HOW TO CREATE A DEVICE MAINTENANCE LOG FOR COMPLIANCE: A COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE FOR HEALTHCARE ORGANIZATIONS

In today’s complex healthcare environment, maintaining accurate device maintenance logs is not just a best practice—it’s a regulatory requirement that can make the difference between successful compliance audits and costly violations. Healthcare organizations face increasing scrutiny from regulatory bodies such as the FDA, The Joint Commission, and CMS, all of which require meticulous documentation of medical equipment maintenance activities.
Creating an effective device maintenance log system requires understanding regulatory requirements, implementing structured documentation processes, and establishing procedures that ensure long-term compliance while supporting optimal equipment performance. This comprehensive guide provides healthcare professionals with the knowledge and tools necessary to develop robust maintenance logging systems that meet all compliance standards while enhancing operational efficiency.
The consequences of inadequate maintenance documentation extend far beyond regulatory penalties. Poor record-keeping can lead to equipment failures, patient safety incidents, increased liability exposure, and loss of accreditation. Conversely, well-maintained logs serve as powerful tools for preventing equipment downtime, optimizing maintenance schedules, and demonstrating organizational commitment to quality patient care.
UNDERSTANDING REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS FOR DEVICE MAINTENANCE LOGS

The regulatory landscape governing medical device maintenance documentation is complex and multifaceted, involving federal agencies, accreditation bodies, and international standards organizations. Understanding these requirements forms the foundation for creating effective maintenance logging systems.
FDA Requirements and Quality System Regulation
The FDA’s Quality System Regulation (21 CFR Part 820) establishes fundamental requirements for medical device manufacturers and healthcare facilities regarding equipment maintenance documentation. Under these regulations, healthcare organizations must maintain comprehensive records that demonstrate proper equipment maintenance, calibration, and performance verification.
The FDA requires documentation of all maintenance activities performed on medical devices, including routine preventive maintenance, corrective actions, and calibration procedures. These records must be readily available for inspection and maintained for the life of the device or as specified by the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Key FDA documentation requirements include:
- Complete equipment identification and specifications
- Maintenance schedules and procedures
- Records of all maintenance activities performed
- Calibration certificates and verification records
- Personnel qualifications and training records
- Equipment failure reports and corrective actions taken
The Joint Commission Standards
The Joint Commission has established comprehensive standards for medical equipment management that require 100% compliance for accreditation. These standards mandate that healthcare organizations maintain detailed maintenance logs for all medical equipment used in patient care.
The Joint Commission’s Environment of Care standards (EC.02.04.01) require organizations to maintain equipment inventories, establish maintenance programs, and document all maintenance activities. MedTrainer The organization conducts unannounced surveys every 18 to 36 months, during which maintenance records are thoroughly reviewed.
CMS Guidelines and Requirements
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has adopted specific guidelines for medical equipment maintenance that healthcare facilities must follow to maintain certification and reimbursement eligibility. These guidelines require facilities to maintain accurate maintenance records and demonstrate compliance with manufacturer recommendations and applicable safety standards.
CMS requires documentation of equipment maintenance policies, procedures, and programs, as well as specific equipment maintenance inventories, activities, and schedules. Healthcare facilities must also maintain records of equipment failures and document whether any failures resulted in harm to individuals.
Essential Components of a Comprehensive Device Maintenance Log

An effective device maintenance log must capture specific, detailed information to ensure proper equipment maintenance and regulatory compliance. The log should be designed to provide a complete picture of each device’s maintenance history while facilitating easy access to critical information during audits and inspections.
Equipment Identification and Basic Information
Every maintenance log entry must begin with complete equipment identification information. This foundational data enables accurate tracking and ensures that maintenance records can be properly associated with specific devices throughout their operational life.
Essential identification elements include:
- Equipment make, model, and serial number: Unique identifiers that distinguish each device from others
- Asset tag or facility identification number: Internal tracking numbers assigned by the healthcare organization
- Location and department assignment: Current physical location and responsible department
- Installation date and warranty information: Critical dates affecting maintenance requirements
- Manufacturer specifications and requirements: Reference to official maintenance guidelines
Maintenance Activity Documentation
The core of any maintenance log lies in the detailed documentation of all maintenance activities performed on each device. This information serves as the primary evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements and manufacturer recommendations.
