PROS AND CONS OF CLOUD-CONNECTED MEDICAL DEVICES: TRANSFORMING HEALTHCARE THROUGH DIGITAL INNOVATION
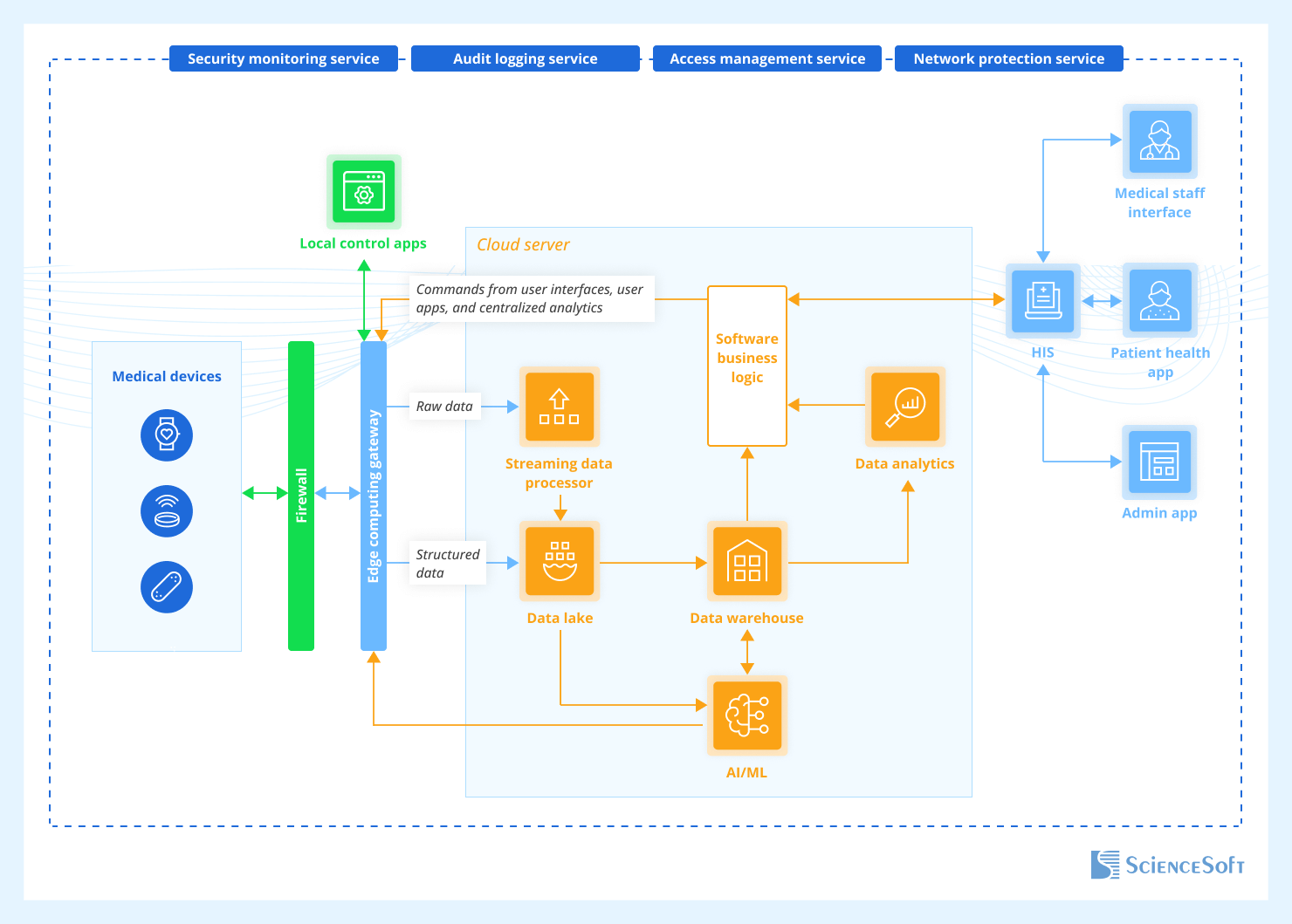
The healthcare industry is experiencing a revolutionary transformation through the adoption of cloud-connected medical devices, fundamentally changing how we deliver, monitor, and manage patient care. These sophisticated technologies represent the convergence of medical expertise with cutting-edge digital infrastructure, creating unprecedented opportunities for improved health outcomes while simultaneously introducing complex challenges that healthcare organizations must navigate carefully.
