based data analytics for population health insights
Artificial Intelligence Integration:
- Predictive analytics for equipment failures
- Personalized dosing recommendations
- Pattern recognition for early problem detection
- Automated documentation and reporting
Advanced Sensors:
- Improved occlusion detection sensitivity
- Enhanced air-in-line detection
- Pressure monitoring and flow verification
- Temperature and humidity sensing

Comparative Safety Analysis
When compared to traditional gravity-fed infusion methods or manual medication administration, battery-powered infusion pumps demonstrate superior safety profiles:
Accuracy and Precision Benefits
- Flow Rate Accuracy: Typically ±5% or better compared to ±25% for gravity systems
- Dosing Consistency: Maintains prescribed rates regardless of patient position or activity
- Documentation: Automatic recording of delivered volumes and timing
- Error Reduction: Smart pump features prevent many common medication errors
Reliability Metrics
Modern infusion pumps demonstrate:
- Mean time between failures (MTBF) exceeding 5,000 hours
- Battery life reliability with 95% confidence intervals
- Software stability with extensive validation testing
- Hardware durability through accelerated aging tests
Special Population Considerations
Battery-powered infusion pumps require special considerations when used with vulnerable populations including pediatric patients, elderly individuals, and those with cognitive impairments.
Pediatric Safety Measures
- Weight-based dosing calculations with enhanced precision
- Smaller volume delivery capabilities
- Child-resistant features and tamper detection
- Specialized alarm settings for pediatric environments
- Age-appropriate patient and family education materials
Geriatric Considerations
- Enhanced visual and audible alarm features
- Simplified user interfaces for caregiver operation
- Fall prevention considerations for ambulatory use
- Medication interaction monitoring
- Cognitive assessment integration for home use safety

Quality Assurance and Regulatory Oversight
Comprehensive quality assurance programs ensure ongoing safety and effectiveness of battery-powered infusion pumps throughout their operational lifecycle.
Manufacturing Quality Controls
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance
- Statistical process control for critical components
- Batch testing and release protocols
- Traceability systems for all components
- Post-market surveillance programs
Post-Market Monitoring
- Adverse event reporting and analysis
- Software update deployment and monitoring
- Battery performance tracking
- User feedback integration
- Continuous improvement programs
International Safety Standards and Harmonization
Global harmonization of safety standards ensures consistent safety profiles across different markets and healthcare systems.
Key International Standards
- ISO 14971: Risk management for medical devices
- IEC 60601-1: General requirements for basic safety and essential performance
- IEC 60601-2-24: Particular requirements for infusion pumps and controllers
- ISO 62304: Medical device software lifecycle processes
- ISO 13485: Quality management systems for medical devices
Conclusion: Comprehensive Safety Assessment
Battery-powered infusion pumps represent a mature, well-regulated medical technology with extensive safety features and proven clinical effectiveness. When properly manufactured, maintained, and operated according to established protocols, these devices demonstrate excellent safety profiles that significantly enhance patient care while maintaining mobility and quality of life.
The key factors contributing to infusion pump safety include:
Regulatory Excellence: Comprehensive FDA oversight and international standards compliance ensure rigorous safety testing and validation before market release.
Advanced Technology: Modern battery systems, smart pump features, and sophisticated alarm systems provide multiple layers of protection against potential failures or errors.
Clinical Evidence: Extensive real-world data demonstrates improved outcomes and reduced adverse events compared to alternative medication delivery methods.
Ongoing Improvement: Continuous technological advancement and post-market surveillance ensure that safety features continue to evolve and improve.
Proper Implementation: Success depends on appropriate training, maintenance, and operational protocols that support safe clinical use.
While no medical device is entirely risk-free, battery-powered infusion pumps have demonstrated remarkable safety improvements over the past decade through technological advancement, regulatory oversight, and clinical best practices. Healthcare providers and patients can have confidence in these devices when they are properly selected, implemented, and maintained according to established safety protocols.
The future of infusion pump safety continues to evolve with emerging technologies including artificial intelligence, advanced connectivity, and enhanced user interfaces that promise even greater safety margins and improved patient outcomes. As these technologies mature, battery-powered infusion pumps will continue to play an increasingly important role in delivering safe, effective, and patient-centered care across all healthcare settings.
