HOW TO ADD VOICE AI TO MEDICAL DEVICES: A COMPREHENSIVE IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE
The integration of voice artificial intelligence (AI) into medical devices represents one of the most transformative advances in healthcare technology today. As healthcare professionals increasingly seek ways to streamline workflows, reduce administrative burdens, and enhance patient care, voice AI emerges as a critical solution that bridges the gap between advanced technology and practical clinical applications.
The global voice technology in healthcare market, valued at approximately $4.23 billion in 2023, is projected to reach around $21.67 billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.9%. This explosive growth underscores the critical importance of understanding how to effectively implement voice AI in medical devices Polaris Market Research.
UNDERSTANDING VOICE AI IN MEDICAL DEVICE CONTEXT
Voice AI in medical devices encompasses the integration of speech recognition, natural language processing (NLP), and machine learning technologies to enable hands-free, voice-controlled operation of medical equipment. This technology transforms traditional medical devices from passive tools requiring manual interaction into intelligent, responsive systems that can understand and execute voice commands, provide audio feedback, and integrate seamlessly with healthcare workflows.
The core value proposition of voice AI in medical devices extends beyond simple convenience. In sterile environments like operating rooms, voice control eliminates the need for healthcare professionals to break sterile fields to interact with equipment. During patient examinations, voice commands allow physicians to maintain eye contact and physical engagement with patients while simultaneously controlling diagnostic equipment or updating electronic health records (EHRs).
CORE TECHNOLOGIES BEHIND MEDICAL VOICE AI
AUTOMATED SPEECH RECOGNITION (ASR)
The foundation of any voice-enabled medical device lies in its automated speech recognition capabilities. Modern ASR systems leverage deep learning neural networks trained on massive datasets of healthcare-specific speech patterns. Leading medical ASR models achieve over 90% accuracy on medical dictation tasks, a critical threshold for clinical applications where errors can have serious consequences.
Medical ASR faces unique challenges that distinguish it from consumer applications. Healthcare environments present acoustic challenges including equipment alarms, public announcements, and ambient conversations that can degrade audio quality. Additionally, medical terminology includes complex Latin-based words, drug names, and anatomical references that require specialized training datasets.
Advanced medical ASR systems employ several key technologies:
Acoustic Modeling: Specialized models trained to handle the unique acoustic properties of healthcare environments, including noise from medical equipment, ventilators, and monitoring devices.
Language Modeling: Medical-specific language models trained on clinical documentation, medical literature, and healthcare conversations to understand medical context and terminology.
Speaker Adaptation: Systems that can adapt to individual healthcare professionals’ speech patterns, accents, and speaking styles to improve accuracy over time.
NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING FOR HEALTHCARE
Natural language processing in medical voice AI goes beyond simple speech-to-text conversion. Advanced NLP systems must understand medical context, extract relevant clinical entities, and interpret the intent behind voice commands within the healthcare domain.
Key NLP capabilities for medical voice AI include:
Clinical Entity Recognition: The ability to identify and extract medical concepts such as symptoms, diagnoses, medications, procedures, and anatomical references from spoken language.
Intent Classification: Understanding the purpose behind voice commands, whether the user wants to control device settings, access patient information, or document clinical observations.
Contextual Understanding: Maintaining awareness of the clinical context, patient information, and current workflow state to provide appropriate responses and actions.
Medical Sentiment Analysis: Detecting emotional cues and urgency levels in speech to prioritize responses and alerts appropriately.
Speech Synthesis and Voice Generation
Modern medical voice AI systems require sophisticated text-to-speech (TTS) capabilities to provide clear, professional audio feedback. Medical TTS systems must pronounce complex medical terminology accurately while maintaining natural-sounding speech that builds trust with healthcare professionals and patients.
Advanced medical TTS systems incorporate:
Domain-Specific Training: TTS models fine-tuned on medical terminology to ensure accurate pronunciation of clinical terms, drug names, and anatomical references.
