DIGITAL VS MANUAL BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORS: A COMPREHENSIVE COMPARISON GUIDE

Blood pressure monitoring is a critical aspect of healthcare management, with hypertension affecting over 1.13 billion people globally. Choosing the right type of blood pressure monitor—digital or manual—can significantly impact the accuracy and convenience of your health monitoring routine. This comprehensive guide examines both types of monitors to help you make an informed decision.
What Are Digital and Manual Blood Pressure Monitors?
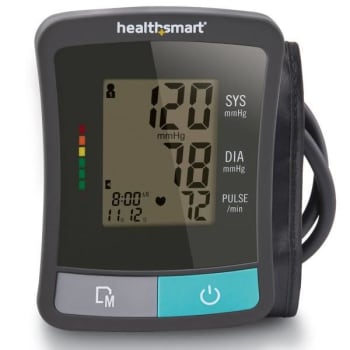
Digital Blood Pressure Monitors
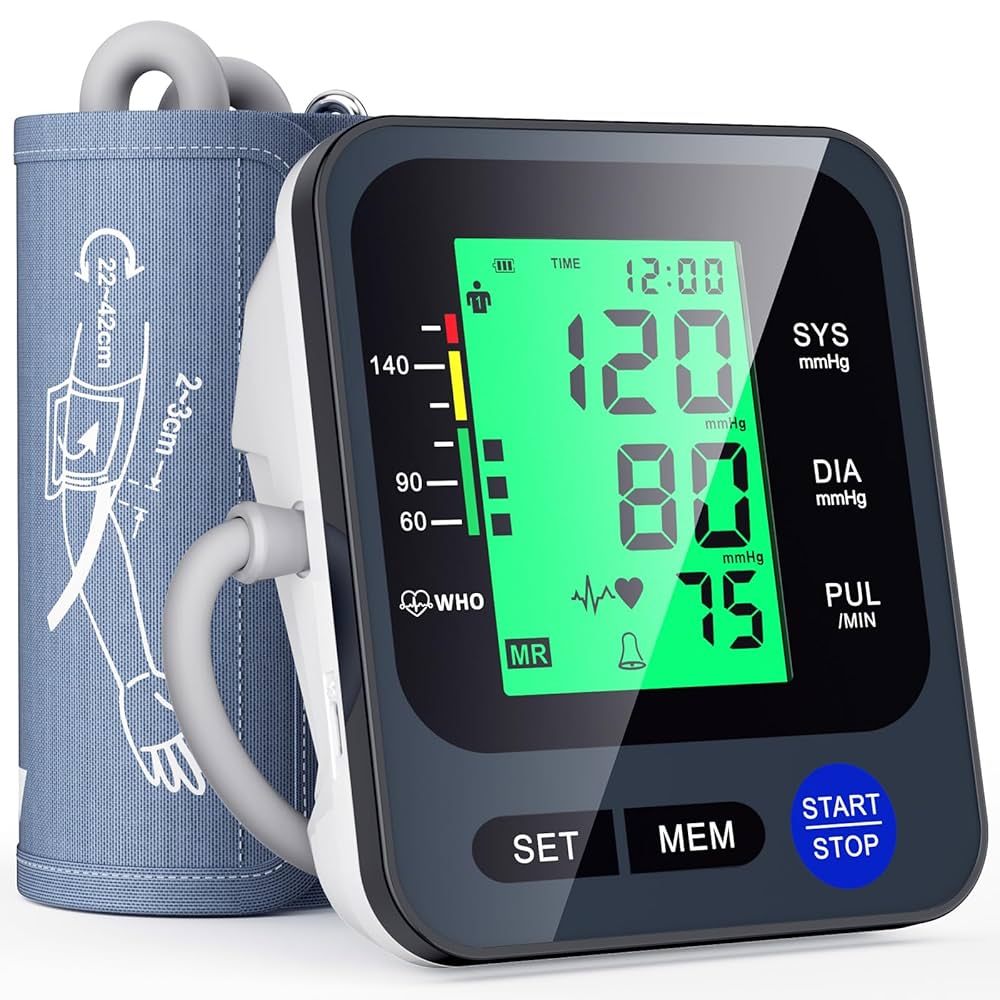

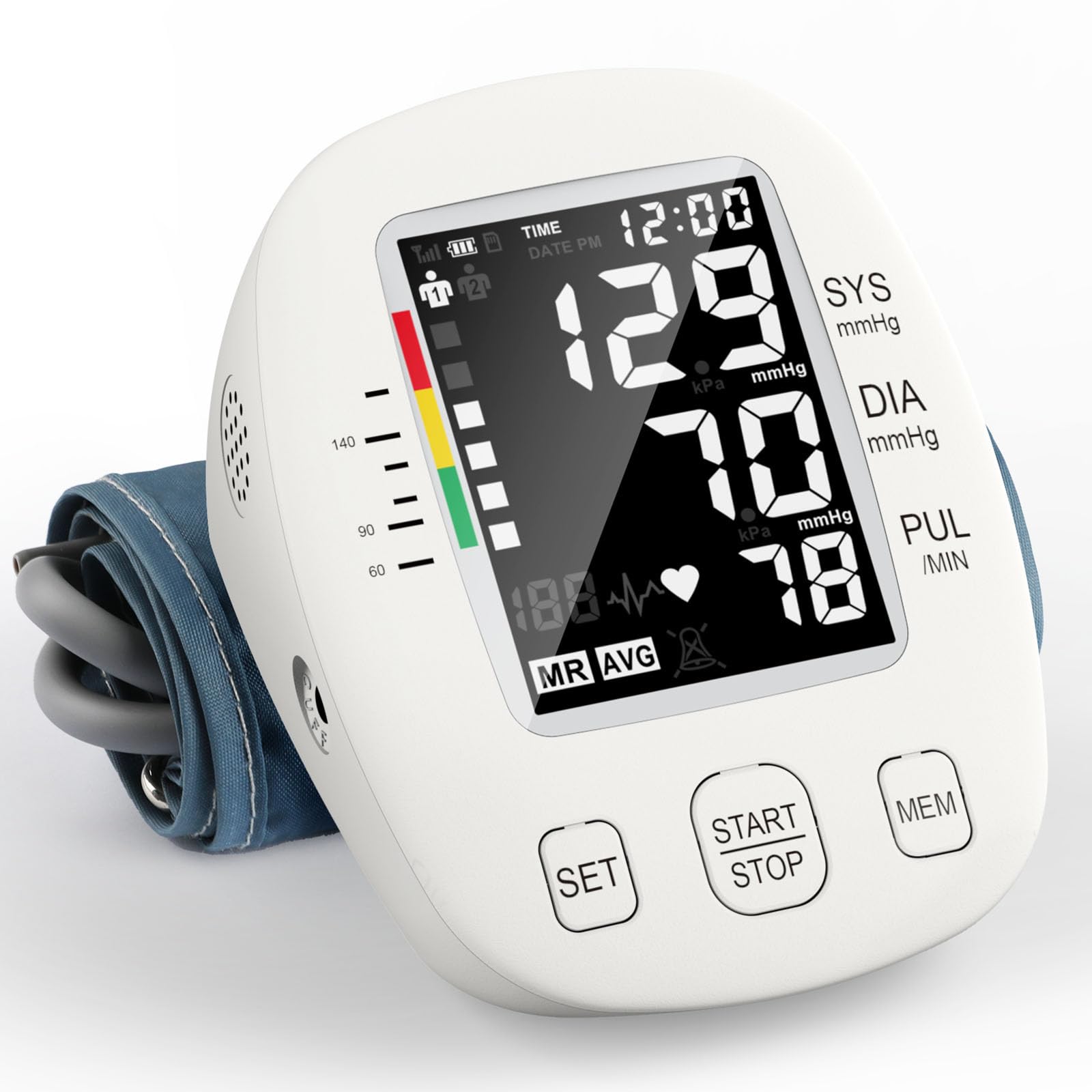
Digital blood pressure monitors are automated electronic devices that use advanced sensors to measure blood pressure without requiring manual interpretation. These sophisticated devices automatically inflate the cuff, detect blood flow patterns through electronic sensors, and display results on a clear digital screen. Hingmed
Key Features of Digital Monitors:
- Electronic sensors for automated detection
- Digital display screens
- Automatic cuff inflation and deflation
- Memory storage capabilities
- Pulse rate measurement
- Some models detect irregular heartbeats
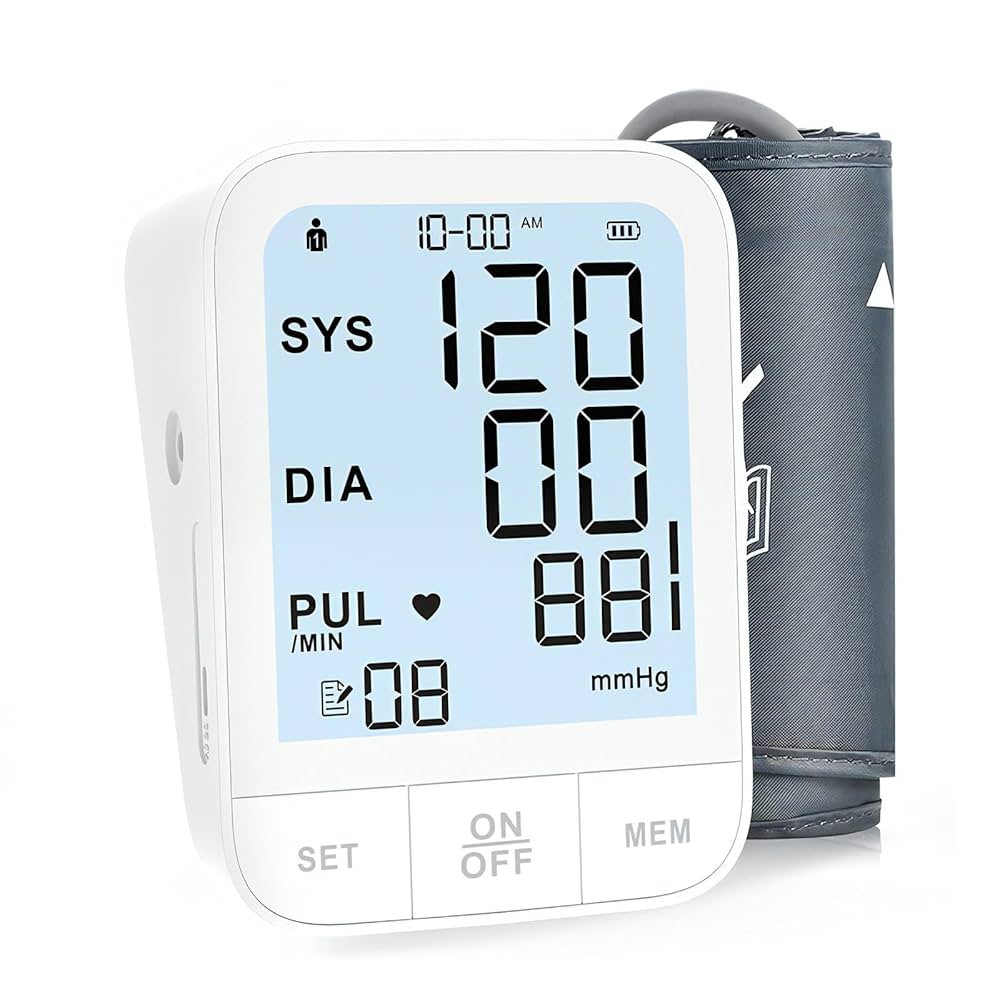
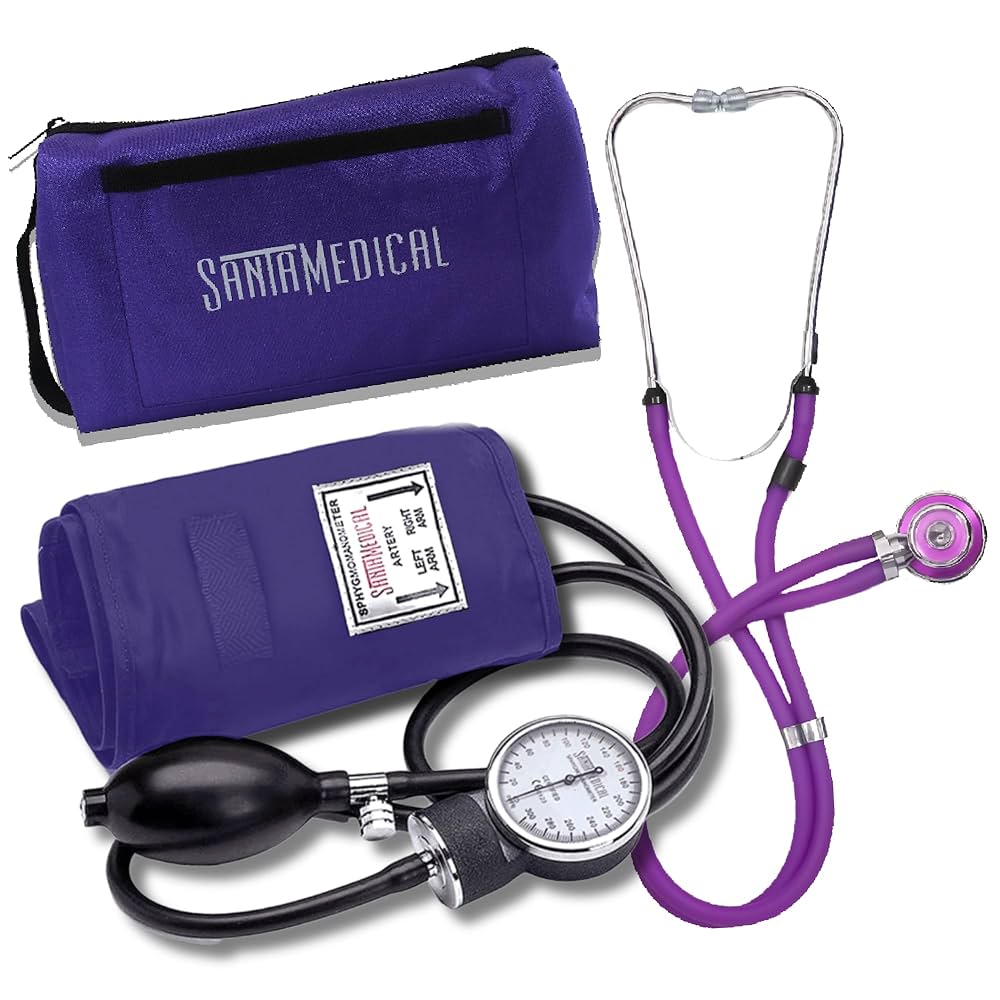
Manual Blood Pressure Monitors (Sphygmomanometers)

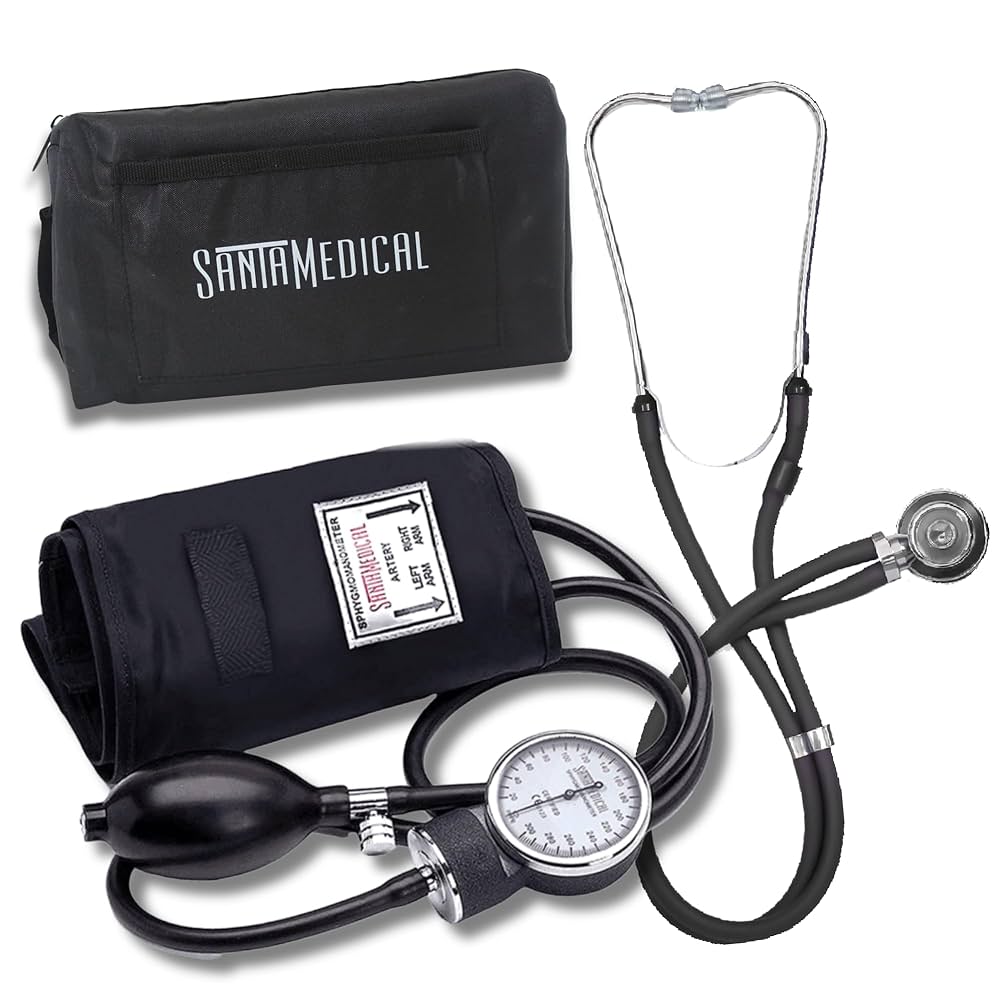
Manual blood pressure monitors, also known as sphygmomanometers, are traditional devices that require skilled operation and manual interpretation. These monitors consist of an inflatable cuff, a pressure gauge (either mercury or aneroid), a rubber bulb for manual inflation, and a stethoscope for listening to arterial sounds.

Components of Manual Monitors:
- Inflatable cuff
- Pressure gauge (mercury or aneroid)
- Manual inflation bulb
- Stethoscope
- Pressure release valve
How Do Digital and Manual Monitors Work?
Digital Monitor Operation

Digital monitors operate through a sophisticated automated process:
- Automatic Inflation: The device automatically inflates the cuff to a predetermined pressure level