Comprehensive maintenance activity records should include:
- Date and time of maintenance: Precise timing of all maintenance activities
- Type of maintenance performed: Whether preventive, corrective, or emergency maintenance
- Detailed description of work completed: Specific tasks performed and procedures followed
- Parts and supplies used: Complete inventory of components replaced or consumed
- Tools and equipment utilized: Specialized tools or test equipment used during maintenance
- Duration of maintenance activity: Time required to complete maintenance tasks
Personnel and Qualification Records
Regulatory requirements mandate that only qualified personnel perform maintenance on medical devices. Maintenance logs must document the credentials and qualifications of all individuals involved in maintenance activities.
Required personnel documentation includes:
- Names and signatures of maintenance personnel: Clear identification of individuals performing work
- Certification and training records: Evidence of appropriate qualifications and ongoing education
- Supervisor approval and oversight: Documentation of management review and approval
- External contractor information: Complete records when third-party service providers are utilized
Equipment Status and Performance Data
Maintenance logs must capture comprehensive information about equipment status before, during, and after maintenance activities. This data enables trend analysis and helps identify potential issues before they impact patient care.
Critical status information includes:
- Pre-maintenance equipment condition: Baseline performance data and any observed issues
- Test results and measurements: Quantitative data from performance verification tests
- Calibration data and certificates: Results of calibration activities and associated documentation
- Post-maintenance verification: Confirmation that equipment meets performance specifications
- Return-to-service authorization: Formal approval for equipment to resume clinical use
Implementing Best Practices for Maintenance Log Creation

Creating effective maintenance logs requires implementing structured processes and best practices that ensure consistency, accuracy, and regulatory compliance. These practices form the foundation for sustainable maintenance documentation systems that support long-term organizational success.
Standardization and Consistency
Standardized procedures ensure that all maintenance activities are documented using consistent formats and terminology. This standardization facilitates data analysis, trend identification, and regulatory compliance verification.
Key standardization elements include:
- Uniform documentation formats: Consistent templates and forms for all maintenance activities
- Standardized terminology and abbreviations: Clear definitions and consistent usage throughout the organization
- Structured data entry procedures: Step-by-step processes for completing maintenance records
- Quality control checkpoints: Regular reviews to ensure compliance with documentation standards
Digital vs. Paper-Based Systems
Modern healthcare organizations face important decisions regarding the format and technology used for maintenance documentation. Each approach offers distinct advantages and challenges that must be carefully considered.
Digital maintenance management systems provide several significant advantages:
- Real-time access to maintenance records and schedules
- Automated alerts and notifications for scheduled maintenance
- Enhanced data analysis and reporting capabilities
- Improved security and backup procedures
- Integration with other healthcare information systems
Paper-based systems may be appropriate for smaller organizations or specific applications:
- Lower initial implementation costs
- No dependency on computer systems or network connectivity
- Familiar processes for staff accustomed to paper documentation
- Immediate availability without system startup delays
Integration with Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS)
Advanced healthcare organizations increasingly rely on sophisticated CMMS platforms to manage equipment maintenance activities and documentation. These systems provide comprehensive tools for scheduling, tracking, and documenting maintenance activities while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Modern CMMS platforms offer:
- Automated maintenance scheduling: System-generated work orders based on manufacturer recommendations
- Inventory management integration: Automatic tracking of parts and supplies used during maintenance
- Mobile access capabilities: Field technicians can update records in real-time using tablets or smartphones
- Regulatory compliance reporting: Automated generation of compliance reports for audits and inspections
- Predictive maintenance analytics: Advanced algorithms that identify potential equipment failures before they occur
Compliance Documentation Requirements by Device Type

Different types of medical devices have varying documentation requirements based on their classification, risk level, and regulatory oversight. Understanding these specific requirements ensures that maintenance logs capture all necessary information for each device category.
Class I Medical Devices
Class I devices generally have the lowest risk profile and may have simplified documentation requirements. However, proper maintenance records remain essential for demonstrating due diligence and ensuring optimal performance.
