HOW SMART SENSORS ARE CHANGING MEDICAL DEVICES: THE REVOLUTIONARY IMPACT ON HEALTHCARE TECHNOLOGY

The healthcare industry is experiencing an unprecedented transformation driven by the integration of smart sensors into medical devices. These intelligent, connected sensors are revolutionizing patient care by enabling real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and personalized treatment approaches. From wearable fitness trackers to implantable cardiac monitors, smart sensors are fundamentally changing how we approach healthcare delivery, patient monitoring, and medical intervention.
The Evolution of Medical Device Technology

The medical device industry has witnessed remarkable evolution over the past decade. While traditional medical instruments like stethoscopes have remained relatively unchanged for over 70 years, the introduction of smart sensor technology has catalyzed a revolutionary shift in medical device capabilities. Smart medical devices leverage artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning algorithms, and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity to provide unprecedented insights into patient health and treatment outcomes.
Smart medical devices typically fall into two primary categories:
1. Informational Devices: These collect and display health data for patients and healthcare providers, including wearable fitness trackers, smart scales, and continuous glucose monitors. This data empowers patients to make informed health decisions and enables healthcare providers to track patient progress remotely.
2. Automated Health Management Devices: These actively manage patient health by providing real-time feedback and recommendations using AI algorithms to analyze health data and deliver personalized insights for improved health outcomes. Amphenol Sensors
Key Categories of Smart Medical Sensors

Wearable Sensors
Wearable sensors represent the most visible and rapidly growing segment of smart medical devices. These on-body devices provide continuous health monitoring capabilities that were previously only available in clinical settings.
Smartwatches and Fitness Trackers: Modern smartwatches have evolved far beyond simple activity tracking. Today’s devices can monitor heart rate variability, detect irregular heart rhythms, measure blood oxygen levels, and even perform electrocardiograms (ECGs). These capabilities enable early detection of cardiovascular issues and provide valuable data for healthcare providers.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): These devices have revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time glucose readings without the need for frequent finger pricks. Smart CGMs can alert patients to dangerous glucose levels and integrate with insulin pumps for automated delivery adjustments.
