HOW VOICE INTERFACES WILL IMPROVE HOSPITAL EQUIPMENT: REVOLUTIONIZING HEALTHCARE THROUGH SMART TECHNOLOGY
The healthcare industry stands at the precipice of a technological revolution, where voice interfaces are poised to fundamentally transform how medical professionals interact with hospital equipment. As hospitals worldwide grapple with increasing patient loads, staff shortages, and the critical need for infection control, voice-activated technology emerges as a game-changing solution that addresses these challenges while enhancing patient care quality and operational efficiency.
Voice interfaces in healthcare represent more than just a technological upgrade—they embody a paradigm shift toward hands-free, intuitive, and intelligent medical environments. From voice-controlled surgical equipment to AI-powered patient room management systems, these innovations are reshaping the landscape of modern healthcare delivery, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient outcomes while reducing healthcare-associated infections and streamlining clinical workflows.
THE CURRENT STATE OF HOSPITAL EQUIPMENT AND TECHNOLOGY

Modern hospitals are complex ecosystems filled with sophisticated medical equipment that requires precise control and constant monitoring. Traditional hospital equipment interfaces rely heavily on physical controls—buttons, touch screens, switches, and manual adjustments—which create several significant challenges in today’s healthcare environment.
Healthcare professionals routinely interact with dozens of different devices during their shifts, from patient monitoring systems and ventilators to diagnostic equipment and infusion pumps. Each device typically has its own unique interface, creating a steep learning curve and potential for user error. The cognitive load of managing multiple complex interfaces while providing patient care contributes to clinician fatigue and can impact patient safety.
Research published in BMC Health Services Research demonstrates that traditional control methods in hospital wards create inefficiencies and infection control challenges. BMC Health Services Research The study found that patients and healthcare workers frequently struggle with the fragmented nature of equipment controls, leading to reduced efficiency and increased risk of contamination through surface contact.
The integration of multiple systems within hospitals also presents significant challenges. Medical equipment often operates in isolation, requiring healthcare workers to manually transfer information between systems, increasing the risk of errors and consuming valuable time that could be better spent on patient care.
UNDERSTANDING VOICE INTERFACE TECHNOLOGY IN HEALTHCARE

Voice interface technology, also known as Intelligent Speech Technology (IST), represents a revolutionary approach to human-computer interaction in healthcare settings. This technology encompasses speech recognition, natural language processing, and artificial intelligence to enable hands-free control of medical equipment and systems.
Core Components of Healthcare Voice Interfaces
Voice interfaces in medical settings comprise several sophisticated components working in harmony:
- Speech Recognition Engines: Advanced algorithms that convert spoken words into digital commands with high accuracy, even in noisy hospital environments
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Systems that understand context, medical terminology, and complex instructions
- Machine Learning Models: AI systems that adapt to individual users’ speech patterns and improve accuracy over time
- HIPAA-Compliant Processing: Secure, on-device processing that ensures patient privacy and regulatory compliance
According to Sensory Inc., a leading provider of voice AI technology for medical devices, on-device voice recognition offers several critical advantages in healthcare settings. Sensory Inc. The technology provides HIPAA-compliant, hands-free control for medical assistants, patients, and healthcare providers while maintaining the highest levels of data security and privacy.
Advanced Voice Recognition Capabilities
Modern healthcare voice interfaces incorporate sophisticated features designed specifically for medical environments:
- Medical Terminology Recognition: Systems trained on extensive medical vocabularies to accurately interpret clinical commands
- Multi-Language Support: Capability to understand instructions in multiple languages, accommodating diverse healthcare workforces
- Contextual Understanding: AI that comprehends the clinical context of commands and responds appropriately
- Ambient Sound Filtering: Technology that distinguishes voice commands from background hospital noise
Benefits of Voice Interfaces in Hospital Equipment

The implementation of voice interfaces in hospital equipment offers transformative benefits that address critical healthcare challenges while improving operational efficiency and patient outcomes.
Enhanced Infection Control and Safety
One of the most compelling advantages of voice interfaces is their contribution to infection control. Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) represent a significant threat to patient safety, with contaminated surfaces serving as common transmission vectors. Voice-controlled equipment eliminates the need for physical contact with device interfaces, dramatically reducing the risk of pathogen transmission.
SoundHound’s research on hands-free devices in healthcare demonstrates that voice user interfaces help control disease spread in hospitals by providing touchless interactions with commonly used control systems. SoundHound This technology proved particularly valuable during the COVID-19 pandemic, when minimizing surface contact became critical for healthcare worker safety.
