BEST POWER BACKUP SYSTEMS FOR MEDICAL EQUIPMENT: A COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE 2024
Medical equipment reliability is paramount in healthcare settings, where even momentary power interruptions can have life-threatening consequences. Whether in hospitals, clinics, or home healthcare environments, uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems serve as the critical bridge between primary power failure and emergency generators, ensuring continuous operation of life-saving medical devices.
The global medical UPS market has experienced significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of power reliability requirements and stringent healthcare regulations. Modern medical-grade UPS systems not only provide backup power but also condition incoming electricity, protecting sensitive equipment from voltage fluctuations, surges, and electrical noise that could compromise patient safety or damage expensive medical devices.
UNDERSTANDING MEDICAL-GRADE UPS SYSTEMS
Medical-grade UPS systems differ significantly from standard commercial units in their design, certification, and performance standards. These specialized power protection devices are engineered to meet the rigorous demands of healthcare environments, where patient safety is the primary concern.
KEY CHARACTERISTICS OF MEDICAL-GRADE UPS:
Enhanced Safety Features: Medical UPS systems incorporate advanced leakage current protection, ensuring patient safety even during power transitions. They comply with IEC 60601-1 standards for medical electrical equipment, providing additional layers of protection against electrical hazards.
Higher Reliability Standards: Medical environments demand 99.9% or higher availability. Medical-grade UPS systems feature redundant components, hot-swappable batteries, and advanced monitoring capabilities to minimize downtime risks.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): These systems generate minimal electromagnetic interference, preventing disruption of sensitive medical equipment like MRI machines, patient monitors, and diagnostic devices.
Extended Runtime Options: Unlike standard UPS systems designed for brief power outages, medical UPS units often support extended runtime configurations to bridge longer power interruptions until emergency generators can take over.
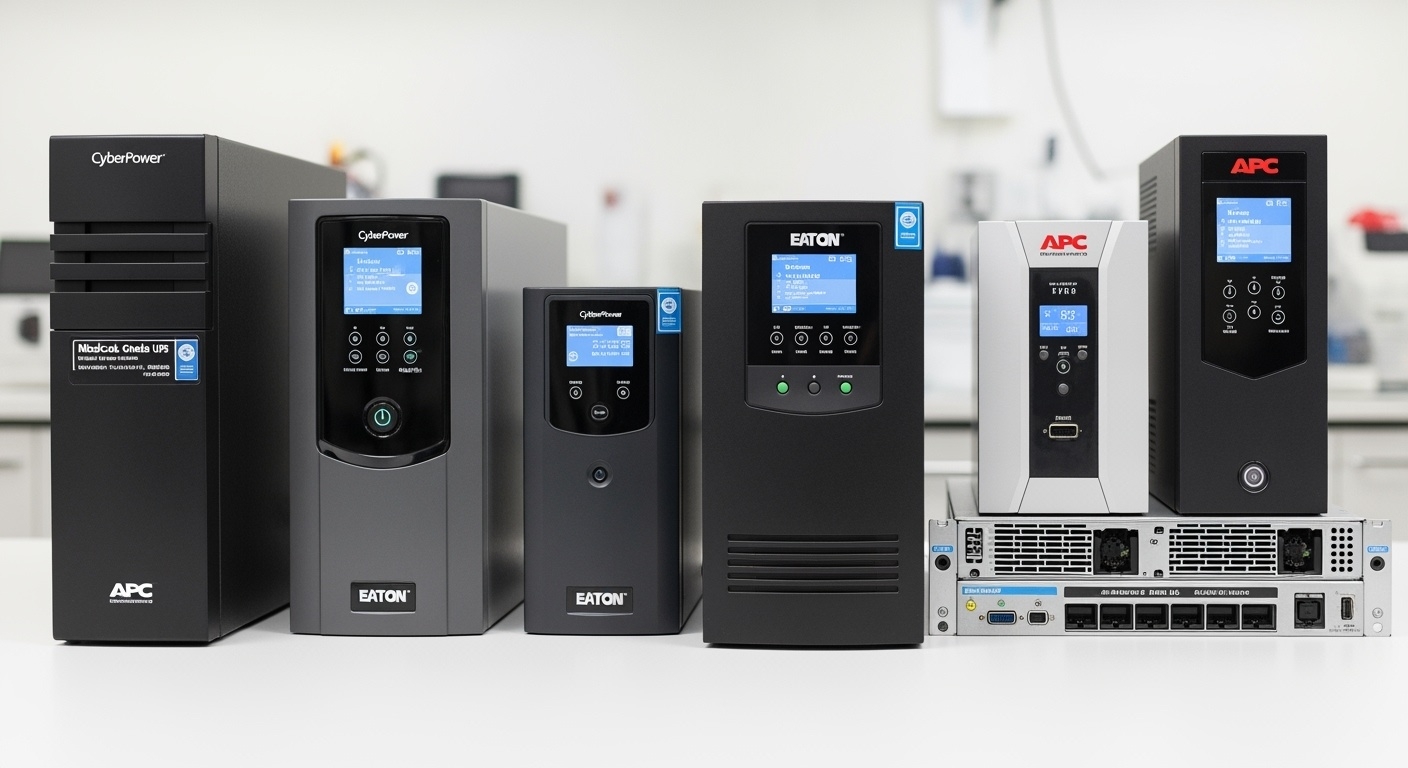
TOP MEDICAL-GRADE UPS MANUFACTURERS AND MODELS
CYBERPOWER MEDICAL-GRADE UPS SYSTEMS
CyberPower has established itself as a leading manufacturer of medical-grade UPS systems, offering a comprehensive range designed specifically for healthcare applications.
CyberPower M1100XL Medical-Grade UPS
The M1100XL represents CyberPower’s flagship medical UPS, delivering 1100VA/750W of clean, reliable power. This unit features simulated sine wave output, providing stable power for most medical equipment types. With a runtime of approximately 30 minutes at half load and 12 minutes at full load, it offers sufficient backup time for most clinical scenarios.