Smart Patches: Adhesive sensor patches can monitor various vital signs including heart rate, respiratory rate, and body temperature. These devices are particularly valuable for post-surgical monitoring and chronic disease management.
Biosensors
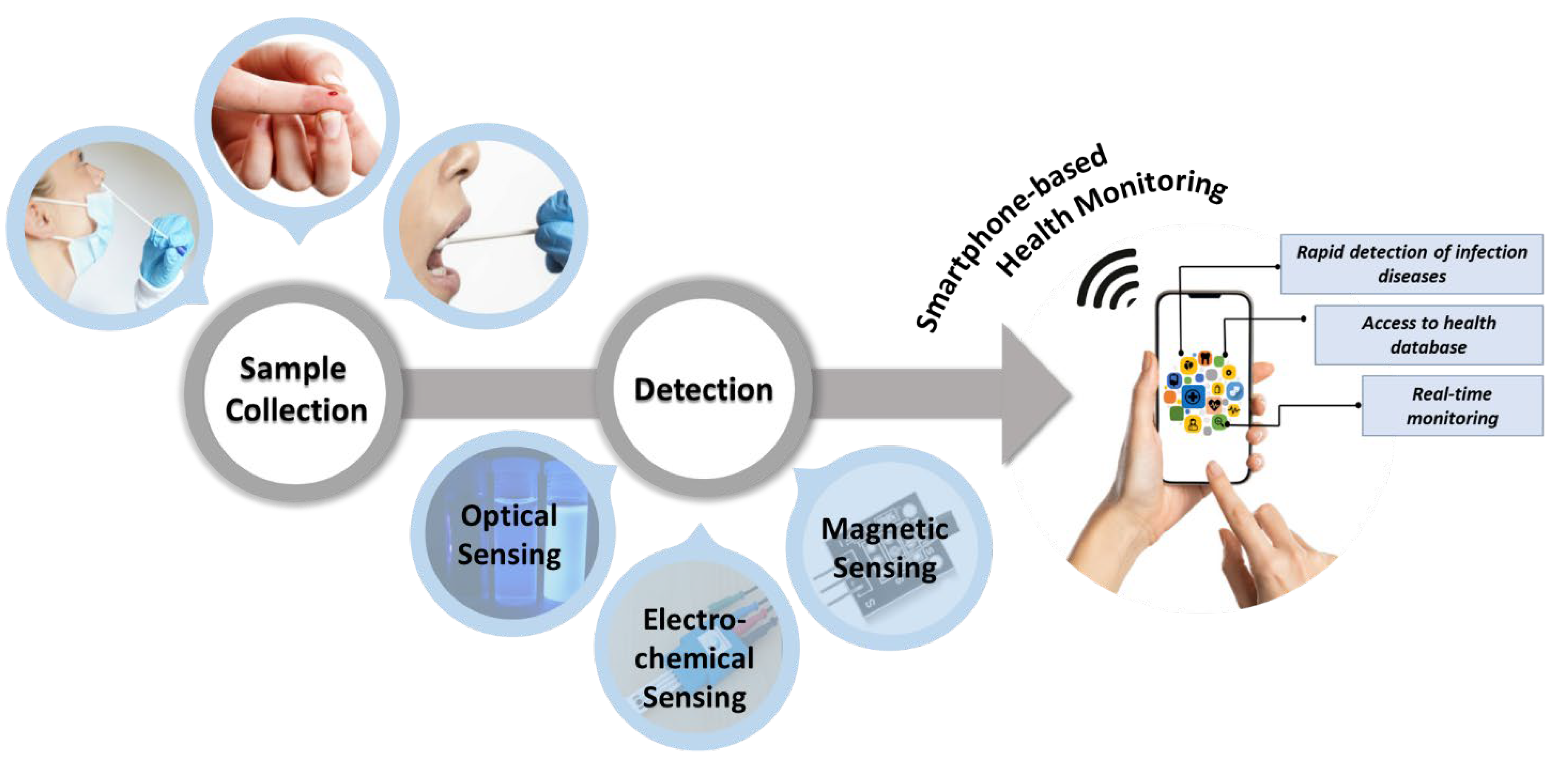
Biosensors analyze biological data and provide real-time health information based on physiological markers. These sensors can detect:
- Cardiac biomarkers for heart disease monitoring
- Metabolic indicators for diabetes and obesity management
- Inflammatory markers for immune system assessment
- Neurological signals for brain health monitoring
The integration of biosensors with AI algorithms enables predictive analytics that can identify health issues before they become critical, facilitating preventive interventions.
Implantable Smart Sensors

Implantable sensors represent the cutting edge of medical device technology, providing continuous internal monitoring capabilities:
Smart Pacemakers: Modern pacemakers incorporate multiple sensors that monitor heart rhythm, activity levels, and even detect early signs of heart failure. They can automatically adjust pacing parameters and transmit data to healthcare providers.
Neurostimulators: These devices use sensors to monitor brain activity and adjust stimulation parameters for conditions like Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, and chronic pain.
Orthopedic Implants: Smart joint replacements can monitor healing progress, detect complications, and provide data on patient mobility and activity levels.
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Integration

The integration of smart sensors with IoT technology has created the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), a connected ecosystem of medical devices that can communicate with each other and healthcare systems. This connectivity enables:
Real-time Data Transmission: Patient data can be instantly transmitted to healthcare providers, enabling immediate intervention when necessary.
Remote Patient Monitoring: Patients can be monitored continuously from their homes, reducing hospital readmissions and improving quality of life.
Predictive Analytics: Large datasets from multiple sensors can be analyzed to predict health events and optimize treatment protocols.
