HOW TO TRAIN STAFF ON NEW DIAGNOSTIC EQUIPMENT: A COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE FOR HEALTHCARE EXCELLENCE

Figure 1: Healthcare professionals engaged in comprehensive medical equipment training
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, diagnostic equipment represents the cornerstone of accurate patient care, effective treatment protocols, and optimal clinical outcomes. From advanced imaging systems like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scanners to sophisticated laboratory analyzers and point-of-care testing devices, modern diagnostic equipment demands highly skilled operators who can maximize both safety and efficiency. The successful integration of new diagnostic equipment into healthcare facilities requires comprehensive staff training programs that address technical competency, regulatory compliance, and patient safety standards.
Training healthcare staff on new diagnostic equipment is not merely an operational necessity—it is a critical investment in patient safety, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. When staff members are inadequately trained on sophisticated diagnostic tools, the consequences can be severe, ranging from misdiagnosis and delayed treatment to equipment damage and regulatory violations. Conversely, well-designed training programs ensure that healthcare professionals can operate equipment with confidence, accuracy, and full understanding of both capabilities and limitations.
This comprehensive guide explores evidence-based strategies for developing, implementing, and maintaining effective training programs for new diagnostic equipment. Drawing from industry best practices, regulatory requirements, and proven educational methodologies, this document provides healthcare administrators, training coordinators, and clinical supervisors with the tools necessary to establish world-class training initiatives that enhance both patient care quality and organizational performance.
Understanding the Scope of Diagnostic Equipment Training
Diagnostic equipment encompasses a vast array of sophisticated technologies that require specialized knowledge and skills to operate effectively. Modern healthcare facilities typically utilize equipment ranging from basic handheld devices to complex imaging systems worth millions of dollars. Understanding the full scope of equipment categories is essential for developing targeted training programs that address the unique requirements of each technology type.
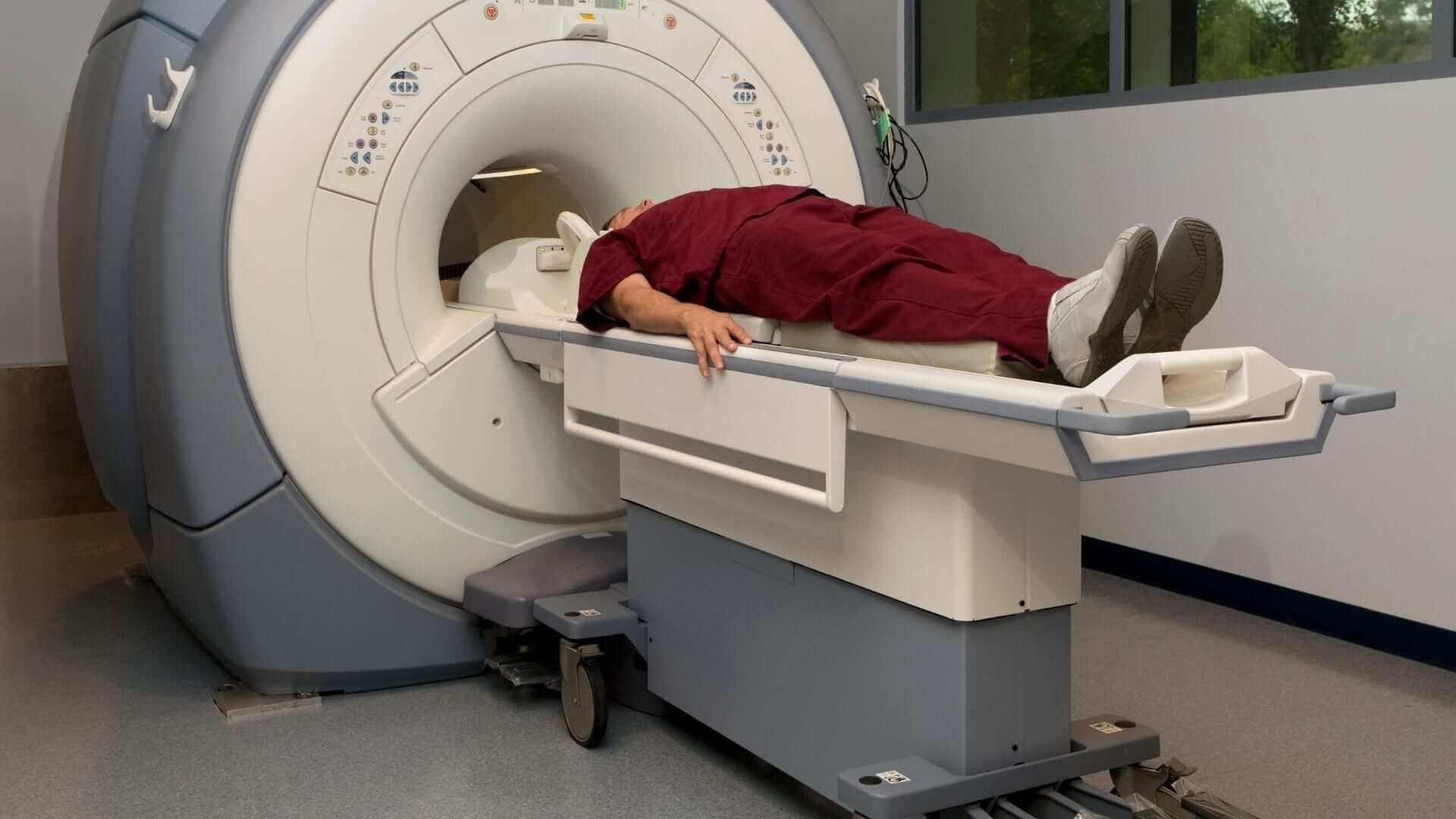
Figure 2: Advanced MRI training facility demonstrating sophisticated diagnostic imaging technology