Key specifications include:
- Output Power: 1100VA/750W
- Runtime: 30 minutes (half load), 12 minutes (full load)
- Outlets: 6 hospital-grade outlets (5-15R-HG)
- Waveform: Simulated sine wave
- Form Factor: Mini-tower design for space efficiency
The M1100XL incorporates advanced surge protection, voltage regulation, and battery management features. Its compact design makes it ideal for deployment in patient rooms, clinics, and small medical facilities.
CyberPower M750L Medical UPS
For smaller medical applications, the M750L provides 750VA/600W of protected power with similar safety features as its larger counterpart. This model offers excellent value for protecting individual medical devices or small equipment clusters.
Eaton/Tripp Lite Medical UPS Solutions
Eaton, through its Tripp Lite division, offers sophisticated medical-grade UPS systems that combine advanced technology with healthcare-specific features.
Tripp Lite SMX1200XLHGL Hospital-Grade UPS
This 1000VA/750W lithium battery UPS represents the latest in medical power protection technology. The lithium battery technology provides longer service life, faster recharge times, and better performance in temperature extremes compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
Notable features include:
- Lithium Battery Technology: 3-5 times longer battery life than lead-acid
- Full Isolation: Complete electrical isolation for patient safety
- Runtime: Up to 28 minutes at half load
- Hospital-Grade Outlets: 6 C13 outlets for international compatibility
- Expandable Runtime: Support for external battery packs
The unit’s full isolation transformer provides complete galvanic isolation between input and output, eliminating any possibility of ground loops or leakage currents that could compromise patient safety.
APC (Schneider Electric) Medical Solutions
APC’s medical-grade UPS systems focus on high-reliability applications requiring maximum uptime and advanced monitoring capabilities.
APC Smart-UPS X Series Medical
The Smart-UPS X series offers scalable power protection from 750VA to 3000VA, accommodating various medical facility requirements. These units feature pure sine wave output, essential for sensitive medical equipment with precision timing requirements.
Key advantages include:
- Pure Sine Wave Output: Compatible with all medical equipment types
- Hot-Swappable Batteries: Maintenance without power interruption
- Network Management: Remote monitoring and control capabilities
- Energy Efficiency: ENERGY STAR qualified for reduced operating costs
Power Requirements for Common Medical Equipment
Understanding the power consumption characteristics of medical equipment is crucial for proper UPS sizing and selection. Different medical devices have varying power requirements, runtime needs, and sensitivity to power quality issues.