Typical Class I device documentation includes:
- Basic maintenance schedules and completion records
- User training and competency verification
- Cleaning and disinfection logs
- Performance verification testing results
- Incident reports and corrective actions
Class II Medical Devices
Class II devices require more comprehensive documentation due to their increased complexity and potential patient safety impact. These devices often require FDA clearance and must comply with specific performance standards.
Enhanced documentation requirements include:
- Detailed preventive maintenance procedures and schedules
- Calibration records and certificates
- Software validation and update documentation
- Environmental monitoring data
- Comprehensive performance testing results
Class III Medical Devices
Class III devices represent the highest risk category and require the most stringent documentation requirements. These life-supporting or life-sustaining devices demand comprehensive maintenance records that demonstrate complete compliance with all applicable regulations.
Comprehensive documentation requirements include:
- FDA-approved maintenance protocols and procedures
- Qualified personnel certification and ongoing training records
- Detailed risk assessments and mitigation strategies
- Complete traceability of all maintenance activities
- Immediate reporting of any device failures or safety concerns
Creating Effective Maintenance Schedules and Procedures
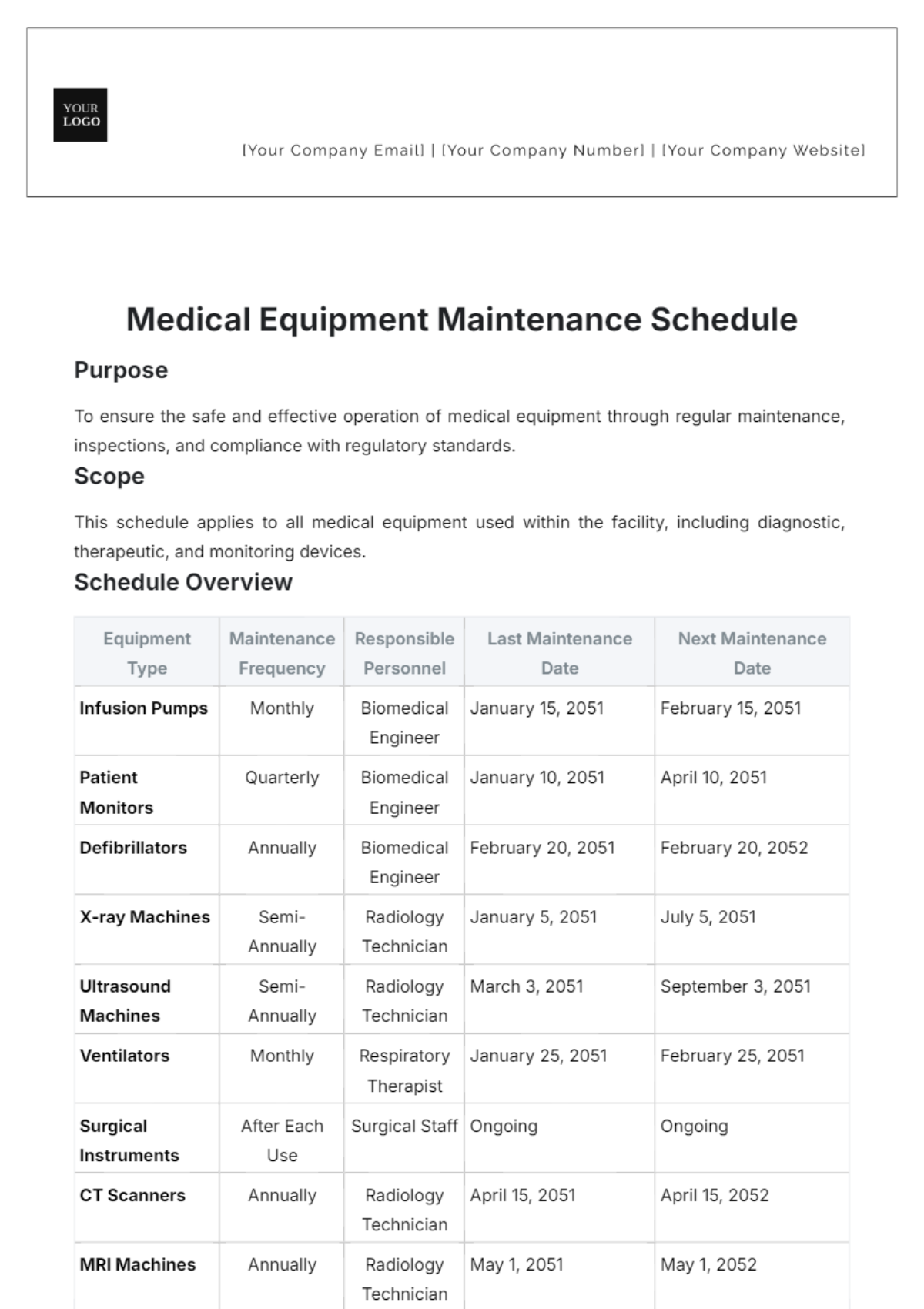
Effective maintenance logging begins with well-designed maintenance schedules and procedures that align with manufacturer recommendations, regulatory requirements, and organizational capabilities. These foundational elements ensure that maintenance activities are performed consistently and documented appropriately.