Cloud-connected medical devices utilize network connections—including Wi-Fi, cellular, Bluetooth, BLE, or NB-IoT—to transmit health-related data such as glucose levels, ECG readings, and vital signs to and from cloud servers. This connectivity offers centralized, scalable storage for vast amounts of health data while eliminating the need for costly on-premises infrastructure, providing a reliable foundation for remote patient monitoring and advanced healthcare analytics.

The global healthcare cloud computing market is forecasted to grow from $53.8 billion in 2024 to $120.6 billion in 2029, driven primarily by the growing adoption of wearable devices, the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics. ScienceSoft Leading medical device companies, including Philips, Medtronic, Siemens Healthineers, GE HealthCare, Johnson & Johnson, Roche, and BD, are increasingly investing in cloud-connected devices, recognizing their transformative potential.
The Significant Advantages of Cloud-Connected Medical Devices
Enhanced Remote Patient Monitoring and Real-Time Care

Cloud-connected medical devices have revolutionized remote patient monitoring by enabling continuous, real-time data collection and analysis. These devices continuously capture patient health data—including heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, and other vital signs—using built-in sensors and transmit this information to cloud servers instantaneously. Healthcare providers can monitor patients’ conditions 24/7, receiving immediate alerts when vital signs exceed predefined thresholds for normal health parameters.
This capability proves particularly valuable for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory disorders. For instance, continuous glucose monitors (CGM) and smart insulin pens can record and recommend optimal timing and dosing for insulin injections, providing diabetic patients with unprecedented control over their condition. Similarly, smart inhalers connected to mobile applications help patients with asthma and pulmonary diseases understand symptom triggers and predict allergens, enabling proactive management of their conditions.
Remote monitoring capabilities extend beyond individual patient care to population health management. Healthcare providers can track trends across patient populations, identify emerging health issues, and implement preventive interventions before conditions deteriorate. This proactive approach significantly improves patient outcomes while reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
Dramatic Healthcare Cost Reduction

One of the most compelling advantages of cloud-connected medical devices is their potential to substantially reduce healthcare costs across multiple dimensions. By enabling remote monitoring and early intervention, these devices significantly decrease the need for costly hospital readmissions, emergency room visits, and prolonged inpatient stays.
Patients with chronic illnesses often incur high costs associated with continuous medical care, including rehospitalization, transportation, time away from work, and general disease management support. Cloud-connected devices bring care directly to patients, allowing them to check in remotely with doctors, ask questions, and perform simple tests on connected devices that share data in real-time. IoT for All
A medical device manufacturer reported saving $3.5 million annually by implementing remote monitoring capabilities, demonstrating the significant financial benefits of cloud-connected medical devices. These cost savings result from reduced maintenance visits, improved device efficiency, and enhanced patient compliance monitoring.
The economic benefits extend to patients as well. Remote monitoring reduces travel costs, time away from work, and the need for frequent in-person appointments. Insurance companies and healthcare systems benefit from reduced claims for preventable complications and emergency interventions.
Improved Treatment Management and Clinical Decision Support
Cloud-connected medical devices significantly enhance treatment management by providing healthcare providers with comprehensive, real-time data about patient responses to therapies. These devices can track medication administration, monitor treatment adherence, and provide detailed insights into how patients respond to different interventions.
Advanced analytics capabilities embedded in cloud-connected systems can process structured patient data to uncover health trends, detect anomalies, and generate clinical insights such as treatment response patterns. AI and machine learning engines can identify subtle patterns in vital signs, symptoms, and device performance data, predicting adverse health events and sending alerts to clinicians before critical situations develop.
This enhanced decision support capability enables healthcare providers to make more informed treatment decisions, adjust therapies based on real-time data, and personalize care plans to individual patient needs. The result is more effective treatments, reduced medical errors, and improved patient safety.
Enhanced Patient Engagement and Empowerment
Cloud-connected medical devices fundamentally transform the patient experience by providing individuals with unprecedented access to their own health data. Patient health applications connected to these devices offer real-time visibility into vital signs, medication adherence, and treatment responses, empowering patients to take a more active role in managing their health.
This increased transparency and engagement leads to better patient compliance with treatment protocols, as individuals can see the immediate impact of their actions on their health metrics. Patients report higher satisfaction levels when they have access to their health data and can communicate directly with their care providers through connected platforms.
