THE ROLE OF USER EXPERIENCE IN MEDICAL DEVICE DESIGN: TRANSFORMING HEALTHCARE THROUGH HUMAN-CENTERED INNOVATION
User experience (UX) has emerged as a critical factor in medical device design, fundamentally transforming how healthcare professionals interact with technology and, ultimately, how patient care is delivered. As medical devices become increasingly sophisticated and complex, the need for intuitive, safe, and effective user interfaces has never been more paramount. The integration of comprehensive UX design principles into medical device development represents a paradigm shift from purely functional engineering toward human-centered design that prioritizes usability, safety, and clinical outcomes.
The healthcare industry’s growing recognition of UX importance stems from mounting evidence that poor interface design contributes significantly to medical errors, reduced efficiency, and compromised patient safety. According to FDA guidelines, human factors and usability engineering have become essential components of medical device development, with regulatory bodies increasingly emphasizing the need for systematic approaches to user-centered design throughout the product lifecycle.
The Evolution of Medical Device User Experience
The journey toward user-centered medical device design has been driven by both technological advancement and regulatory recognition of the critical role human factors play in healthcare safety. Historically, medical devices were designed primarily from an engineering perspective, with user interface considerations often relegated to secondary importance. However, the increasing complexity of medical technology, coupled with growing awareness of use-related hazards, has necessitated a fundamental shift in design philosophy.
Historical Context and Regulatory Drivers
The FDA’s guidance on “Applying Human Factors and Usability Engineering to Medical Devices” represents a watershed moment in medical device development. This comprehensive framework requires manufacturers to follow systematic human factors and usability engineering processes throughout the design and development lifecycle. The guidance emphasizes that usability engineering should not be an afterthought but rather an integral part of the design control process from conception through post-market surveillance.
The regulatory framework has evolved to recognize that even well-engineered medical devices can pose significant risks if users cannot operate them safely and effectively. This recognition has led to mandatory requirements for human factors validation, usability testing, and comprehensive risk assessment related to user interactions with medical devices.
Market Forces and Clinical Demands
Healthcare organizations increasingly recognize that medical devices with superior user experiences deliver tangible benefits including reduced training time, decreased error rates, improved workflow efficiency, and enhanced job satisfaction among healthcare professionals. These factors directly impact the bottom line through reduced liability, improved patient outcomes, and enhanced operational efficiency.
The competitive healthcare market has also driven demand for more intuitive medical devices. Healthcare systems evaluating equipment purchases now routinely consider usability factors alongside traditional criteria such as clinical efficacy, cost, and technical specifications. This shift has made UX design a key differentiator in the medical device marketplace.
FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF MEDICAL DEVICE UX DESIGN
Medical device UX design operates within a unique context that distinguishes it from consumer product design. The stakes are inherently higher, as design decisions directly impact patient safety and clinical outcomes. Several fundamental principles guide effective medical device UX design:
Safety-First Design Philosophy
Patient safety represents the paramount concern in medical device UX design. Every interface decision must be evaluated through the lens of potential harm reduction. This safety-first approach requires designers to anticipate and mitigate use errors that could result in patient injury or death. The design process must systematically identify potential hazards, assess their likelihood and severity, and implement design solutions that minimize risk.
Safety considerations extend beyond preventing obvious errors to addressing more subtle issues such as alarm fatigue, cognitive overload, and attention management. Modern medical devices often present clinicians with vast amounts of information, requiring careful information architecture and visual hierarchy to ensure critical data receives appropriate attention.
Contextual Understanding and Environmental Factors
Medical devices operate within complex, high-stress environments where interruptions are frequent, lighting conditions vary, and users may be wearing protective equipment that impacts dexterity and vision. Effective UX design must account for these contextual factors and ensure devices remain usable across the full range of clinical scenarios.
Environmental considerations include factors such as:
- Physical constraints: Limited space, awkward positioning, and need for sterile operation
- Cognitive demands: High-pressure situations requiring rapid decision-making
- Workflow integration: Seamless integration with existing clinical processes
- Multi-user scenarios: Devices that may be operated by different healthcare professionals with varying skill levels
Regulatory Compliance and Standards Integration
Medical device UX design must comply with numerous regulatory standards and guidelines. The IEC 62366 standard provides a comprehensive framework for usability engineering in medical devices, specifying processes for analyzing, developing, and evaluating device usability as it relates to safety. This standard emphasizes the need for systematic approaches to user research, risk assessment, and validation testing.