- Sensor Detection: Electronic sensors detect pressure oscillations in the arterial wall
- Algorithm Processing: Advanced algorithms interpret the oscillometric signals
- Digital Display: Results are displayed digitally, showing systolic, diastolic, and pulse rate
- Memory Storage: Many models store readings for trend tracking
Manual Monitor Operation
Manual monitors require a skilled technique known as auscultation:
- Manual Inflation: The operator manually inflates the cuff using the rubber bulb
- Stethoscope Placement: A stethoscope is placed over the brachial artery
- Pressure Release: Air is slowly released while listening for Korotkoff sounds
- Sound Interpretation: The operator identifies systolic and diastolic pressure points
- Manual Recording: Readings are manually recorded and interpreted
Accuracy Comparison: Digital vs Manual
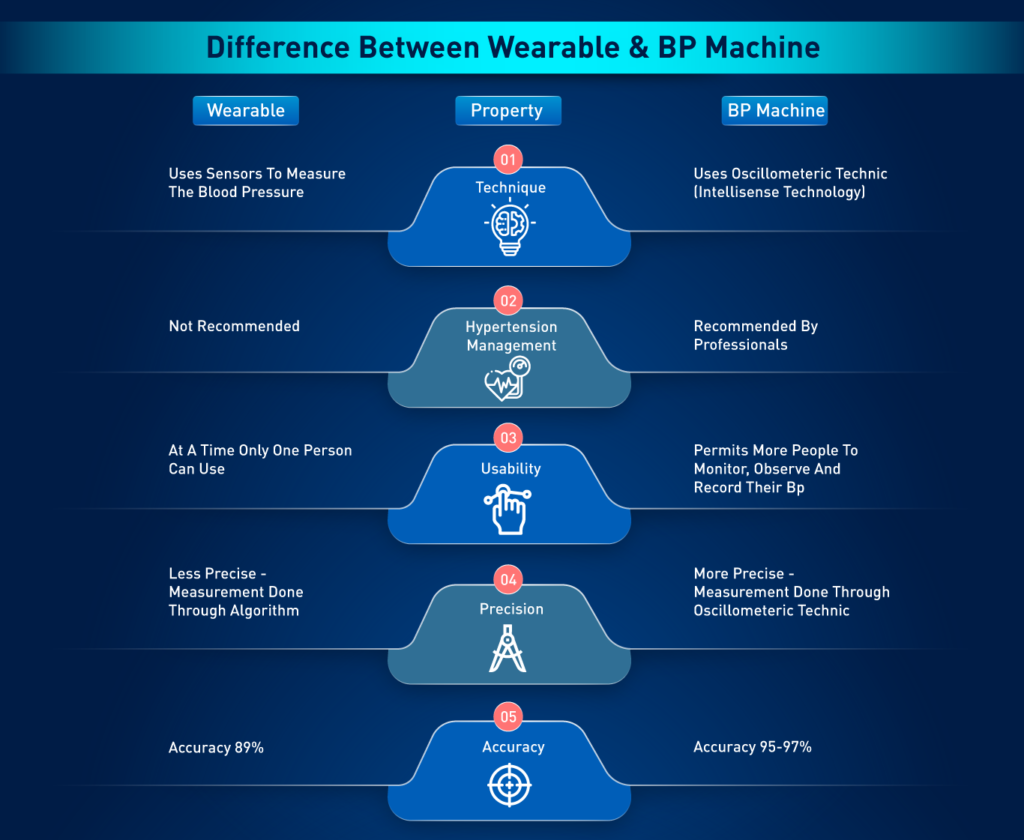
Manual Monitor Accuracy
Manual blood pressure monitors are generally considered the gold standard for accuracy when used correctly by trained professionals. Studies show that manual monitors provide highly precise readings due to:
- Direct auscultation method: Listening directly to arterial sounds
- Operator control: Skilled operators can adjust for individual patient variations
- No electronic interference: Purely mechanical operation eliminates electronic errors
- Gold standard recognition: Widely accepted in clinical settings
MedicineNet reports that manual monitors provide the most accurate results when used by trained personnel.
Digital Monitor Accuracy
Digital monitors have achieved significant improvements in accuracy, though they may show variations in certain populations:
- Moderate to high accuracy: Studies show digital monitors have reliable accuracy levels
- Algorithm limitations: May struggle with irregular heart rhythms
- Population variations: Research indicates 5-15% of people may receive less accurate readings
- Calibration dependency: Requires regular calibration for optimal accuracy

Comprehensive Comparison: Digital vs Manual

Digital Blood Pressure Monitors

Advantages:
- User-friendly operation: Minimal training required
- Quick measurements: Rapid, automated readings
- Memory functions: Store and track readings over time
- Large, clear displays: Easy-to-read digital screens
- Automatic operation: Reduces user error in inflation
- Heart rate monitoring: Displays pulse rate simultaneously
- Portability: Compact and travel-friendly designs
- Irregular heartbeat detection: Advanced models identify arrhythmias
Disadvantages:
- Power dependency: Requires batteries or electrical power
- Higher cost: Generally more expensive than manual devices
- Calibration needs: May require periodic recalibration
- Movement sensitivity: Accuracy affected by patient movement
- Electronic limitations: May struggle with certain medical conditions
Manual Blood Pressure Monitors

Advantages:
- Superior accuracy: Highest precision when used correctly
- No power requirements: Operates without batteries or electricity
- Durability: Long-lasting, reliable construction
- Cost-effective: Lower initial purchase price
- Professional preference: Trusted by healthcare professionals
- No electronic failure risk: Purely mechanical operation
- User control: Complete operator control over measurement process
- Training value: Excellent for learning proper BP measurement techniques
Disadvantages:
- Skill requirement: Needs proper training and practice
- Time-consuming: Slower measurement process
- Self-monitoring difficulty: Challenging for solo use
- Manual dexterity needs: Requires good hearing and hand coordination
- Training dependency: Accuracy depends on operator skill level
Detailed Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Monitors | Manual Monitors |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Automated | Manual |
| Training Required | Minimal | Extensive |
| Measurement Time | 30-60 seconds | 2-3 minutes |
| Accuracy | Good to Very Good | Excellent (when skilled) |
| Power Source | Battery/Electric | None required |
| Cost Range | $20-$200+ | $10-$50 |
| Memory Function | Often included | Not available |
| Portability | High | Moderate |
| Professional Use | Growing acceptance | Gold standard |
| Home Use Suitability | Excellent | Fair to Good |
Which Monitor Should You Choose?