The gamification elements often built into these systems—such as achievement badges for medication adherence or fitness goals—further motivate patients to engage actively in their care, leading to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Advanced Data Analytics and Research Capabilities

Cloud-connected medical devices generate enormous volumes of health data that provide unprecedented opportunities for medical research and population health analysis. This continuous stream of real-world evidence enables researchers to conduct large-scale studies, identify new treatment approaches, and develop more effective interventions.
The aggregated data from thousands of patients can reveal patterns and correlations that would be impossible to detect through traditional clinical studies. This capability accelerates medical discovery, supports evidence-based practice improvements, and contributes to the development of precision medicine approaches tailored to individual patient characteristics.
Healthcare authorities can use this data to track disease outbreaks, monitor public health trends, and develop more effective health policies. The research potential of cloud-connected medical devices represents a paradigm shift toward data-driven healthcare decision-making.
Significant Challenges and Disadvantages
Critical Security and Privacy Vulnerabilities
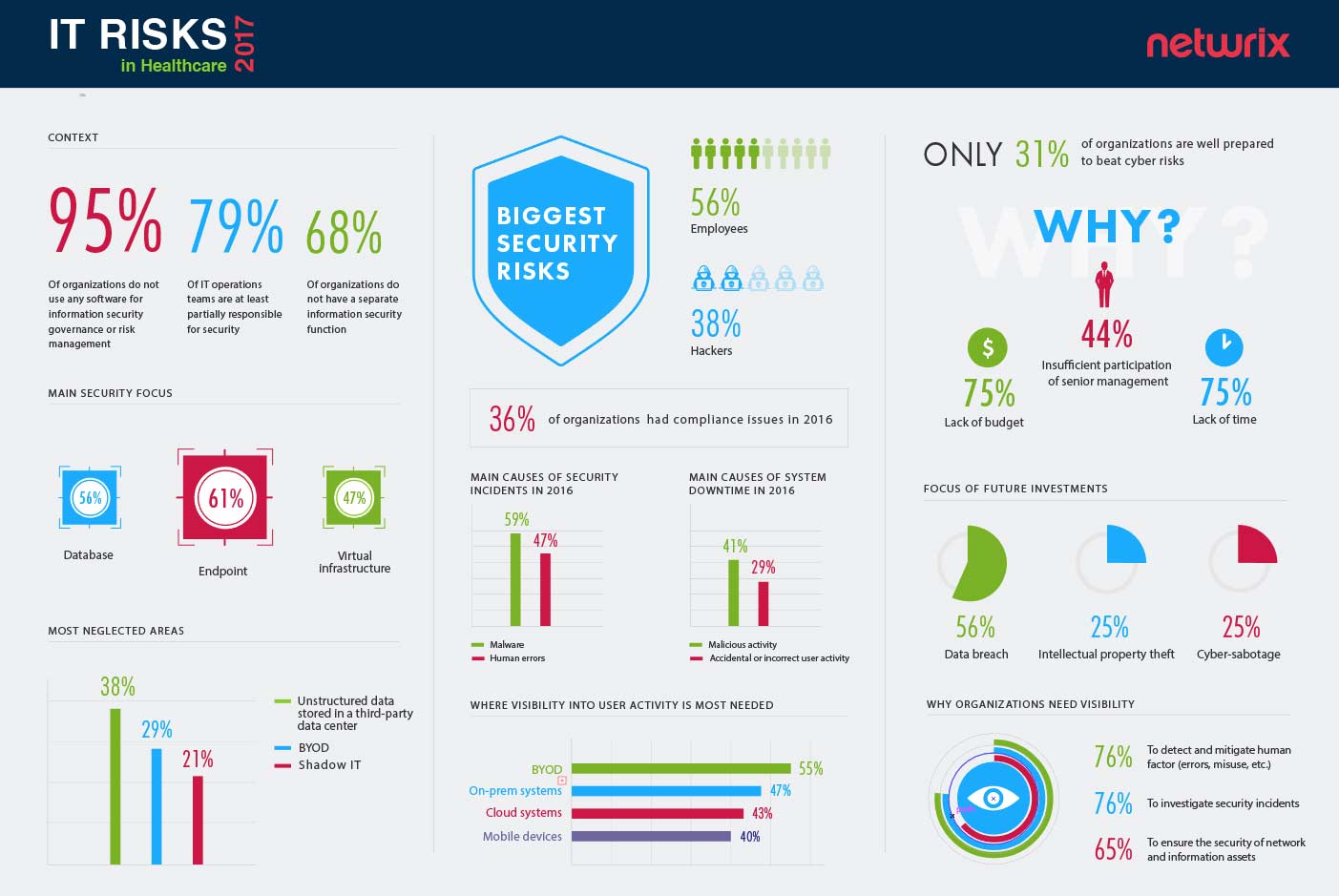
Security and privacy concerns represent the most significant challenge facing cloud-connected medical devices. These devices often lack robust security features, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access. As many IoT devices in healthcare are not designed with security as a primary consideration, they become attractive targets for cybercriminals seeking to access sensitive patient information.