Critical Care Equipment
Mechanical Ventilators: Modern ICU ventilators typically consume 100-200 watts during normal operation, with peak consumption during startup reaching 300-400 watts. These devices require pure sine wave power and cannot tolerate even brief power interruptions.
Patient Monitors: Multi-parameter monitors used in ICUs and patient rooms consume 50-150 watts, depending on the number of parameters monitored and display size. These devices are highly sensitive to electrical noise and require clean, stable power.
Infusion Pumps: Critical for medication delivery, infusion pumps consume 20-50 watts per channel. Multiple pumps are often used simultaneously, requiring careful load calculation for UPS sizing.
Dialysis Machines: Hemodialysis equipment represents one of the highest power consumers in medical facilities, with some units requiring 800-1200 watts. These machines require extended runtime support due to the critical nature of dialysis treatments.
Home Medical Equipment
CPAP/BiPAP Machines: Sleep apnea treatment devices consume 30-90 watts during operation. While not immediately life-threatening, power interruptions can significantly impact patient comfort and treatment effectiveness.
Oxygen Concentrators: Home oxygen therapy devices typically consume 300-600 watts, depending on flow rate and concentration settings. These devices are essential for patients with respiratory conditions and require reliable backup power.
Home Ventilators: Similar to hospital ventilators but designed for home use, these devices consume 100-300 watts and require the highest level of power protection due to their life-sustaining function.
UPS Sizing and Selection Criteria
Proper UPS sizing involves calculating both the power requirements of connected equipment and the desired runtime during power outages. This process requires careful consideration of multiple factors:
Load Calculation
Total Power Consumption: Sum the power requirements of all connected medical devices, including startup surges. Add a 20-25% safety margin to account for future expansion and equipment changes.
Power Factor Considerations: Medical equipment often has varying power factors, affecting the relationship between apparent power (VA) and real power (watts). UPS systems must be sized based on the higher of the two requirements.
Startup Current: Many medical devices require higher current during startup. UPS systems must handle these inrush currents without triggering overload conditions.
Runtime Requirements
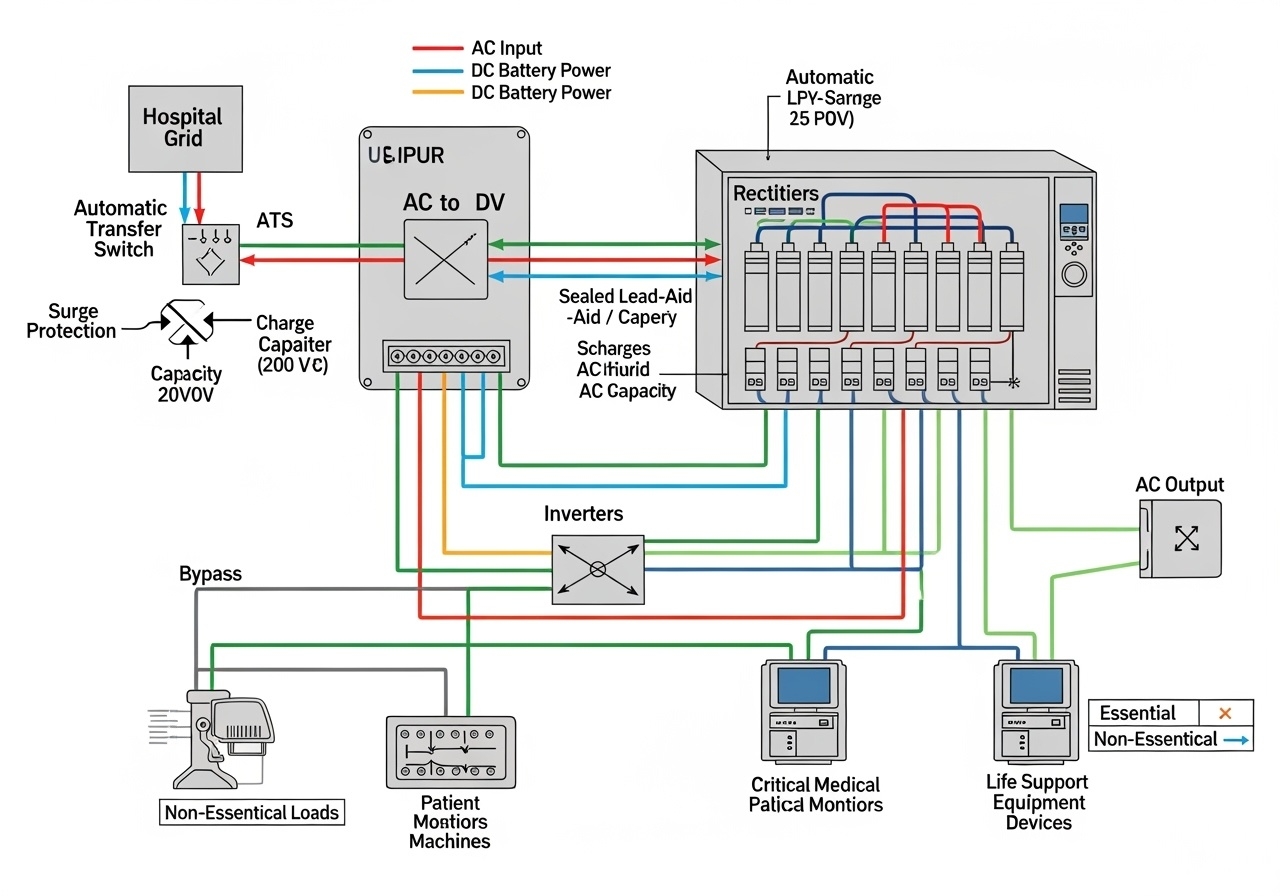
Critical vs. Non-Critical Loads: Differentiate between life-sustaining equipment requiring extended runtime and non-critical devices that can safely shut down during extended outages.
Generator Transfer Time: In facilities with emergency generators, UPS runtime must bridge the generator startup and transfer time, typically 10-30 seconds for automatic systems.