Improved Workflow Efficiency and Productivity
Voice interfaces significantly streamline clinical workflows by enabling multitasking and reducing the time required to interact with equipment. Healthcare professionals can adjust device settings, access patient information, and control multiple systems simultaneously while maintaining focus on patient care.
Research indicates that voice-controlled systems can reduce equipment interaction time by up to 40%, allowing healthcare workers to dedicate more time to direct patient care activities. The technology also minimizes the cognitive load associated with remembering complex button sequences or navigating multiple menu systems.
Enhanced Accessibility and Inclusivity
Voice interfaces make medical equipment more accessible to healthcare workers with physical limitations or mobility challenges. Professionals who may struggle with fine motor control or have visual impairments can effectively operate sophisticated medical equipment through voice commands, promoting inclusivity in healthcare environments.
The technology also benefits patients with limited mobility, allowing them to control room environment settings, call for assistance, or adjust bed positions without physical effort. This enhanced autonomy contributes to improved patient satisfaction and dignity during hospitalization.
Specific Applications in Hospital Equipment

Voice interfaces are being integrated across a wide spectrum of hospital equipment, each application offering unique benefits and capabilities that enhance healthcare delivery.
Patient Monitoring Systems
Voice-activated patient monitoring systems allow healthcare professionals to adjust alarm thresholds, request specific vital sign readings, and access historical data through simple voice commands. Nurses can say “Show blood pressure trend for the last 24 hours” or “Set heart rate alarm to 120 BPM” while continuing to provide hands-on patient care.
These systems also enable automatic documentation, where vital signs and observations are recorded through voice dictation, reducing manual data entry errors and improving documentation accuracy. The integration with electronic health records (EHR) systems ensures seamless information flow throughout the healthcare facility.
Surgical Equipment Control
In operating rooms, voice interfaces enable surgeons to control lighting, adjust table positions, and operate imaging equipment without breaking sterile technique. Commands like “Increase lighting intensity by 20%” or “Move to lateral position” allow surgical teams to maintain focus on procedures while optimizing the surgical environment.