Emotional Tone Matching: The ability to adjust voice tone to match the clinical context, from urgent alerts to routine confirmations.
Multi-Language Support: Support for diverse languages and dialects to serve global healthcare markets and multilingual patient populations.
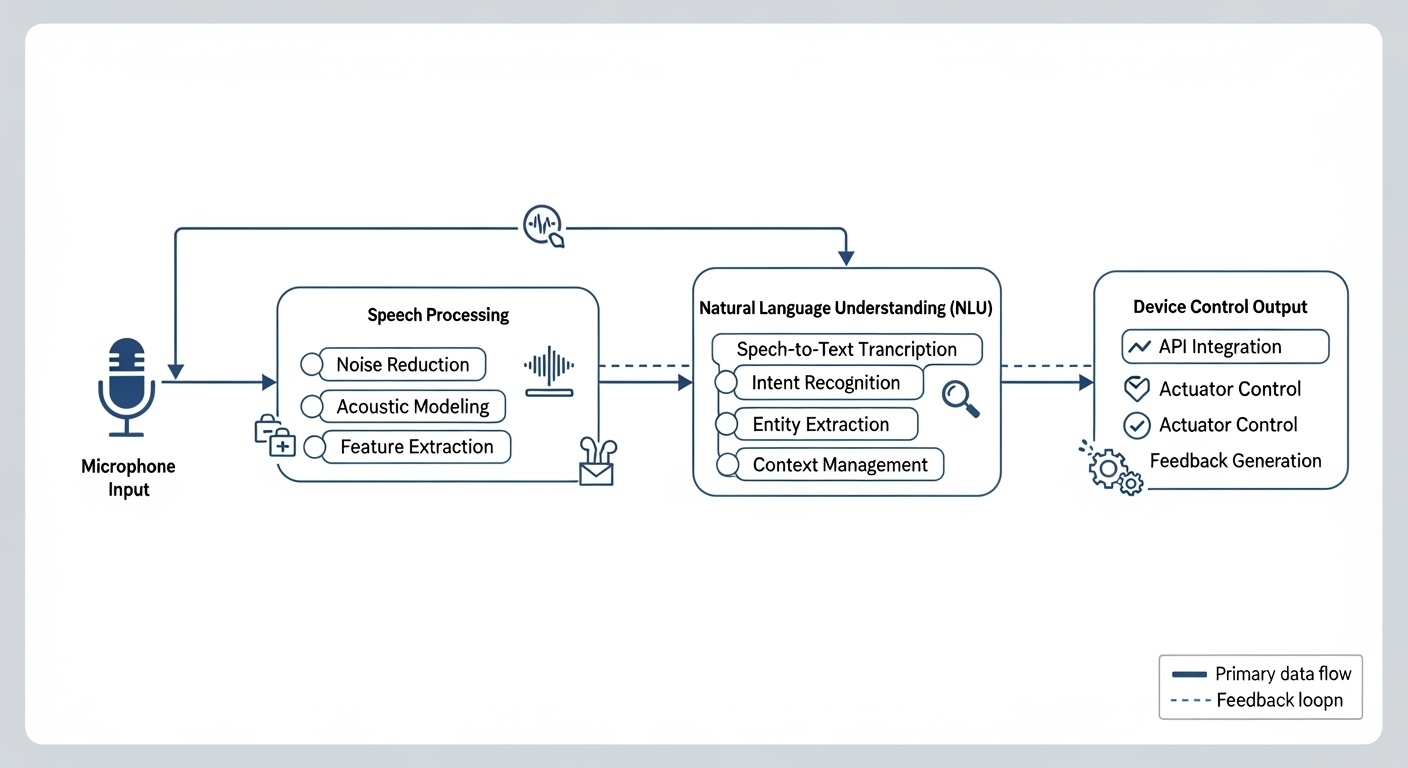
IMPLEMENTATION ARCHITECTURE AND DESIGN PATTERNS
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW
Implementing voice AI in medical devices requires a carefully designed architecture that balances performance, security, and regulatory compliance. The typical architecture consists of several key components:
Edge Processing Layer: Local processing capabilities for wake word detection, basic command recognition, and privacy-sensitive operations that must remain on-device.