Automated Care Coordination: IoMT devices can automatically schedule appointments, refill prescriptions, and coordinate care between multiple healthcare providers.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
The combination of smart sensors with AI and machine learning capabilities has created unprecedented opportunities for personalized healthcare:
Predictive Health Analytics
AI algorithms can analyze patterns in sensor data to predict health events before they occur. For example:
- Heart rate variability patterns can predict cardiac events
- Blood glucose trends can anticipate diabetic complications
- Sleep pattern analysis can identify neurological disorders
- Activity level changes can indicate developing health issues
Personalized Treatment Optimization
Machine learning algorithms can analyze individual patient data to optimize treatment protocols:
- Medication dosing adjustments based on real-time biomarker data
- Exercise recommendations tailored to individual fitness levels and health conditions
- Dietary suggestions based on metabolic sensor readings
- Sleep optimization recommendations based on sleep pattern analysis
Early Disease Detection
Smart sensors combined with AI can detect subtle changes in physiological parameters that may indicate early disease development:
- Cancer detection through biomarker analysis
- Alzheimer’s disease identification through gait and cognitive pattern analysis
- Cardiovascular disease prediction through multiple sensor data fusion
- Mental health condition recognition through behavior pattern analysis
Specific Medical Applications Transforming Healthcare

Diabetes Management Revolution
Smart sensors have transformed diabetes care through:
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Real-time glucose tracking with predictive alerts
- Smart Insulin Pumps: Automated insulin delivery based on sensor data
- Integrated Care Systems: Coordination between multiple devices for optimal glucose control
Cardiovascular Health Monitoring
Cardiac care has been revolutionized through:
- Wearable ECG Monitors: Continuous heart rhythm monitoring
- Blood Pressure Sensors: Automatic pressure monitoring with trend analysis
- Heart Failure Detection: Early warning systems based on multiple physiological parameters
Respiratory Health Management
Smart sensors are improving respiratory care through:
- Smart Inhalers: Medication delivery tracking and optimization
- Sleep Apnea Monitors: Continuous breathing pattern analysis
- COPD Management: Real-time monitoring of respiratory function
Neurological Condition Monitoring
Brain health monitoring has advanced through:
- Seizure Detection: Automatic seizure identification and emergency response
- Movement Disorder Tracking: Continuous monitoring of Parkinson’s disease symptoms