Advanced surgical robots increasingly incorporate voice control capabilities, allowing surgeons to make precise adjustments to robotic instruments through verbal commands. This technology enhances surgical precision while reducing the need for additional support staff to operate equipment controls.
Diagnostic Equipment Integration
Voice interfaces in diagnostic equipment streamline the imaging and testing process by enabling technicians to initiate scans, adjust parameters, and document findings through voice commands. Radiology technicians can say “Begin CT scan with contrast protocol” while positioning patients, improving workflow efficiency and reducing examination times.
The technology also facilitates real-time reporting, where radiologists can dictate findings directly into reporting systems while reviewing images, accelerating diagnosis turnaround times and improving patient care continuity.
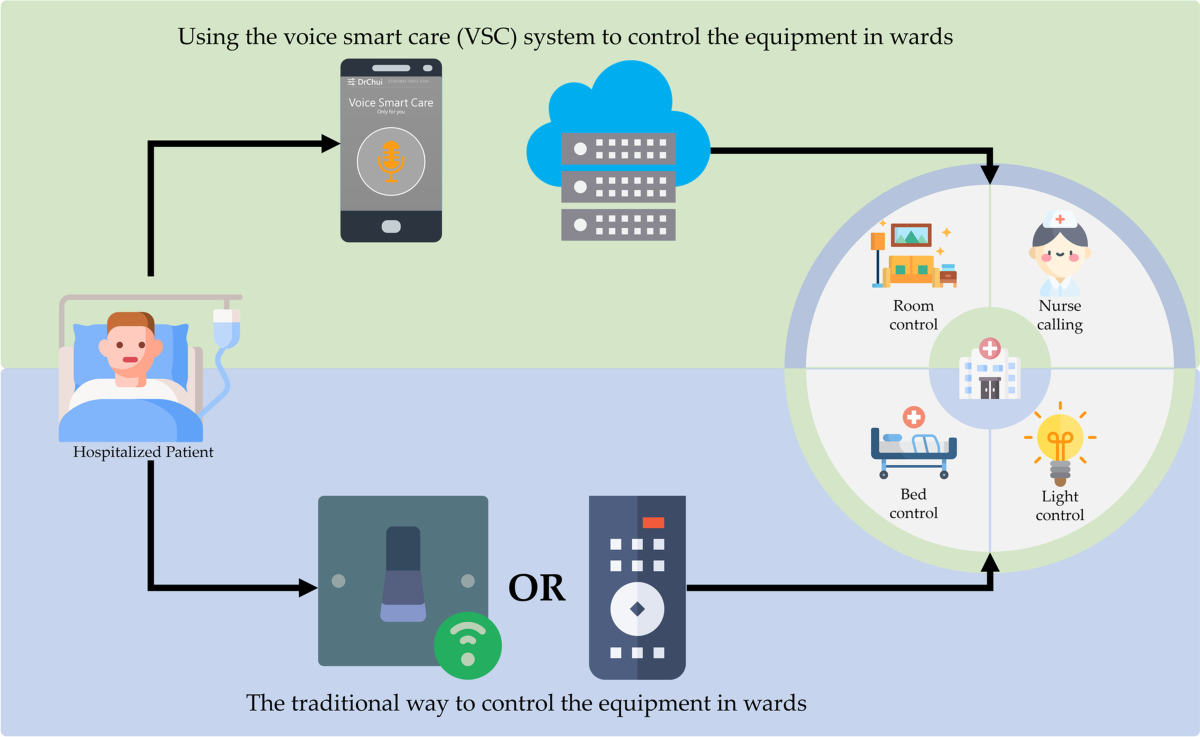
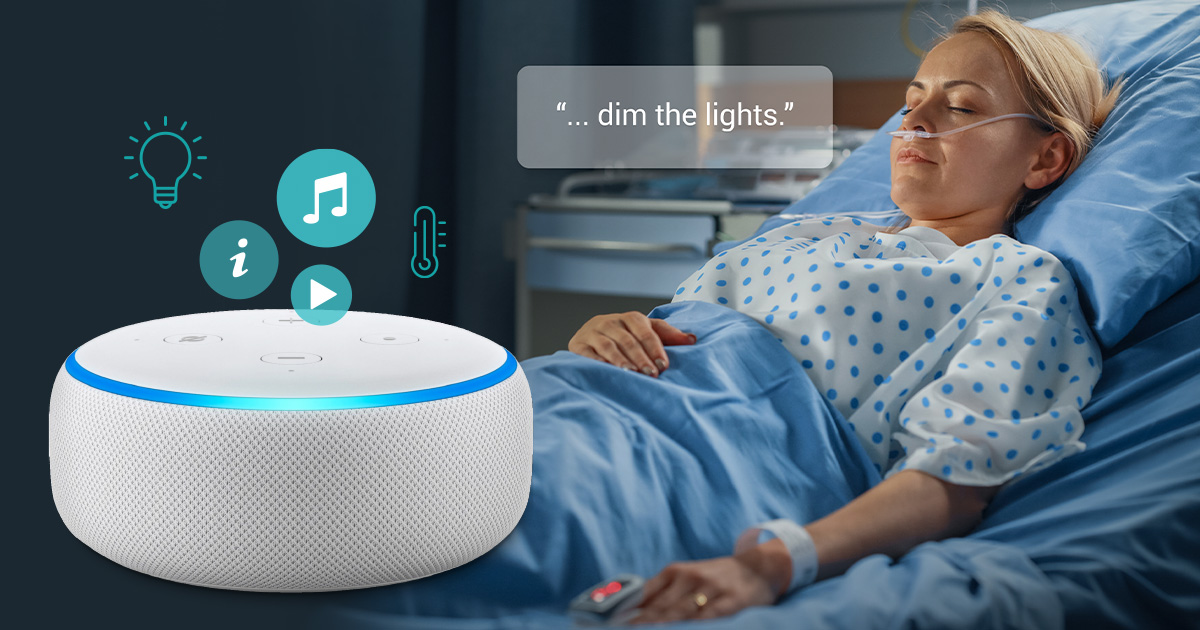
Patient Room Environment Control
Smart patient rooms equipped with voice interfaces allow patients to control lighting, temperature, television, and call nurse systems through simple voice commands. Patients can say “Dim the lights to 30%” or “Call my nurse for pain medication,” enhancing comfort and autonomy during hospitalization.
These systems also enable voice-activated entertainment and communication features, allowing patients to make phone calls, access educational content, or participate in telemedicine consultations without requiring physical interaction with devices.
Challenges and Implementation Considerations

While voice interfaces offer tremendous potential for improving hospital equipment, successful implementation requires careful consideration of various challenges and technical requirements.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Healthcare voice interfaces must comply with strict privacy regulations, including HIPAA in the United States and similar regulations globally. On-device processing becomes crucial to ensure that sensitive patient information never leaves the secure hospital environment. Voice recognition systems must incorporate robust encryption, secure authentication mechanisms, and comprehensive audit trails.
The challenge lies in balancing functionality with security requirements. Cloud-based voice processing offers superior recognition accuracy and feature sets but raises concerns about data transmission and storage. On-device processing addresses privacy concerns but may require more powerful local hardware and ongoing maintenance.