Manufacturer Recommendations and Guidelines
Medical device manufacturers provide detailed maintenance recommendations that serve as the baseline for organizational maintenance programs. These guidelines specify required maintenance activities, frequencies, and procedures necessary to maintain device safety and effectiveness.
Critical manufacturer information includes:
- Preventive maintenance schedules: Specific timelines for routine maintenance activities
- Required maintenance procedures: Step-by-step instructions for each maintenance task
- Replacement part specifications: Authorized components and supplies for maintenance activities
- Performance verification requirements: Tests and measurements required after maintenance
- Safety precautions and warnings: Special considerations for maintenance personnel
Risk-Based Maintenance Planning
Healthcare organizations must balance manufacturer recommendations with practical considerations such as equipment criticality, patient safety impact, and resource availability. Risk-based maintenance planning helps organizations prioritize maintenance activities based on potential consequences of equipment failure.
Risk assessment factors include:
- Patient safety impact: Potential harm to patients if equipment fails
- Operational criticality: Effect of equipment downtime on healthcare services
- Failure probability: Historical data and manufacturer reliability information
- Regulatory requirements: Mandatory maintenance activities and frequencies
- Resource availability: Staff, parts, and budget constraints
Documentation of Maintenance Procedures
Comprehensive maintenance procedures provide detailed instructions for performing each maintenance task while ensuring consistent documentation of completed activities. These procedures serve as training materials and quality control tools.
Effective maintenance procedures include:
- Clear step-by-step instructions: Detailed guidance for performing each maintenance task
- Required tools and materials: Complete lists of equipment and supplies needed
- Safety precautions and warnings: Specific hazards and protective measures
- Documentation requirements: Exact information that must be recorded during maintenance
- Quality control checkpoints: Verification steps to ensure proper completion
Quality Control and Audit Preparation

Robust quality control processes ensure that maintenance logs meet regulatory requirements and provide accurate information for decision-making. These processes also prepare organizations for regulatory audits and accreditation surveys.
Regular Review and Validation Procedures
Systematic review processes identify potential documentation gaps, inconsistencies, or compliance issues before they become problems during audits or inspections. Regular validation ensures that maintenance logs accurately reflect actual maintenance activities and equipment status.
Key review procedures include:
- Monthly log completeness audits: Verification that all required maintenance activities are documented
- Quarterly compliance assessments: Comprehensive review of documentation against regulatory requirements
- Annual system evaluations: Complete assessment of maintenance logging processes and effectiveness
- Continuous improvement initiatives: Regular updates to procedures based on lessons learned and best practices
Audit Trail and Record Retention
Comprehensive audit trails demonstrate the integrity of maintenance records and provide evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements. Proper record retention ensures that historical data remains available for analysis and regulatory review.
Essential audit trail elements include:
- Document creation and modification dates: Complete history of record changes and updates
- User identification and authentication: Clear records of who performed each maintenance activity
- Approval and review signatures: Evidence of supervisory oversight and quality control
- System backup and recovery procedures: Protection against data loss or corruption
- Long-term archive strategies: Secure storage of historical records beyond active use periods
Corrective Action and Improvement Processes
When maintenance logs reveal equipment problems, safety concerns, or process deficiencies, organizations must implement effective corrective action processes. These processes demonstrate organizational commitment to continuous improvement and regulatory compliance.