Imaging equipment represents one of the most complex categories of diagnostic tools, requiring extensive technical knowledge and hands-on experience. Magnetic resonance imaging systems, computed tomography scanners, ultrasound machines, and digital radiography equipment each demand specialized training protocols that address both technical operation and clinical application. Staff members must understand not only how to operate these systems but also how to optimize imaging parameters for different patient populations and clinical indications.
Laboratory diagnostic equipment presents another significant training challenge, encompassing automated chemistry analyzers, hematology instruments, molecular diagnostic platforms, and point-of-care testing devices. These systems often require understanding of complex analytical processes, quality control procedures, and result interpretation guidelines. Training programs must address both technical operation and the clinical significance of diagnostic results, ensuring that staff members can troubleshoot problems and maintain accuracy standards.
Cardiovascular diagnostic equipment, including electrocardiography machines, echocardiography systems, and cardiac stress testing equipment, requires specialized training that combines technical skills with clinical knowledge. Staff members must understand cardiac physiology, recognize normal and abnormal findings, and respond appropriately to emergency situations that may arise during diagnostic procedures.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance Requirements
Healthcare organizations must navigate a complex regulatory environment that mandates specific training requirements for diagnostic equipment operators. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), and various accrediting organizations establish standards that healthcare facilities must meet to maintain operational licenses and reimbursement eligibility. Understanding these requirements is essential for developing compliant training programs that meet both regulatory expectations and clinical quality standards.

Figure 3: Comprehensive medical device training protocols ensuring regulatory compliance
The Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) establish specific training requirements for laboratory personnel operating diagnostic equipment. These regulations mandate that personnel demonstrate competency through initial training, ongoing education, and periodic assessment. Training programs must document competency verification, maintain training records, and ensure that only qualified personnel perform diagnostic tests. Failure to comply with CLIA requirements can result in regulatory sanctions, reimbursement penalties, and potential facility closure.