Healthcare data breaches have increased dramatically, with the healthcare sector experiencing some of the highest costs associated with cybersecurity incidents. IEEE Innovation at Work The potential consequences of security breaches in cloud-connected medical devices extend far beyond financial losses—they can directly impact patient safety and care quality.
Specific security vulnerabilities include:
- Weak authentication mechanisms that allow unauthorized device access
- Inadequate encryption during data transmission and storage
- Unpatched software vulnerabilities that create entry points for attackers
- Insecure device communication protocols that can be intercepted or manipulated
- Poor access controls that allow excessive permissions to system components
The interconnected nature of these devices means that a single compromised device can potentially provide access to an entire network of medical systems, amplifying the potential impact of security breaches.
Complex Regulatory Compliance and Privacy Challenges
Cloud-connected medical devices must comply with stringent healthcare regulations, including HIPAA in the United States, GDPR in Europe, and various other regional privacy laws. Ensuring compliance across multiple jurisdictions while maintaining device functionality and user experience presents significant challenges for healthcare organizations and device manufacturers.
Key compliance challenges include:
- Data sovereignty requirements that restrict where patient data can be stored and processed
- Patient consent management for data collection, sharing, and analysis
- Audit trail maintenance for all data access and modifications
- Right to erasure compliance when patients request data deletion
- Cross-border data transfer restrictions that limit global deployment options
The complexity of regulatory compliance increases development costs, extends time-to-market for new devices, and requires ongoing monitoring and updates to maintain compliance as regulations evolve.
Device Reliability and Technical Failure Risks
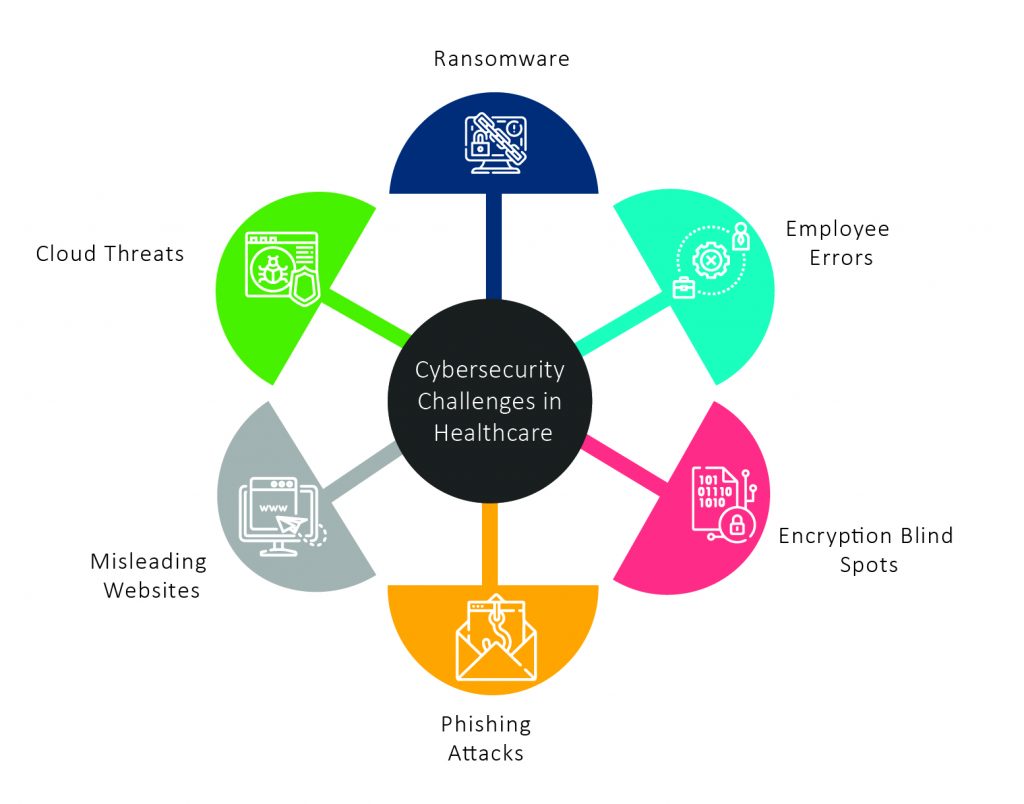
Cloud-connected medical devices introduce new points of failure that can directly impact patient care. Hardware malfunctions, software bugs, network connectivity issues, and power failures can all compromise device performance and potentially endanger patient safety.