Effective corrective action processes include:
- Problem identification and assessment: Systematic evaluation of identified issues
- Root cause analysis: Detailed investigation to determine underlying causes
- Corrective action planning: Development of specific actions to address identified problems
- Implementation monitoring: Ongoing verification that corrective actions are effective
- Process improvement integration: Incorporation of lessons learned into standard procedures
Technology Solutions and Digital Integration
Modern technology solutions offer significant advantages for creating, maintaining, and managing device maintenance logs. These digital tools enhance accuracy, accessibility, and compliance while reducing administrative burden on healthcare staff.
Electronic Health Record Integration
Integration between maintenance management systems and electronic health records provides comprehensive visibility into equipment history and patient care activities. This integration enables correlation between equipment performance and patient outcomes while supporting clinical decision-making.
Integration benefits include:
- Real-time equipment status information: Immediate access to maintenance history during clinical procedures
- Patient safety alerts: Automatic notifications when equipment issues might affect patient care
- Comprehensive audit trails: Complete records linking equipment maintenance to patient encounters
- Regulatory reporting automation: Streamlined generation of required compliance reports
Mobile Applications and Field Data Entry
Mobile technology enables maintenance technicians to update records in real-time while performing maintenance activities. This capability improves accuracy and timeliness while reducing administrative delays.
Mobile application features include:
- Offline data entry capabilities: Record maintenance activities even without network connectivity
- Barcode and QR code scanning: Rapid equipment identification and data entry
- Digital photography integration: Visual documentation of equipment condition and maintenance activities
- Electronic signature capture: Immediate approval and authentication of completed work
Predictive Analytics and Maintenance Optimization
Advanced analytics platforms analyze historical maintenance data to identify patterns, predict equipment failures, and optimize maintenance schedules. These tools help organizations transition from reactive to predictive maintenance strategies.
Analytics capabilities include:
- Failure prediction algorithms: Early warning systems for potential equipment problems
- Maintenance schedule optimization: Data-driven recommendations for maintenance timing and procedures
- Cost-benefit analysis: Financial impact assessment of different maintenance strategies
- Performance trending: Long-term analysis of equipment reliability and maintenance effectiveness
Training and Staff Development
Successful maintenance logging programs require comprehensive training and ongoing staff development to ensure that all personnel understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining compliance.
Personnel Qualification Requirements
Regulatory requirements specify minimum qualifications for personnel performing maintenance on medical devices. Organizations must ensure that all maintenance staff meet these requirements and maintain appropriate certifications.
Qualification requirements include:
- Technical education and training: Formal education or apprenticeship programs in relevant technical fields
- Device-specific training: Manufacturer-provided training on specific equipment maintenance procedures
- Regulatory compliance education: Understanding of applicable regulations and documentation requirements
- Ongoing competency assessment: Regular evaluation of technical skills and knowledge retention
Documentation Training Programs
Comprehensive training programs ensure that all staff understand proper documentation procedures and compliance requirements. These programs should address both technical aspects of maintenance logging and regulatory compliance considerations.
Training program elements include:
- Documentation standards and procedures: Detailed instruction on required information and formatting
- Regulatory requirement overview: Understanding of applicable regulations and compliance implications
- System training: Hands-on instruction for maintenance management software and tools
- Quality control processes: Training on review procedures and error prevention strategies
Continuous Education and Updates
The regulatory environment and technology landscape continue to evolve, requiring ongoing education and training updates. Organizations must establish processes for keeping staff current with new requirements and best practices.
Continuous education strategies include:
- Regular training updates: Periodic refresher training on documentation procedures and requirements
- Industry conference participation: Attendance at professional meetings and educational seminars
- Professional certification maintenance: Support for ongoing certification requirements and continuing education
- Internal knowledge sharing: Regular meetings to discuss lessons learned and best practices
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Understanding common mistakes in maintenance logging helps organizations develop effective prevention strategies and avoid costly compliance issues.