Cloud Processing Layer: Advanced NLP, speech recognition, and machine learning capabilities hosted in secure, HIPAA-compliant cloud environments.
Integration Layer: APIs and middleware that connect voice AI capabilities with existing medical device functionality and healthcare IT systems.
Security Layer: End-to-end encryption, access controls, and audit logging to ensure patient data protection and regulatory compliance.
HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS AND CONSIDERATIONS
Medical devices incorporating voice AI require specific hardware components optimized for healthcare environments:
Microphone Arrays: Multiple microphones arranged to provide optimal voice capture in noisy environments. Medical-grade microphone arrays typically feature noise cancellation, echo suppression, and far-field voice capture capabilities exceeding 9 meters.
Processing Units: Sufficient computational power for local voice processing, typically including specialized AI chips or GPUs for neural network operations.
Audio Output Systems: High-quality speakers or headphone connections for clear audio feedback, with volume controls appropriate for healthcare settings.
Network Connectivity: Reliable internet connections for cloud-based processing, with failover capabilities for critical operations.
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT KIT (SDK) INTEGRATION
Modern voice AI implementation relies heavily on specialized SDKs and APIs that provide pre-built voice capabilities. Leading healthcare voice AI vendors offer comprehensive SDKs that include:
Speech Recognition APIs: RESTful APIs for converting speech to text with medical-specific models and terminology support.
Natural Language Understanding APIs: Services for extracting medical entities, understanding intent, and providing contextual responses.
Text-to-Speech APIs: Voice synthesis capabilities optimized for medical terminology and clinical communication.
Integration SDKs: Pre-built components for embedding voice capabilities into existing medical device software, with support for multiple programming languages and platforms.
The integration process typically involves:
-
API Key Management: Secure management of authentication credentials for cloud-based voice services.
-
Audio Pipeline Configuration: Setting up audio capture, preprocessing, and streaming to voice recognition services.
-