Compliance with regulatory requirements extends beyond meeting minimum standards to embracing the spirit of human-centered design. Leading medical device manufacturers use regulatory frameworks as a foundation for building superior user experiences that exceed basic compliance requirements.
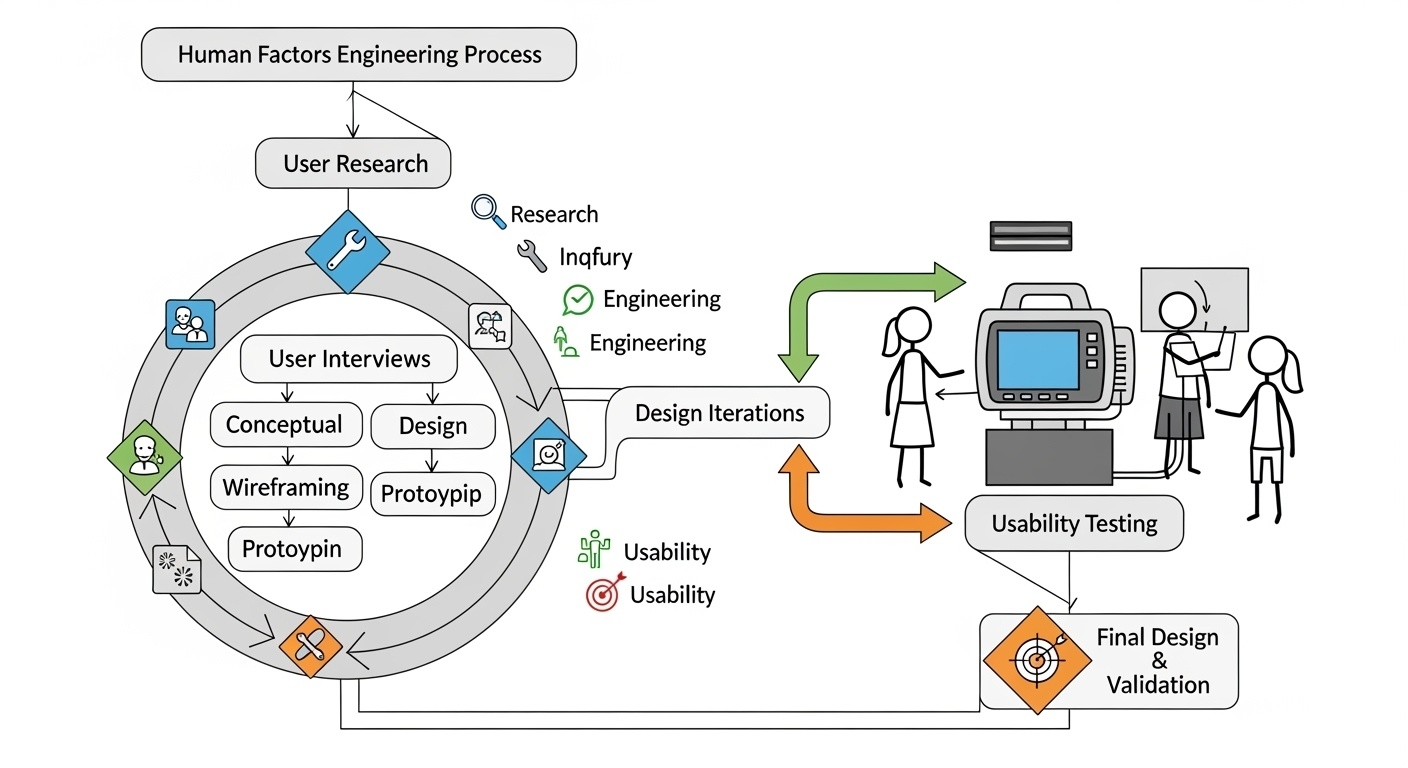
The Human Factors Engineering Process
Human factors engineering (HFE) provides the scientific foundation for medical device UX design. This systematic approach ensures that devices are designed to accommodate human capabilities and limitations while minimizing the potential for use errors.
User Research and Needs Assessment
Comprehensive user research forms the cornerstone of effective medical device UX design. This process involves deep investigation into user needs, workflows, pain points, and preferences through various research methodologies including:
Ethnographic Studies: Observational research conducted in real clinical environments provides invaluable insights into actual user behavior, workflow patterns, and contextual factors that impact device use. These studies reveal the gap between intended use and actual practice, highlighting opportunities for design improvement.
Structured Interviews: In-depth interviews with healthcare professionals across different specialties and experience levels help identify specific needs, preferences, and concerns related to medical device use. These interviews should explore not only functional requirements but also emotional and psychological factors that influence user acceptance.