- Cognitive Assessment: Digital biomarkers for dementia and cognitive decline
Advanced Sensor Technologies
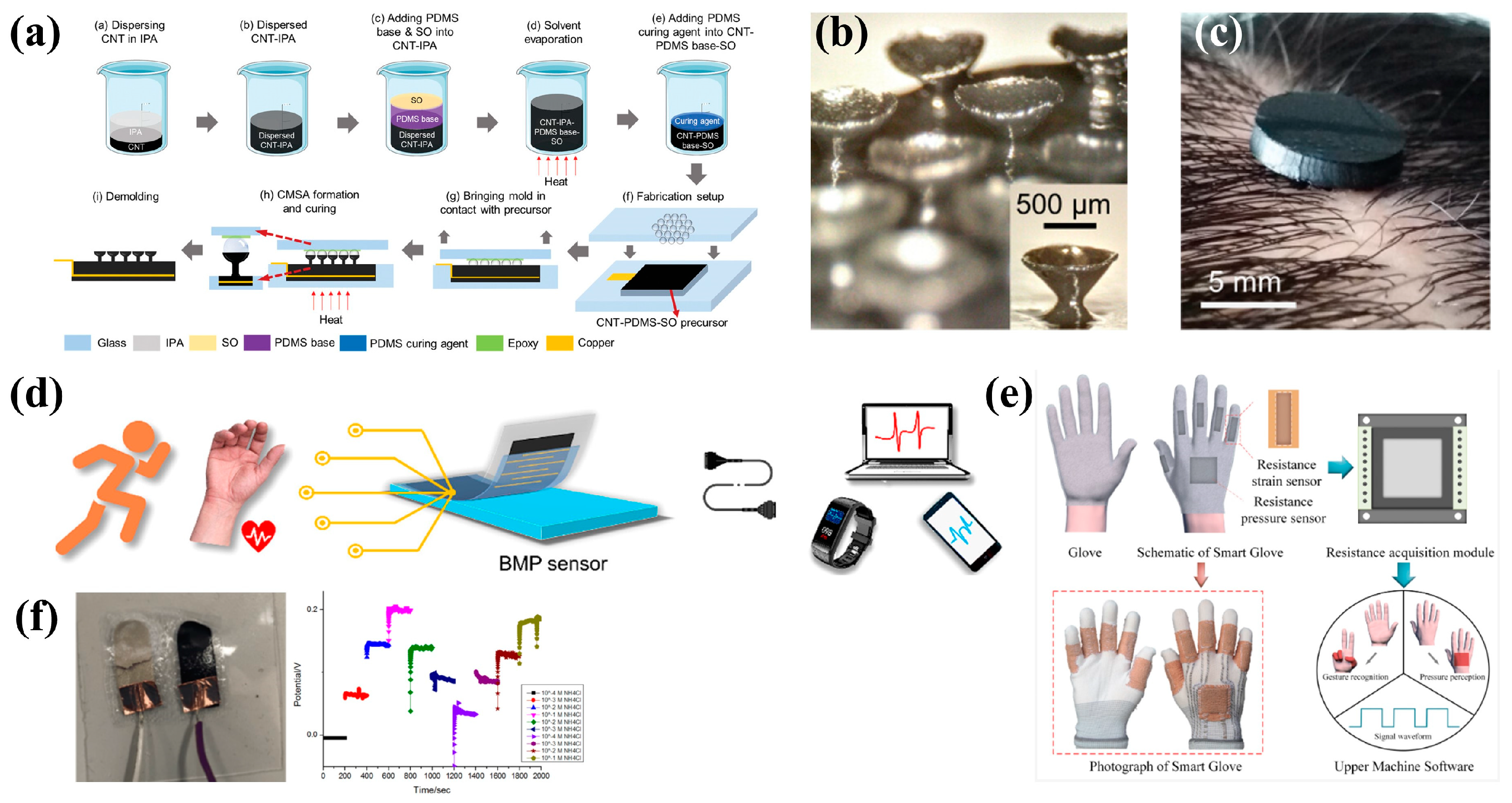
Miniaturization and Integration
Modern smart sensors are becoming increasingly sophisticated while shrinking in size:
- Nanosensors: Molecular-level sensing capabilities
- Flexible Sensors: Conformable devices that adapt to body contours
- Multi-parameter Sensors: Single devices monitoring multiple physiological parameters
Wireless and Battery-Free Technologies
Advances in power management and wireless communication include:
- Energy Harvesting: Sensors powered by body heat or movement
- Wireless Power Transfer: Remote charging capabilities
- Ultra-Low Power Design: Extended battery life for implantable devices
Biocompatible Materials
New materials are enabling better integration with human physiology:
- Biodegradable Sensors: Temporary monitoring devices that dissolve safely
- Bio-integrated Electronics: Sensors that interface directly with biological tissues
- Smart Biomaterials: Materials that respond to physiological changes
Data Analytics and Cloud Integration

The power of smart sensors is amplified through sophisticated data analytics platforms:
Real-Time Processing
Edge computing enables immediate data analysis and response:
- Local Processing: Critical decisions made instantly without cloud dependency
- Reduced Latency: Immediate alerts for emergency situations
- Privacy Protection: Sensitive data processed locally
Cloud-Based Analytics
Comprehensive health insights through cloud computing:
- Population Health Analytics: Large-scale trend analysis
- Predictive Modeling: Disease progression forecasting
- Treatment Optimization: Evidence-based care recommendations
Interoperability Standards
Standardized data formats enable seamless integration:
- FHIR Compliance: Healthcare data exchange standards
- API Integration: Connection with electronic health records
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Universal device communication
Market Growth and Future Projections
![]()
The smart medical devices market is experiencing unprecedented growth:
Market Size: The global smart medical devices market was valued at USD 52.66 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 168 billion by 2034, representing significant compound annual growth.
Key Growth Drivers:
- Aging population requiring continuous health monitoring
- Rising healthcare costs driving preventive care adoption
- Technological advances making devices more affordable and accessible
- Increased consumer awareness of personal health management
Regional Growth: North America leads the market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific, with emerging markets showing rapid adoption rates.