Critical reliability concerns include:
- Network connectivity dependencies that can disrupt device functionality
- Cloud service outages that affect data access and device control
- Battery life limitations in wearable and implantable devices
- Software update failures that can introduce new bugs or security vulnerabilities
- Sensor accuracy degradation over time affecting data quality
Unlike traditional medical devices that operate independently, cloud-connected devices rely on multiple interconnected systems, creating cascading failure scenarios where problems in one component can affect the entire system. Healthcare providers must develop comprehensive backup procedures and failover mechanisms to ensure continuity of care when technical issues arise.
Interoperability and Integration Challenges
The lack of standardized protocols and communication standards across different manufacturers creates significant interoperability challenges. Healthcare organizations often use medical devices from multiple vendors, and ensuring these devices can communicate effectively with each other and with existing hospital information systems requires substantial technical expertise and investment.
Integration challenges include:
- Proprietary communication protocols that limit device interoperability
- Data format inconsistencies that complicate data aggregation and analysis
- Legacy system compatibility issues that require expensive interface development
- Vendor lock-in scenarios that limit future device and system choices
- Workflow integration complexities that require staff retraining and process redesign
These challenges can significantly increase implementation costs and extend deployment timelines, potentially limiting the realized benefits of cloud-connected medical devices.
High Implementation and Maintenance Costs

While cloud-connected medical devices promise long-term cost savings, the initial implementation costs can be substantial. Healthcare organizations must invest in new infrastructure, staff training, security measures, and ongoing maintenance to successfully deploy these systems.
Major cost considerations include:
- Infrastructure upgrades to support increased network bandwidth and security requirements
- Staff training programs to ensure proper device use and data interpretation
- Cybersecurity investments including monitoring tools, threat detection systems, and incident response capabilities
- Compliance management costs for regulatory adherence and audit preparation
- Ongoing maintenance and support for device updates, security patches, and technical assistance
These upfront investments can strain healthcare budgets, particularly for smaller organizations with limited resources. The return on investment may take several years to realize, requiring careful financial planning and commitment from healthcare leadership.
Future Implications and Considerations