Response Handling: Processing voice AI responses and translating them into device-specific actions or information displays.
-
Error Handling: Implementing robust error handling for network connectivity issues, recognition failures, and system errors.
REAL-WORLD IMPLEMENTATION EXAMPLES
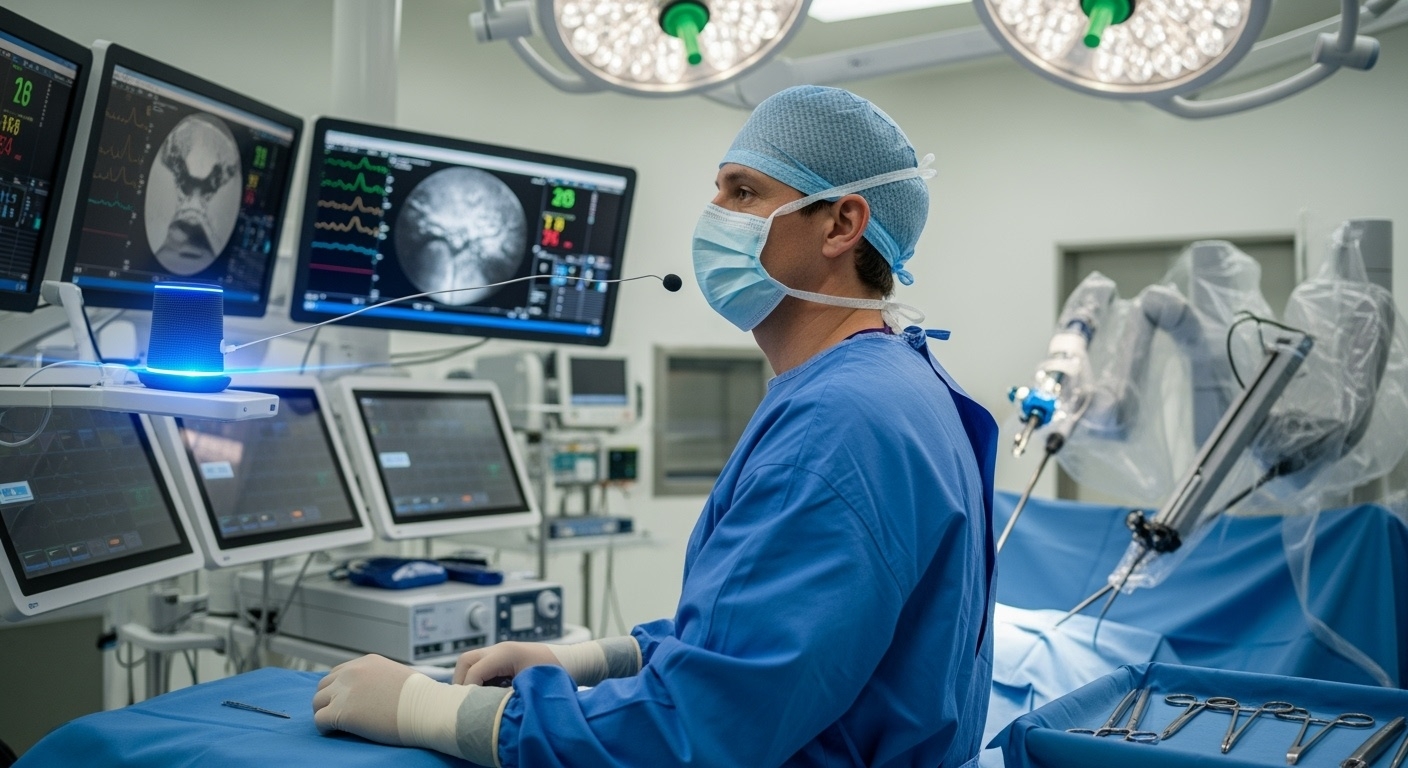
SURGICAL SUITE INTEGRATION
Modern operating rooms represent one of the most compelling use cases for voice AI integration. Surgeons require hands-free access to patient information, imaging systems, and surgical equipment while maintaining sterile conditions.
Example Implementation: A leading medical device manufacturer integrated voice AI into their surgical imaging system, allowing surgeons to control X-ray positioning, zoom levels, and image capture through voice commands. The system recognizes commands like “Move C-arm to lateral position,” “Zoom in 50%,” and “Capture image” while filtering out background conversations and equipment noise.
The implementation required:
- Custom acoustic models trained on operating room environments
- Medical terminology specific to radiology and surgery
- Integration with existing imaging equipment APIs
- Real-time processing capabilities for immediate response
Results: The voice-controlled imaging system reduced procedure time by an average of 15 minutes per surgery and eliminated breaks in sterile technique, leading to improved patient outcomes and increased operational efficiency.
PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEMS
Voice AI integration in patient monitoring systems enables healthcare professionals to interact with monitoring equipment, update patient information, and receive alerts through natural language interactions.
Example Implementation: A major patient monitoring manufacturer developed voice-enabled vital signs monitors that allow nurses to verbally log observations, adjust alarm parameters, and request patient history information. The system supports commands like “Record blood pressure 120 over 80,” “Set heart rate alarm to 100,” and “Show 24-hour trend.”
Key implementation features included:
- Multi-speaker recognition to identify different healthcare professionals
- Context-aware responses based on current patient status
- Integration with electronic health record systems
- Compliance with HIPAA privacy requirements
Results: The voice-enabled monitoring system reduced documentation time by 40% and improved data accuracy by eliminating manual transcription errors.