Integration with Existing Systems
Modern hospitals rely on complex networks of interconnected systems, from electronic health records to equipment management platforms. Voice interfaces must seamlessly integrate with these existing systems without disrupting current workflows or creating new points of failure.
Legacy equipment poses particular challenges, as older medical devices may require significant retrofitting or replacement to accommodate voice control capabilities. Healthcare facilities must carefully evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of upgrading versus replacing existing equipment.
Training and User Adoption
Successful voice interface implementation requires comprehensive training programs for healthcare staff. Users must learn proper voice commands, understand system limitations, and develop confidence in the technology’s reliability. Resistance to change and concerns about technology reliability can slow adoption rates.
Healthcare organizations must develop structured training programs that address both technical proficiency and clinical integration. Ongoing support and feedback mechanisms ensure that users can maximize the benefits of voice-controlled equipment while maintaining patient safety standards.
Environmental Considerations
Hospital environments present unique challenges for voice recognition technology. Background noise from equipment alarms, conversations, and general hospital activity can interfere with speech recognition accuracy. Voice interfaces must incorporate advanced noise cancellation and speaker identification technologies to function reliably in these challenging environments.
The technology must also accommodate the diverse linguistic landscape of modern healthcare, with healthcare workers speaking various languages and accents. Robust multilingual support and accent adaptation capabilities become essential for widespread adoption.
Future Developments and Emerging Technologies

The future of voice interfaces in hospital equipment promises even more sophisticated capabilities that will further transform healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Next-generation voice interfaces will incorporate advanced AI capabilities that enable predictive responses and proactive system management. These systems will learn from user behavior patterns, anticipate needs, and suggest optimal equipment settings based on clinical context and historical data.
AI-powered voice assistants will serve as intelligent intermediaries between healthcare professionals and complex medical equipment, translating clinical intentions into precise equipment controls while monitoring for potential safety issues or conflicts.
Ambient Intelligence and Context Awareness
Future voice interfaces will incorporate ambient intelligence capabilities that understand the broader clinical context without explicit commands. These systems will monitor clinical activities, patient conditions, and environmental factors to automatically adjust equipment settings and provide relevant information.
Context-aware voice interfaces will distinguish between different users and adapt responses based on role, location, and current clinical activities. A surgeon’s voice commands in an operating room will be interpreted differently than a nurse’s commands in a patient room, ensuring appropriate responses and maintaining safety protocols.
Enhanced Natural Language Processing
Advances in natural language processing will enable more conversational interactions with medical equipment. Instead of memorizing specific command phrases, healthcare professionals will be able to communicate with equipment using natural language, making the technology more intuitive and reducing training requirements.
These systems will understand complex, multi-step instructions and execute coordinated actions across multiple devices. A command like “Prepare the patient for cardiac catheterization” could automatically adjust multiple pieces of equipment, configure monitoring systems, and update relevant documentation.
Integration with Wearable Technology
Voice interfaces will increasingly integrate with wearable devices worn by healthcare professionals, enabling seamless communication with equipment throughout the hospital. Smart badges, wearable communicators, and augmented reality headsets will serve as voice interface platforms, providing continuous access to equipment controls regardless of location.
This integration will enable mobile voice control capabilities, allowing healthcare workers to adjust equipment settings while moving between patient rooms or during transport situations.
Clinical Outcomes and Evidence-Based Benefits
Emerging research demonstrates measurable improvements in clinical outcomes and operational efficiency when voice interfaces are implemented in hospital equipment.
Reduced Healthcare-Associated Infections
Studies show significant reductions in healthcare-associated infections when voice-controlled equipment replaces traditional touch-based interfaces. A pilot study at Saratoga Hospital demonstrated that hands-free voice technology helped save personal protective equipment while ensuring staff safety during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The elimination of frequently touched surfaces reduces pathogen transmission pathways, contributing to improved patient safety and reduced healthcare costs associated with treating preventable infections.
Improved Documentation Accuracy
Voice-enabled documentation systems show marked improvements in accuracy and completeness compared to manual data entry. Healthcare professionals can document observations and measurements in real-time while maintaining focus on patient care, reducing errors associated with delayed or rushed documentation.
Real-time voice documentation also enables immediate data availability for other healthcare team members, improving communication and care coordination across shifts and departments.
Enhanced Patient Satisfaction
Patients in voice-controlled smart rooms report higher satisfaction levels with their hospital experience. The ability to control room environments and communicate needs through voice commands contributes to a sense of autonomy and dignity during hospitalization.
Voice interfaces also reduce response times for patient requests, as staff can receive and respond to voice-activated alerts more efficiently than traditional call systems.