Task Analysis: Systematic breakdown of clinical procedures involving medical devices helps identify critical interaction points, decision-making processes, and potential failure modes. This analysis provides the foundation for designing interfaces that support natural workflow progression.
Use Error Analysis and Risk Assessment
Use error analysis represents a critical component of medical device UX design, involving systematic identification and evaluation of potential user mistakes and their consequences. This process requires collaboration between UX designers, human factors engineers, and clinical experts to ensure comprehensive coverage of potential hazards.
The analysis process typically includes:
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): Systematic evaluation of potential failure modes and their impact on patient safety
- Use scenario modeling: Development of comprehensive scenarios covering normal use, edge cases, and error conditions
- Risk prioritization: Assessment of use error probability and severity to guide design decisions
Iterative Design and Prototyping
Medical device UX design employs iterative design processes that allow for continuous refinement based on user feedback and usability testing. This approach ensures that design decisions are validated with actual users before final implementation.
Prototyping strategies for medical devices often include:
- Low-fidelity prototypes: Paper sketches and wireframes for early concept validation
- Interactive prototypes: Functional simulations that allow users to experience interface flows
- High-fidelity prototypes: Near-final implementations for comprehensive usability testing
Usability Testing and Validation
Usability testing represents the critical validation phase of medical device UX design, providing empirical evidence that devices can be used safely and effectively by their intended users. The FDA requires summative usability testing for most medical devices, with specific requirements for test methodology, participant selection, and outcome measurement.
Formative vs. Summative Testing
Medical device usability testing typically occurs in two phases:
Formative Testing: Conducted during the design development process to identify usability issues and guide design improvements. This testing focuses on uncovering problems and exploring design alternatives rather than validating final performance.
Summative Testing: Formal validation testing conducted with near-final or final designs to demonstrate that devices meet usability requirements. This testing provides the evidence required for regulatory submissions and must follow strict protocols to ensure validity and reliability.
Testing Methodology and Best Practices
Effective usability testing for medical devices requires careful attention to methodology to ensure results accurately reflect real-world performance. Key considerations include:
Representative Participants: Test participants must accurately represent the intended user population in terms of clinical background, experience level, and demographic characteristics. Testing should include users across the full spectrum of intended operators.
Realistic Scenarios: Testing scenarios should reflect actual clinical use conditions and include both routine and emergency situations. Scenarios should be developed based on comprehensive task analysis and validated by clinical experts.
Appropriate Metrics: Success metrics should focus on safety-critical outcomes such as task completion rates, error frequencies, and time to complete critical tasks. Subjective measures such as user satisfaction and perceived workload provide additional insights into user experience quality.
Validation and Regulatory Submission
Summative usability testing results form a critical component of regulatory submissions, providing evidence that devices meet safety and effectiveness requirements. The testing must demonstrate that users can operate devices safely and effectively without additional training or support.
Regulatory submissions must include comprehensive documentation of:
- Testing methodology and rationale
- Participant selection criteria and demographics
- Scenario development and validation
- Results analysis and interpretation
- Risk assessment and mitigation strategies
Emerging Trends in Medical Device UX
The field of medical device UX design continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancement, changing user expectations, and emerging regulatory requirements. Several key trends are shaping the future of medical device user experience:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
AI and machine learning technologies are increasingly being integrated into medical devices, creating new opportunities and challenges for UX design. These technologies can enhance user experience through intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and personalized interfaces that adapt to individual user preferences and behaviors.
However, AI integration also raises important questions about transparency, trust, and user control. UX designers must balance the benefits of intelligent automation with the need to maintain user understanding and control over critical medical decisions.
Digital Health and Connected Devices
The proliferation of connected medical devices creates new opportunities for enhanced user experiences through data sharing, remote monitoring, and integrated workflows. However, this connectivity also introduces new complexity in terms of information management, security, and cross-platform compatibility.
UX designers must consider the broader ecosystem of connected devices and ensure that individual device interfaces contribute to coherent, integrated user experiences across multiple touchpoints.
Inclusive Design and Accessibility
Growing awareness of the importance of inclusive design is driving efforts to ensure medical devices are accessible to users with diverse abilities and backgrounds. This includes considerations for users with physical disabilities, cognitive impairments, and varying levels of technical literacy.
Inclusive design principles require UX designers to consider a broader range of user needs and design solutions that accommodate diverse capabilities without compromising usability for any user group.