DIAGNOSTIC EQUIPMENT INTEGRATION
Diagnostic equipment represents another significant opportunity for voice AI integration, particularly in imaging systems, laboratory equipment, and point-of-care testing devices.
Example Implementation: An ultrasound equipment manufacturer integrated voice AI to enable hands-free operation during examinations. Sonographers can adjust imaging parameters, take measurements, and annotate findings using voice commands while maintaining optimal probe positioning and patient contact.
The voice AI system includes:
- Specialized vocabulary for ultrasound terminology
- Real-time measurement calculations based on verbal input
- Automatic report generation with voice-to-text documentation
- Integration with picture archiving and communication systems (PACS)
Results: The voice-enabled ultrasound system improved examination efficiency by 25% and enhanced image quality through reduced probe movement during manual equipment adjustments.
TECHNICAL IMPLEMENTATION PROCESS
PHASE 1: REQUIREMENTS ANALYSIS AND PLANNING
The first phase of voice AI implementation involves comprehensive analysis of clinical workflows, user requirements, and technical constraints. This phase typically includes:
Clinical Workflow Analysis: Detailed study of how healthcare professionals currently interact with the medical device, identifying opportunities for voice enhancement and potential usability improvements.
User Requirements Gathering: Extensive interviews with target users to understand their voice command preferences, environmental constraints, and integration expectations.
Technical Feasibility Assessment: Evaluation of existing device capabilities, hardware requirements, and software architecture to determine optimal implementation approach.
Regulatory Compliance Planning: Analysis of applicable regulations including FDA medical device requirements, HIPAA privacy rules, and international standards for medical software.
PHASE 2: VOICE AI MODEL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINING
The second phase focuses on developing and training the AI models that will power the voice capabilities:
Dataset Preparation: Collection and curation of medical speech datasets specific to the target application, including diverse speakers, accents, and clinical scenarios.
Model Training: Development of custom ASR and NLP models optimized for the specific medical domain and device application.
Testing and Validation: Comprehensive testing of voice recognition accuracy, response time, and reliability across diverse conditions and user scenarios.
Performance Optimization: Fine-tuning of models to achieve optimal balance between accuracy, speed, and resource utilization.
PHASE 3: SYSTEM INTEGRATION AND DEVELOPMENT
The third phase involves integrating voice AI capabilities with existing medical device systems:
Hardware Integration: Installation and configuration of microphones, speakers, and processing components required for voice AI functionality.
Software Development: Implementation of voice AI SDKs, APIs, and custom code to connect voice capabilities with device functionality.
User Interface Design: Development of visual and audio interfaces that provide clear feedback about voice AI status, commands, and responses.
Security Implementation: Implementation of encryption, access controls, and audit logging to ensure patient data protection and regulatory compliance.
Phase 4: Clinical Testing and Validation
The fourth phase involves extensive testing in real healthcare environments:
Pilot Testing: Limited deployment in controlled clinical settings to validate functionality and gather initial user feedback.
Clinical Trials: Formal studies to measure the impact of voice AI on clinical outcomes, workflow efficiency, and user satisfaction.
Usability Testing: Comprehensive evaluation of user interface design, command recognition accuracy, and overall user experience.
Performance Validation: Measurement of system performance under real-world conditions, including accuracy, response time, and reliability metrics.
PHASE 5: DEPLOYMENT AND CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
The final phase focuses on full deployment and ongoing optimization:
Training and Education: Comprehensive training programs for healthcare professionals on voice AI capabilities and best practices.
Rollout Management: Phased deployment across target healthcare facilities with careful monitoring and support.
Continuous Monitoring: Ongoing assessment of system performance, user satisfaction, and clinical impact.
Model Updates: Regular updates to voice AI models based on new data, user feedback, and evolving clinical requirements.
REGULATORY COMPLIANCE AND SECURITY CONSIDERATIONS
HIPAA COMPLIANCE REQUIREMENTS
Healthcare voice AI systems must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which mandates specific protections for patient health information. Key compliance requirements include Augnito AI:
Data Encryption: All voice data containing protected health information (PHI) must be encrypted both in transit and at rest using advanced encryption standards.