Operational Efficiency Gains
Healthcare facilities implementing voice interfaces report measurable improvements in operational efficiency, including reduced equipment setup times, faster response to patient needs, and streamlined clinical workflows. These efficiency gains translate to cost savings and improved resource utilization.
IMPLEMENTATION STRATEGIES AND BEST PRACTICES

Successful implementation of voice interfaces in hospital equipment requires strategic planning, careful execution, and ongoing optimization based on user feedback and clinical outcomes.
Phased Implementation Approach
Healthcare organizations should adopt a phased implementation strategy, beginning with pilot programs in selected departments or equipment types. This approach allows for thorough testing, user feedback collection, and system refinement before broader deployment.
Initial phases should focus on high-impact, low-risk applications such as patient room environment controls or non-critical monitoring equipment. Success in these areas builds confidence and momentum for more complex implementations involving critical care equipment.
Stakeholder Engagement and Training
Comprehensive stakeholder engagement ensures that voice interface implementations meet the actual needs of healthcare professionals and patients. Regular feedback sessions, user testing, and iterative improvements based on real-world usage patterns contribute to successful adoption.
Training programs must address both technical competency and clinical integration, ensuring that healthcare workers understand how voice interfaces enhance rather than replace existing workflows. Ongoing education and support maintain proficiency and encourage advanced feature utilization.
Quality Assurance and Safety Protocols
Robust quality assurance programs ensure that voice-controlled equipment maintains the same safety standards as traditional interfaces. Regular system testing, accuracy monitoring, and fail-safe mechanisms protect against potential voice recognition errors or system failures.
Safety protocols must include backup control methods, clear escalation procedures for system failures, and comprehensive documentation of all voice-activated actions for audit and review purposes.
Economic Impact and Return on Investment
The economic implications of voice interface implementation in hospital equipment extend beyond initial technology costs to encompass operational savings, improved outcomes, and enhanced competitive positioning.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
While voice interface implementation requires significant upfront investment in technology and training, the long-term benefits often justify these costs through reduced infection rates, improved efficiency, and enhanced patient satisfaction. Healthcare facilities report return on investment periods ranging from 18 to 36 months, depending on implementation scope and utilization rates.
Reduced healthcare-associated infections alone can generate substantial cost savings, as treating these preventable conditions represents a significant expense for healthcare systems. Voice interfaces contribute to infection prevention while improving overall care quality.
Operational Savings
Voice interfaces generate operational savings through reduced equipment interaction times, streamlined workflows, and decreased training requirements for new staff. Healthcare professionals can operate multiple systems simultaneously, reducing staffing requirements during peak demand periods.
The technology also reduces equipment maintenance costs by minimizing physical wear on buttons, switches, and touch screens, extending equipment lifespan and reducing replacement frequency.
CONCLUSION: THE FUTURE OF HEALTHCARE TECHNOLOGY

Voice interfaces represent a transformative technology that will fundamentally reshape how healthcare professionals interact with hospital equipment. As these systems continue to evolve and mature, they promise to address critical challenges in modern healthcare while opening new possibilities for improved patient care and operational efficiency.
The benefits of voice-controlled hospital equipment extend far beyond mere convenience—they encompass infection control, workflow optimization, accessibility enhancement, and patient empowerment. As healthcare systems worldwide face increasing pressure to deliver high-quality care while controlling costs, voice interfaces offer a pathway to achieving these seemingly conflicting objectives.
The successful implementation of voice interfaces requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and ongoing optimization based on real-world usage patterns and clinical outcomes. Healthcare organizations that embrace this technology early and implement it thoughtfully will gain significant competitive advantages while improving patient care quality and staff satisfaction.
As artificial intelligence continues to advance and integration capabilities expand, voice interfaces will become increasingly sophisticated, offering predictive capabilities, contextual awareness, and seamless integration across healthcare ecosystems. The future of hospital equipment lies not in more complex manual interfaces, but in intelligent, voice-activated systems that understand clinical context and respond intuitively to healthcare professionals’ needs.
The transformation of hospital equipment through voice interfaces represents more than technological progress—it embodies a fundamental shift toward more humane, efficient, and safe healthcare delivery. As these systems become more prevalent, they will redefine the relationship between healthcare professionals and technology, creating environments where technology truly serves to enhance rather than complicate the sacred mission of healing and care.
Healthcare organizations that invest in voice interface technology today are not just adopting new tools—they are pioneering the future of medical care delivery, where technology seamlessly integrates with clinical practice to create safer, more efficient, and more compassionate healthcare environments for both patients and providers.