Incomplete Documentation
Incomplete maintenance records represent one of the most common compliance failures. Missing information can result in regulatory citations and may indicate inadequate maintenance activities.
Prevention strategies include:
- Standardized checklists: Required forms that prompt completion of all necessary information
- Electronic validation: System controls that prevent submission of incomplete records
- Regular audits: Systematic review processes to identify and correct documentation gaps
- Staff training: Comprehensive education on documentation requirements and compliance implications
Inconsistent Procedures
Inconsistencies in maintenance procedures and documentation can indicate poor process control and may raise regulatory concerns about system reliability.
Consistency improvement measures include:
- Standardized operating procedures: Detailed written procedures for all maintenance activities
- Regular procedure reviews: Periodic evaluation and updates to ensure continued effectiveness
- Staff competency assessment: Regular verification that personnel follow established procedures
- Quality control monitoring: Ongoing assessment of procedure compliance and effectiveness
Poor Record Organization
Disorganized maintenance records can impede audit preparation and may suggest inadequate system controls. Proper organization facilitates easy access to information and demonstrates professional management practices.
Organization improvement strategies include:
- Systematic filing procedures: Clear guidelines for record organization and storage
- Digital indexing systems: Electronic tools for rapid information retrieval
- Regular record maintenance: Scheduled activities to maintain organization and accessibility
- Backup and archive procedures: Reliable systems for protecting historical records
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement

Effective maintenance logging programs require ongoing measurement and improvement to ensure continued effectiveness and regulatory compliance.
Key Performance Indicators
Organizations should establish specific metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of their maintenance logging programs and identify opportunities for improvement.
Important KPIs include:
- Documentation completeness rates: Percentage of maintenance activities with complete records
- Audit finding trends: Analysis of regulatory citations and recommendations over time
- Equipment reliability metrics: Correlation between maintenance activities and equipment performance
- Staff compliance rates: Assessment of personnel adherence to documentation procedures
Regular Program Evaluation
Systematic evaluation processes help organizations identify strengths and weaknesses in their maintenance logging programs while developing targeted improvement strategies.
Evaluation components include:
- Annual compliance assessments: Comprehensive review of program effectiveness and regulatory compliance
- Stakeholder feedback collection: Input from maintenance staff, clinicians, and administrators
- Benchmark comparison: Analysis against industry best practices and peer organizations
- Cost-benefit analysis: Evaluation of program costs versus benefits and compliance outcomes
Continuous Improvement Implementation
Based on evaluation results, organizations should implement systematic improvement processes that enhance maintenance logging effectiveness while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Improvement strategies include:
- Process optimization initiatives: Streamlining procedures while maintaining compliance requirements
- Technology upgrades: Implementation of new tools and systems to improve efficiency and accuracy
- Training program enhancements: Targeted education to address identified knowledge gaps
- Policy and procedure updates: Regular revisions to reflect best practices and regulatory changes
Conclusion: Building a Foundation for Long-Term Success
Creating effective device maintenance logs for compliance requires a comprehensive approach that addresses regulatory requirements, organizational capabilities, and technological opportunities. Healthcare organizations that invest in robust maintenance logging systems position themselves for long-term success while ensuring optimal patient safety and regulatory compliance.
The key to successful maintenance logging lies in understanding that documentation is not merely an administrative requirement but a critical component of quality patient care. Well-maintained logs provide valuable insights into equipment performance, support evidence-based maintenance decisions, and demonstrate organizational commitment to excellence.
As healthcare continues to evolve with new technologies and changing regulations, maintenance logging systems must adapt and improve. Organizations that embrace continuous improvement and invest in modern technology solutions will be best positioned to meet future challenges while maintaining the highest standards of patient care and regulatory compliance.
The investment in comprehensive maintenance logging systems pays dividends through improved equipment reliability, enhanced patient safety, reduced regulatory risk, and optimized operational efficiency. Healthcare organizations that prioritize maintenance documentation demonstrate their commitment to quality care while building sustainable foundations for future success.
By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this comprehensive guide, healthcare organizations can develop maintenance logging systems that not only meet current regulatory requirements but also provide the flexibility and capability to adapt to future challenges and opportunities in the dynamic healthcare environment.