The Joint Commission and other accrediting organizations establish additional training requirements that address equipment safety, maintenance protocols, and quality assurance procedures. These standards require healthcare organizations to develop comprehensive training programs that address not only technical operation but also safety protocols, emergency procedures, and quality improvement initiatives. Training documentation must demonstrate that staff members understand their responsibilities and can perform their duties safely and effectively.
State and local regulations may impose additional training requirements specific to particular equipment types or clinical applications. Healthcare organizations must stay current with evolving regulatory requirements and ensure that training programs address all applicable standards. This requires ongoing collaboration between training coordinators, regulatory affairs personnel, and clinical supervisors to maintain compliance and avoid regulatory violations.
Developing a Comprehensive Training Framework
Effective training programs for diagnostic equipment require systematic approaches that address learning objectives, competency requirements, and assessment criteria. A well-designed training framework provides structure for curriculum development, instructional delivery, and outcome evaluation. This framework must be flexible enough to accommodate different equipment types while maintaining consistency in quality and effectiveness.
The foundation of any successful training program begins with thorough needs assessment that identifies specific learning requirements for each equipment type and staff category. This assessment should evaluate current competency levels, identify knowledge gaps, and establish training priorities based on clinical importance and regulatory requirements. The needs assessment process should involve input from clinical staff, equipment vendors, regulatory affairs personnel, and training specialists to ensure comprehensive coverage of all relevant topics.
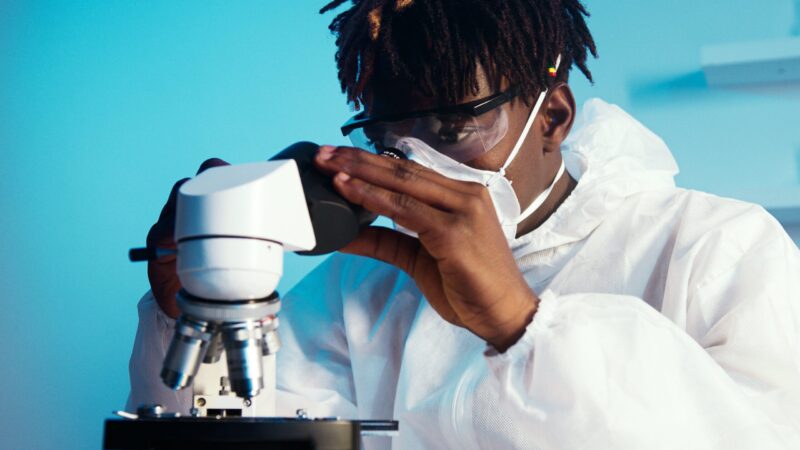

Figure 4: Healthcare professionals engaged in practical laboratory equipment training
Learning objectives must be clearly defined and measurable, specifying exactly what knowledge and skills participants should acquire through training. These objectives should align with job requirements, regulatory standards, and quality improvement goals. Well-written learning objectives provide guidance for curriculum development and serve as benchmarks for assessing training effectiveness. Objectives should address cognitive knowledge, psychomotor skills, and affective attitudes necessary for safe and effective equipment operation.
Competency standards establish the minimum performance criteria that staff members must meet to operate diagnostic equipment independently. These standards should be based on manufacturer specifications, regulatory requirements, and clinical best practices. Competency standards must be specific, measurable, and directly related to job performance requirements. They should address both technical skills and clinical judgment necessary for optimal patient care outcomes.
Training Methodologies and Instructional Approaches
Effective diagnostic equipment training requires diverse instructional methodologies that accommodate different learning styles and skill development requirements. The complexity of modern diagnostic equipment demands training approaches that combine theoretical knowledge with hands-on practice, simulation exercises, and real-world application. Selecting appropriate training methodologies is crucial for achieving learning objectives and ensuring competency development.
Hands-on training represents the most critical component of diagnostic equipment education, allowing participants to develop psychomotor skills and gain confidence through direct interaction with equipment. This approach enables learners to understand equipment controls, practice operational procedures, and develop muscle memory for routine tasks. Hands-on training should progress from basic operation to advanced techniques, allowing participants to build skills systematically while receiving immediate feedback from experienced instructors.