Challenges and Opportunities in Medical Device UX
Despite significant progress in medical device UX design, several challenges continue to impact the field:
Regulatory Complexity and Compliance
The regulatory environment for medical devices is complex and constantly evolving, requiring UX designers to navigate multiple standards and guidelines while maintaining focus on user needs. Balancing regulatory compliance with innovative design solutions requires deep understanding of both regulatory requirements and user experience principles.
Resource Constraints and Development Timelines
Medical device development is typically resource-intensive and subject to long development timelines. UX design must be integrated into these constraints while maintaining the iterative approach necessary for effective user-centered design.
Cross-Cultural and International Considerations
Global medical device markets require consideration of cultural differences in user behavior, preferences, and expectations. UX designers must develop solutions that work effectively across diverse cultural contexts while maintaining consistency and safety.
Technology Integration and Legacy Systems
Medical devices often must integrate with existing healthcare technology infrastructure, including legacy systems that may not support modern user experience standards. UX designers must find ways to create excellent user experiences while accommodating technical constraints and system limitations.
Future Directions and Emerging Technologies
The future of medical device UX design will be shaped by several emerging technologies and trends:
Voice User Interfaces and Natural Language Processing
Voice interfaces offer significant potential for medical device applications, particularly in sterile environments where touch interactions are challenging. However, implementing voice interfaces in medical devices requires careful consideration of accuracy, privacy, and integration with existing workflows.
Augmented and Virtual Reality
AR and VR technologies offer new possibilities for medical device training, visualization, and remote assistance. These technologies can enhance user experience by providing immersive training environments and real-time guidance during device operation.
Haptic Feedback and Tactile Interfaces
Advanced haptic feedback systems can provide users with tactile information that enhances safety and efficiency. These systems are particularly valuable for applications requiring precision or operating in environments with limited visual feedback.
Personalization and Adaptive Interfaces
Advances in user modeling and machine learning enable the development of interfaces that adapt to individual user preferences, experience levels, and working styles. These adaptive systems can optimize user experience while maintaining safety and consistency.
Best Practices for Medical Device UX Design
Based on current research and industry experience, several best practices have emerged for medical device UX design:
Early and Continuous User Involvement
Successful medical device UX design requires early and continuous involvement of actual users throughout the development process. This involvement should extend beyond formal testing to include participatory design sessions, design reviews, and ongoing feedback collection.
MULTIDISCIPLINARY TEAM COLLABORATION
Effective medical device UX design requires close collaboration between UX designers, human factors engineers, clinical experts, regulatory specialists, and engineering teams. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that user experience considerations are integrated throughout the development process.
Evidence-Based Design Decisions
All design decisions should be based on empirical evidence from user research, usability testing, and clinical validation. This evidence-based approach ensures that design choices are grounded in actual user needs and behaviors rather than assumptions or preferences.
Risk-Based Design Approach
Medical device UX design should employ a risk-based approach that prioritizes safety-critical interactions and allocates resources accordingly. This approach ensures that the most important user interactions receive appropriate attention and validation.
CONCLUSION
The role of user experience in medical device design has evolved from a secondary consideration to a critical success factor that directly impacts patient safety, clinical outcomes, and commercial viability. As medical devices become increasingly complex and sophisticated, the need for systematic, user-centered design approaches becomes ever more important.
The integration of comprehensive UX design principles into medical device development represents a fundamental shift toward human-centered innovation in healthcare. This transformation requires not only technical expertise but also deep understanding of clinical workflows, regulatory requirements, and the unique challenges of healthcare environments.
Looking forward, the continued evolution of medical device UX design will be driven by emerging technologies, changing user expectations, and evolving regulatory requirements. Success in this dynamic environment will require ongoing commitment to user-centered design principles, continuous learning, and adaptation to new challenges and opportunities.
The ultimate goal of medical device UX design is to create technologies that seamlessly integrate into clinical workflows, enhance rather than hinder healthcare delivery, and ultimately improve patient outcomes. Achieving this goal requires sustained effort, collaboration, and commitment to the principles of human-centered design.
As the healthcare industry continues to embrace digital transformation and technological innovation, the role of UX design in medical devices will only grow in importance. Organizations that invest in comprehensive UX design capabilities and integrate user-centered design principles throughout their development processes will be best positioned to succeed in the evolving healthcare technology landscape.
The future of medical device design lies in the seamless integration of advanced technology with intuitive, safe, and effective user experiences. By prioritizing user needs, embracing evidence-based design practices, and maintaining unwavering commitment to patient safety, the medical device industry can continue to develop technologies that truly transform healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes worldwide.