Access Controls: Implementation of role-based access controls to limit PHI exposure to the minimum necessary for clinical operations.
Audit Logging: Comprehensive logging of all access to PHI, including voice AI interactions, with detailed audit trails for compliance monitoring.
Business Associate Agreements: Formal agreements with voice AI vendors and cloud service providers ensuring their compliance with HIPAA requirements.
FDA MEDICAL DEVICE REGULATIONS
Voice AI integrated into medical devices may trigger FDA regulatory requirements depending on the device’s intended use and risk classification:
Software as Medical Device (SaMD): Voice AI systems that provide diagnostic information or treatment recommendations may be classified as medical devices requiring FDA approval.
Quality System Regulations: Implementation of quality management systems to ensure consistent design, development, and manufacturing of voice-enabled medical devices.
Clinical Evidence Requirements: Demonstration of safety and effectiveness through clinical studies and performance testing.
Post-Market Surveillance: Ongoing monitoring of device performance and adverse events after commercial deployment.
DATA PRIVACY AND SECURITY IMPLEMENTATION
Comprehensive security measures are essential for voice AI medical devices:
End-to-End Encryption: Implementation of strong encryption for all voice data transmission and storage, using industry-standard protocols such as TLS 1.3 and AES-256.
Secure Authentication: Multi-factor authentication systems for device access and cloud service connections.
Data Minimization: Collection and processing of only the minimum voice data necessary for clinical functionality.
Secure Development Practices: Implementation of secure coding practices, regular security assessments, and vulnerability testing throughout the development lifecycle.
OVERCOMING IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
ACOUSTIC ENVIRONMENT CHALLENGES
Healthcare environments present unique acoustic challenges that must be addressed:
Noise Cancellation: Implementation of advanced noise cancellation algorithms to filter out medical equipment sounds, alarms, and ambient conversations.
Echo Suppression: Acoustic echo cancellation to handle sound reflections in rooms with hard surfaces and medical equipment.
Far-Field Recognition: Microphone arrays capable of accurate voice recognition at distances up to 9 meters to accommodate various clinical scenarios.
Multi-Speaker Environments: Systems capable of distinguishing between different speakers in environments where multiple healthcare professionals may be present.
ACCURACY AND RELIABILITY REQUIREMENTS
Medical applications demand exceptionally high accuracy and reliability:
Continuous Learning: Implementation of machine learning systems that continuously improve based on usage patterns and user feedback.
Error Handling: Robust error handling and confirmation systems to prevent misinterpretation of critical voice commands.
Fallback Mechanisms: Alternative interaction methods available when voice recognition fails or is unavailable.
Quality Assurance: Comprehensive testing and validation processes to ensure consistent performance across diverse conditions and users.
INTEGRATION COMPLEXITY
Integrating voice AI with existing medical systems presents significant technical challenges:
Legacy System Integration: Development of APIs and middleware to connect voice AI with older medical devices and healthcare IT systems.
Interoperability Standards: Adherence to healthcare interoperability standards such as HL7 FHIR to ensure seamless data exchange.
Workflow Integration: Careful design to integrate voice AI capabilities into existing clinical workflows without disrupting established practices.
Scalability Considerations: Architecture design that supports scaling across large healthcare organizations with diverse device ecosystems.
FUTURE TRENDS AND EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
ADVANCED NATURAL LANGUAGE UNDERSTANDING
The future of medical voice AI lies in increasingly sophisticated natural language understanding capabilities:
Contextual Awareness: AI systems that understand the full clinical context, including patient history, current medications, and treatment plans.
Predictive Intelligence: Voice AI that can anticipate user needs and provide proactive suggestions based on clinical patterns and best practices.
Multi-Modal Integration: Combination of voice AI with visual recognition, gesture control, and other input modalities for comprehensive device interaction.