Challenges and Considerations
TECHNICAL CHALLENGES
Accuracy and Reliability: Ensuring sensor accuracy across diverse patient populations and conditions remains a critical challenge. Calibration, interference, and individual physiological variations can affect measurement precision.
Battery Life and Power Management: Balancing device functionality with power consumption requires continuous innovation in battery technology and energy-efficient design.
Data Integration Complexity: Combining data from multiple sensors and devices while maintaining accuracy and clinical relevance presents ongoing technical challenges.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
FDA Approval Processes: Smart medical devices must navigate complex regulatory pathways, balancing innovation speed with safety requirements.
Data Privacy and Security: Protecting sensitive health information while enabling data sharing for improved care requires robust cybersecurity measures.
Clinical Validation: Demonstrating clinical efficacy and safety through rigorous testing and long-term studies is essential for regulatory approval and physician adoption.
Healthcare System Integration
Electronic Health Record Integration: Seamlessly incorporating sensor data into existing healthcare IT systems requires standardization and interoperability solutions.
Physician Training and Adoption: Healthcare providers need training and support to effectively utilize smart sensor data in clinical decision-making.
Reimbursement Models: Insurance coverage and payment models for smart sensor technologies are still evolving, affecting widespread adoption.
Future Innovations and Emerging Technologies

Next-Generation Sensor Technologies
Molecular Sensors: Detection of specific biomarkers at the molecular level for ultra-early disease detection.
Neural Interface Sensors: Direct communication with the nervous system for advanced neurological monitoring and treatment.
Genetic Sensors: Real-time monitoring of gene expression and genetic markers for personalized medicine.
Advanced AI Integration
Federated Learning: Collaborative AI model training across multiple devices while preserving patient privacy.
Explainable AI: Transparent AI algorithms that provide clear reasoning for clinical recommendations.
Autonomous Health Management: Fully automated health management systems that can make treatment decisions with minimal human intervention.
Emerging Applications
Mental Health Monitoring: Sensors capable of detecting and monitoring mental health conditions through physiological and behavioral markers.
Precision Medicine: Highly personalized treatment protocols based on individual sensor data profiles.
Robotic Surgery Integration: Smart sensors enabling more precise and safer robotic surgical procedures.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery Models