Extended Outage Scenarios: Consider scenarios where emergency generators might fail or fuel supplies become exhausted, requiring extended UPS operation.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper installation and ongoing maintenance are critical for ensuring reliable operation of medical UPS systems. Healthcare facilities must implement comprehensive power protection strategies that encompass installation standards, preventive maintenance, and emergency procedures.
Installation Standards
Location Selection: UPS systems should be installed in clean, temperature-controlled environments with adequate ventilation. Avoid areas prone to moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures that could affect battery life and system reliability.
Electrical Connections: All electrical connections must comply with local electrical codes and healthcare facility standards. Use hospital-grade outlets and ensure proper grounding to meet medical equipment safety requirements.
Cable Management: Implement proper cable management to prevent interference with medical equipment and ensure easy access for maintenance. Use hospital-grade power cords and maintain separation between power and data cables.
Preventive Maintenance Programs
Battery Testing: Regular battery testing is essential for ensuring UPS reliability. Implement monthly visual inspections, quarterly load tests, and annual capacity tests to identify potential battery failures before they occur.
Software Updates: Keep UPS management software current to ensure compatibility with modern medical equipment and take advantage of improved monitoring capabilities.
Environmental Monitoring: Monitor ambient temperature, humidity, and ventilation to optimize battery life and system performance. High temperatures significantly reduce battery life and overall system reliability.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Medical UPS systems must comply with numerous regulatory standards and safety requirements designed to protect patients and healthcare workers. Understanding these requirements is essential for proper system selection and implementation.
FDA Regulations
While the FDA doesn’t directly regulate UPS systems, medical devices connected to UPS systems must maintain their FDA clearance and compliance when operating on backup power. Healthcare facilities must ensure that UPS systems don’t interfere with medical device operation or safety features.
IEC 60601-1 Compliance
This international standard governs medical electrical equipment safety and performance. Medical-grade UPS systems must comply with leakage current limits, electrical safety requirements, and electromagnetic compatibility standards specified in IEC 60601-1.
Joint Commission Requirements
The Joint Commission requires healthcare facilities to maintain emergency power systems capable of supporting life safety, critical, and equipment systems. UPS systems play a crucial role in meeting these requirements by providing immediate backup power while emergency generators start and stabilize.