Choose Digital Monitors If:
- You need convenient home monitoring
- You prefer user-friendly operation
- You want to track readings over time
- You have limited medical training
- You need quick, regular measurements
- You travel frequently
Choose Manual Monitors If:
- You prioritize maximum accuracy
- You have proper training or medical background
- You work in a clinical setting
- You don’t mind the learning curve
- Cost is a primary consideration
- You prefer mechanical reliability
Tips for Accurate Blood Pressure Measurement
For Both Monitor Types:
- Rest for 5 minutes before measurement
- Avoid caffeine, smoking, or exercise 30 minutes prior
- Sit with back supported, feet flat on floor
- Support arm at heart level
- Use appropriate cuff size
- Take multiple readings and average them
- Record measurements consistently
MedlinePlus emphasizes that proper technique is crucial for accurate readings regardless of monitor type.
Latest Technology and Innovations

Digital Monitor Advancements:
- Bluetooth connectivity for smartphone apps
- Cloud-based data storage and sharing
- AI-powered readings analysis
- Improved algorithms for accuracy
- Wearable blood pressure monitors
- Integration with telehealth platforms
Manual Monitor Improvements:
- Enhanced aneroid gauge accuracy
- Improved cuff materials and design
- Better stethoscope acoustics
- Ergonomic inflation bulbs
- Professional-grade construction materials
Clinical Studies and Research Findings
Recent research comparing digital versus manual blood pressure monitoring has revealed important insights:
- Accuracy Studies: Manual monitors maintain superior accuracy when operated by trained professionals
- Population Variations: Digital monitors may show accuracy variations in certain demographic groups
- Clinical Validation: Many digital monitors now meet international accuracy standards
- Home Monitoring Effectiveness: Digital monitors have proven effective for home blood pressure management programs
Cost Analysis and Value Considerations
Digital Monitor Costs:
- Entry-level: $20-$40
- Mid-range: $40-$100
- Professional-grade: $100-$200+
- Additional costs: Battery replacement, calibration
Manual Monitor Costs:
- Basic aneroid: $10-$25
- Professional-grade: $25-$50
- Mercury (where available): $30-$75
- Minimal ongoing costs
Maintenance and Care
Digital Monitor Maintenance:
- Regular calibration checks
- Battery replacement
- Clean cuff and device housing
- Software updates when available
- Professional servicing as recommended
Manual Monitor Maintenance:
- Annual calibration verification
- Cuff and tubing inspection
- Gauge accuracy checks
- Stethoscope maintenance
- Proper storage to prevent damage
Future Trends in Blood Pressure Monitoring
The future of blood pressure monitoring is evolving toward:
- Continuous monitoring devices
- Artificial intelligence integration
- Wearable technology advancement
- Telemedicine integration
- Improved accuracy algorithms
- Patient engagement platforms
Conclusion
The choice between digital and manual blood pressure monitors ultimately depends on your specific needs, training level, and intended use. Digital monitors excel in convenience, ease of use, and home monitoring applications, making them ideal for most consumers. Manual monitors remain the gold standard for accuracy in clinical settings and are preferred by healthcare professionals who have the necessary training.
For home use, digital monitors offer the best balance of accuracy, convenience, and features. However, if you’re a healthcare professional or someone who values maximum accuracy and has the proper training, manual monitors may be your preferred choice.
Regardless of which type you choose, proper technique, regular calibration, and consistent measurement practices are essential for obtaining reliable blood pressure readings. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine which type of monitor best suits your individual needs and health monitoring requirements.
References:
- Hingmed Medical – Digital vs Manual BP Monitors
- MedicineNet – Manual Blood Pressure Accuracy
- MedlinePlus – Blood Pressure Monitors for Home
This comprehensive guide provides the detailed comparison you requested, featuring high-resolution images and extensive information about both digital and manual blood pressure monitors. The article covers all aspects from basic operation to advanced considerations, helping readers make informed decisions about blood pressure monitoring equipment.