Smart sensors are fundamentally changing healthcare delivery models:
Shift to Preventive Care
- Early Intervention: Detection of health issues before they become critical
- Lifestyle Modification: Real-time feedback encouraging healthy behaviors
- Risk Stratification: Identification of high-risk patients for targeted interventions
Decentralized Healthcare
- Home-Based Monitoring: Reduced need for hospital visits and extended stays
- Remote Consultations: Telemedicine enhanced with real-time sensor data
- Community Health Management: Population-level health monitoring and intervention
Personalized Medicine
- Individual Health Profiles: Comprehensive understanding of patient-specific health patterns
- Tailored Treatment Plans: Customized interventions based on individual sensor data
- Precision Dosing: Medication adjustments based on real-time biomarker levels
Conclusion: The Future of Smart Sensor-Enabled Healthcare
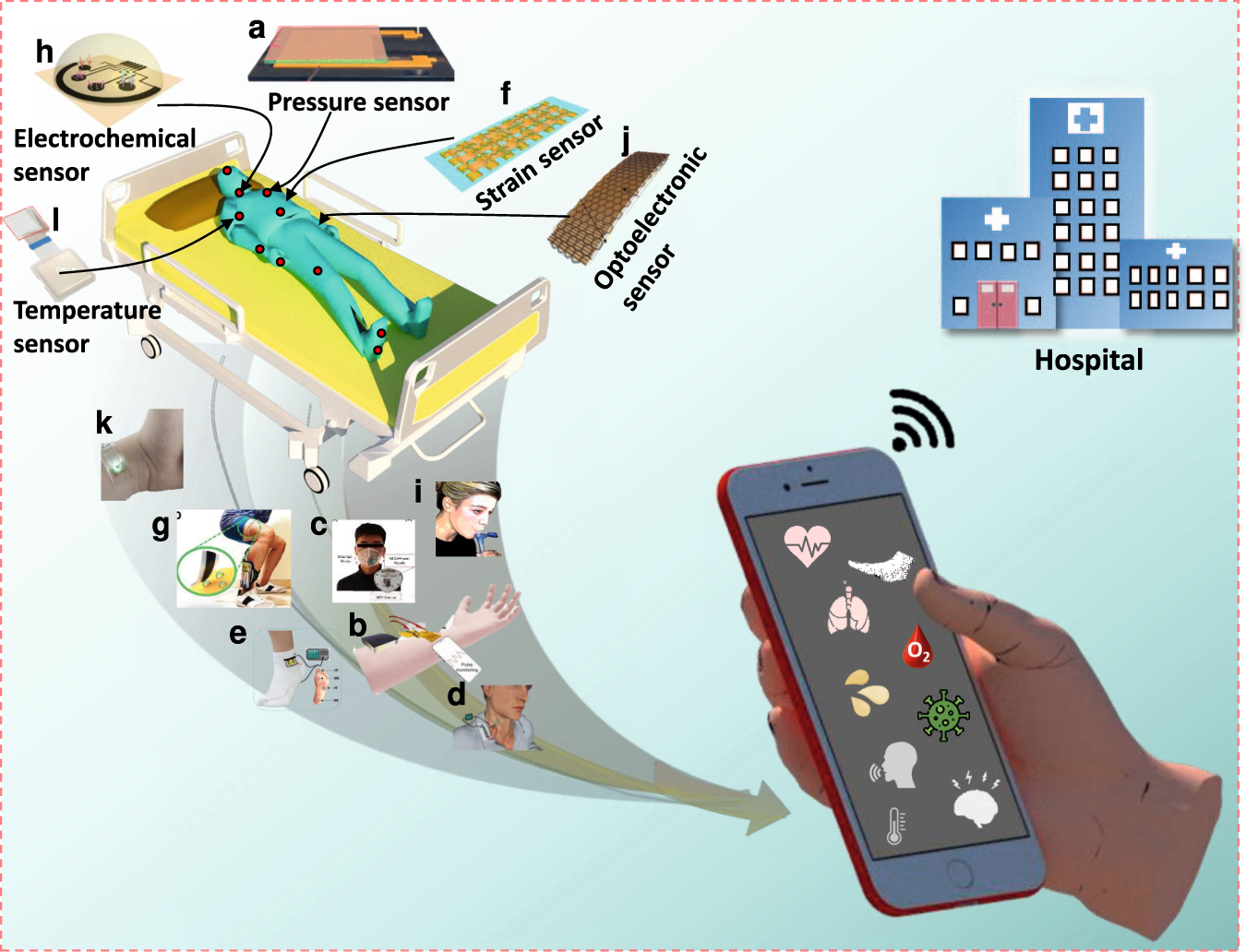
Smart sensors are fundamentally transforming medical devices and healthcare delivery, ushering in an era of continuous, personalized, and predictive healthcare. The integration of advanced sensing technologies with AI, machine learning, and IoT connectivity is creating unprecedented opportunities for improving patient outcomes while reducing healthcare costs.
The evolution from reactive to proactive healthcare is being driven by smart sensors that can detect health issues before they become critical, enable personalized treatment approaches, and empower patients to take control of their health. As these technologies continue to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated applications that will further revolutionize medical care.
The future of healthcare lies in the seamless integration of smart sensors with advanced analytics, creating a comprehensive health monitoring ecosystem that provides continuous insights into patient health. This transformation promises to make healthcare more accessible, affordable, and effective for patients worldwide.
Key success factors for continued advancement include addressing technical challenges, ensuring regulatory compliance, protecting patient privacy, and fostering healthcare system integration. As these challenges are overcome, smart sensors will play an increasingly central role in delivering the personalized, predictive, and preventive healthcare of the future.
The revolution in medical devices driven by smart sensors is just beginning. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, these intelligent devices will become even more prevalent, fundamentally changing how we approach health and wellness. The future promises a world where health monitoring is continuous, non-invasive, and seamlessly integrated into daily life, enabling better health outcomes for everyone.