PERSONALIZED VOICE INTERFACES
Emerging trends point toward highly personalized voice AI experiences:
Individual Adaptation: Systems that learn and adapt to individual healthcare professionals’ speech patterns, preferences, and workflow styles.
Role-Based Interfaces: Voice AI interfaces customized for different healthcare roles, from surgeons to nurses to technicians.
Specialty-Specific Models: AI models trained for specific medical specialties with deep domain knowledge and terminology.
EDGE COMPUTING AND LOCAL PROCESSING
Growing emphasis on local processing capabilities:
On-Device Processing: Advanced AI chips enabling more voice processing to occur locally on medical devices, reducing latency and improving privacy.
Hybrid Architectures: Intelligent distribution of processing between edge devices and cloud services based on task requirements and network conditions.
Offline Capabilities: Voice AI systems capable of basic functionality even when network connectivity is unavailable.
BEST PRACTICES FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION
USER-CENTERED DESIGN PRINCIPLES
Successful voice AI implementation requires deep understanding of user needs:
Clinical Workflow Integration: Design voice interactions that enhance rather than disrupt existing clinical workflows.
Intuitive Command Structure: Development of natural, memorable voice commands that align with clinical terminology and practices.
Feedback and Confirmation: Clear audio and visual feedback to confirm voice command recognition and system responses.
Error Recovery: Graceful error handling and easy methods for users to correct misunderstood commands.
PERFORMANCE OPTIMIZATION STRATEGIES
Achieving optimal performance requires careful attention to system design:
Latency Minimization: Optimization of processing pipelines to minimize response time for voice commands.
Accuracy Maximization: Continuous training and refinement of AI models to achieve the highest possible recognition accuracy.
Resource Efficiency: Efficient use of computational resources to maintain performance while minimizing power consumption and heat generation.
Scalability Planning: Architecture design that supports growth in users, devices, and functionality over time.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Comprehensive testing strategies ensure reliable deployment:
Clinical Environment Testing: Extensive testing in real healthcare environments with actual clinical scenarios and workflows.
Stress Testing: Evaluation of system performance under high-load conditions and challenging acoustic environments.
Security Testing: Regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential security risks.
User Acceptance Testing: Formal testing with target users to validate usability, effectiveness, and satisfaction.
CONCLUSION
The integration of voice AI into medical devices represents a transformative opportunity to enhance healthcare delivery, improve clinical efficiency, and ultimately better serve patients. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve toward more digital, intelligent systems, voice AI emerges as a critical enabling technology that bridges the gap between advanced artificial intelligence and practical clinical applications.
Successful implementation requires careful attention to the unique requirements of healthcare environments, including regulatory compliance, patient privacy protection, and the demanding accuracy standards of medical applications. Organizations that invest in comprehensive planning, user-centered design, and robust security measures will be best positioned to realize the full benefits of voice AI integration.
The market growth projections, with the voice technology in healthcare market expected to reach $21.67 billion by 2032, underscore the significant opportunity for organizations that successfully implement voice AI in medical devices. As approximately 30% of physician practices have already adopted ambient listening AI technologies, early movers have the opportunity to gain competitive advantage and improve patient outcomes through innovative voice-enabled medical devices Matellio.
The future of healthcare technology lies in intelligent, responsive systems that understand and adapt to human needs. Voice AI represents a crucial step toward that future, enabling more natural, efficient, and effective interactions between healthcare professionals, patients, and medical technology. Organizations that embrace this transformation today will be well-positioned to lead the healthcare industry into its next era of innovation and improved patient care.
Looking ahead, the continued advancement of AI technologies, edge computing capabilities, and healthcare interoperability standards will only expand the possibilities for voice AI integration in medical devices. The organizations that invest in building strong foundations today—with robust security, regulatory compliance, and user-centered design—will be best equipped to leverage these future innovations and continue delivering value to healthcare providers and patients alike.