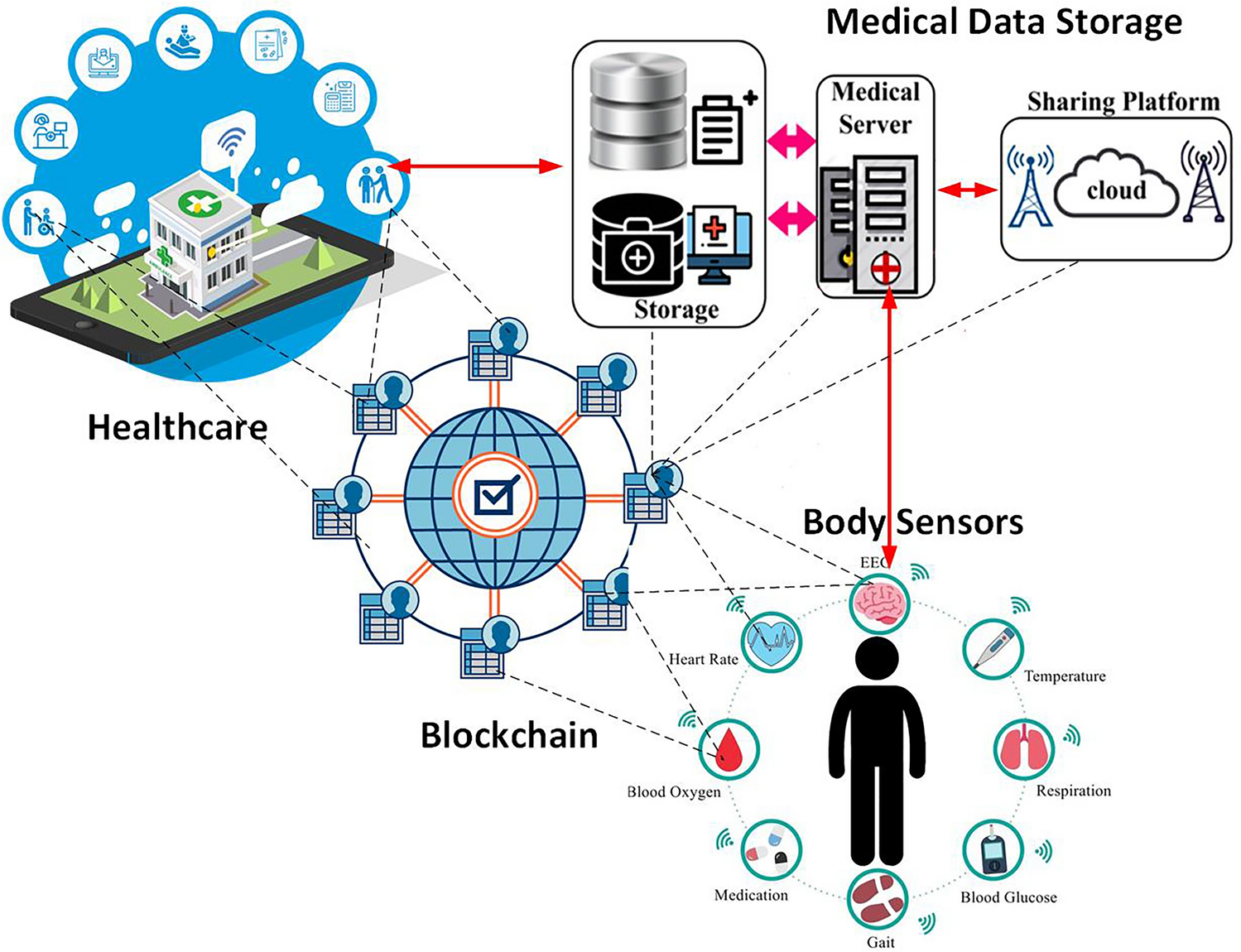
The future of cloud-connected medical devices holds tremendous promise, with market projections indicating continued rapid growth and technological advancement. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics will further enhance the capabilities of these devices, enabling more sophisticated predictive analytics, personalized treatment recommendations, and automated care management.
However, successful adoption requires addressing current challenges through:
- Enhanced security frameworks that protect patient data while maintaining device functionality
- Standardized interoperability protocols that ensure seamless communication between devices and systems
- Comprehensive regulatory guidelines that provide clear compliance pathways for manufacturers and healthcare providers
- Robust training programs that prepare healthcare workers for the digital transformation of medical care
- Sustainable financing models that make cloud-connected medical devices accessible to healthcare organizations of all sizes
Conclusion
Cloud-connected medical devices represent a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance care quality through real-time monitoring, data-driven decision making, and enhanced patient engagement. The benefits of these technologies—including improved remote monitoring, significant cost reductions, enhanced treatment management, and advanced research capabilities—demonstrate their transformative potential for the healthcare industry.
However, the challenges associated with security vulnerabilities, regulatory compliance, device reliability, interoperability issues, and implementation costs require careful consideration and strategic planning. Healthcare organizations must weigh these advantages and disadvantages carefully, developing comprehensive implementation strategies that maximize benefits while effectively mitigating risks.
The continued evolution of cloud-connected medical devices will depend on addressing these challenges through technological innovation, regulatory clarity, industry standardization, and collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, technology companies, and regulatory bodies. As these issues are resolved, cloud-connected medical devices will become increasingly integral to modern healthcare delivery, ultimately improving patient care and health outcomes on a global scale.
The future of healthcare is undoubtedly connected, and organizations that thoughtfully navigate the transition to cloud-connected medical devices will be best positioned to deliver superior patient care in the digital age. Success requires not just technological adoption, but a comprehensive understanding of the benefits, challenges, and strategic considerations that define this transformative healthcare technology landscape.
RESULTS OF YOUR AUTOCLAVE ON YOUR MOBILE