NFPA 99 Standards
The National Fire Protection Association’s NFPA 99 standard provides comprehensive requirements for healthcare facility electrical systems, including emergency power supplies. Compliance with NFPA 99 ensures that UPS systems meet minimum safety and performance standards for healthcare applications.
Emerging Technologies and Future Trends
The medical UPS industry continues to evolve, driven by advances in battery technology, digitalization, and increasing demand for sustainable solutions.
Lithium-Ion Battery Technology
Lithium-ion batteries are increasingly replacing traditional lead-acid batteries in medical UPS applications. Benefits include:
Longer Service Life: 8-10 years compared to 3-5 years for lead-acid batteries Faster Recharge: 2-4 hours compared to 8-12 hours for lead-acid Higher Energy Density: Smaller footprint for equivalent capacity Better Temperature Performance: Maintained capacity across wider temperature ranges
Smart Monitoring and IoT Integration
Modern medical UPS systems incorporate advanced monitoring capabilities that enable predictive maintenance and remote management:
Predictive Analytics: AI-powered algorithms analyze system performance data to predict component failures before they occur Remote Monitoring: Cloud-based monitoring systems provide 24/7 oversight of UPS performance and alert facility managers to potential issues Integration with Building Management Systems: UPS systems can integrate with broader facility management platforms for centralized monitoring and control
Modular and Scalable Designs
Healthcare facilities increasingly demand flexible power protection solutions that can adapt to changing needs:
Modular Architecture: Systems that allow capacity expansion without complete replacement N+1 Redundancy: Multiple UPS modules provide backup for each other, ensuring continuous operation even during maintenance Hot-Swappable Components: Batteries, power modules, and control cards can be replaced without interrupting power to connected equipment
Cost Considerations and ROI Analysis
Investing in quality medical UPS systems requires careful consideration of initial costs, ongoing operational expenses, and potential cost savings from prevented downtime and equipment damage.
Initial Investment Factors
System Capacity: Higher capacity systems cost more initially but provide better value for larger installations Battery Technology: Lithium-ion systems cost more upfront but offer lower total cost of ownership Redundancy Level: N+1 redundant systems increase initial costs but provide superior reliability Monitoring Features: Advanced monitoring capabilities add cost but enable predictive maintenance and reduced downtime
Operational Costs
Energy Efficiency: Modern UPS systems operate at 95-98% efficiency, reducing energy costs compared to older systems Maintenance Requirements: Medical-grade systems typically require more frequent maintenance but prevent costly equipment damage Battery Replacement: Plan for battery replacement every 3-10 years depending on technology and usage patterns
COST OF DOWNTIME PREVENTION
Equipment Protection: UPS systems prevent damage to expensive medical equipment from power quality issues Data Loss Prevention: Protect electronic health records and patient data from corruption during power events Regulatory Compliance: Avoid costly penalties and sanctions related to power-related patient safety incidents Revenue Protection: Prevent lost revenue from canceled procedures and patient diversions during power outages
CONCLUSION
Selecting the best power backup system for medical equipment requires careful consideration of patient safety, regulatory compliance, equipment requirements, and facility-specific needs. Medical-grade UPS systems from reputable manufacturers like CyberPower, Eaton/Tripp Lite, and APC provide the reliability and safety features essential for healthcare applications.
The investment in quality medical UPS systems pays dividends through prevented equipment damage, reduced downtime, regulatory compliance, and most importantly, enhanced patient safety. As medical equipment becomes increasingly sophisticated and dependent on stable power, the role of UPS systems in healthcare facilities will only continue to grow in importance.
Healthcare facilities should work with experienced power protection specialists to conduct thorough load analyses, evaluate UPS options, and implement comprehensive power protection strategies. Regular maintenance, staff training, and system updates ensure that medical UPS systems continue to provide reliable protection throughout their service life.
The future of medical power protection lies in intelligent, connected systems that provide not just backup power, but comprehensive power management and predictive maintenance capabilities. By investing in modern medical UPS technology today, healthcare facilities can ensure reliable power protection for years to come while positioning themselves to take advantage of emerging technologies and capabilities.