Figure 5: Intensive hands-on training session demonstrating proper equipment operation techniques
Simulation-based training provides opportunities for learners to practice skills in controlled environments without risk to patients or equipment. High-fidelity simulators can replicate realistic clinical scenarios, allowing trainees to experience various situations they may encounter in practice. Simulation training is particularly valuable for emergency procedures, troubleshooting exercises, and quality control activities. This approach allows participants to make mistakes and learn from them without consequences, building confidence and competency through repeated practice.
Case-based learning integrates equipment training with clinical decision-making, helping participants understand how diagnostic results impact patient care decisions. This methodology uses real or simulated patient cases to demonstrate the clinical significance of accurate equipment operation and result interpretation. Case-based learning helps bridge the gap between technical skills and clinical application, ensuring that participants understand the broader context of their work and its impact on patient outcomes.
Blended learning approaches combine multiple instructional methodologies to maximize learning effectiveness while accommodating scheduling constraints and resource limitations. These programs typically include online modules for theoretical content, hands-on workshops for skill development, and mentorship programs for ongoing support. Blended learning allows participants to learn at their own pace while ensuring adequate hands-on practice and expert guidance.
Implementation Strategies for Successful Training Programs
Successful implementation of diagnostic equipment training programs requires careful planning, resource allocation, and organizational commitment. The implementation process must address scheduling challenges, resource constraints, and competing priorities while maintaining focus on learning objectives and competency development. Effective implementation strategies ensure that training programs are sustainable, scalable, and continuously improving.
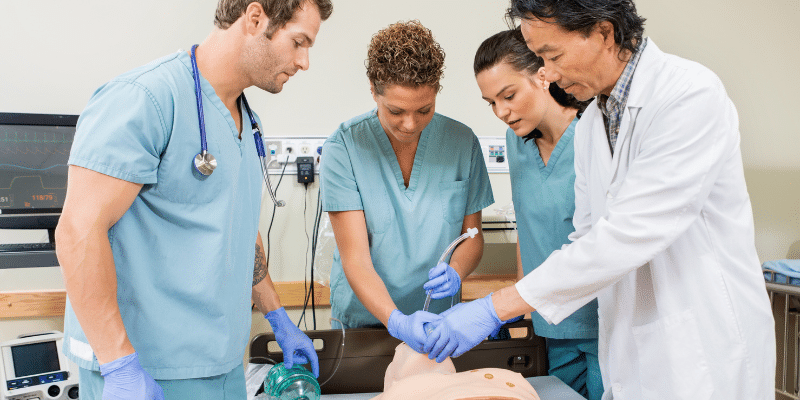
Figure 6: Advanced healthcare simulation training environment supporting comprehensive equipment education
Scheduling training sessions requires careful coordination with clinical operations to minimize disruptions while ensuring adequate participation. Training coordinators must work closely with department managers to identify optimal timing for training activities, considering patient volume patterns, staffing requirements, and equipment availability. Flexible scheduling options, including multiple session offerings and make-up opportunities, help ensure that all required personnel can participate in training programs.
Resource allocation encompasses both human and material resources necessary for effective training delivery. Qualified instructors must be identified and prepared to deliver training content, which may require train-the-trainer programs for internal staff or contracts with external vendors. Training facilities must be equipped with appropriate equipment, audiovisual resources, and learning materials. Budget planning must account for instructor costs, facility expenses, and materials procurement while considering return on investment through improved performance and reduced errors.
Change management strategies help organizations navigate the transition to new equipment and training requirements. Effective communication about training goals, expectations, and benefits helps build support among staff members and supervisors. Leadership engagement demonstrates organizational commitment to training excellence and helps overcome resistance to change. Recognition and incentive programs can motivate participation and reinforce the importance of training activities.
Assessment and Competency Evaluation
Comprehensive assessment strategies ensure that training participants achieve required competency levels and can operate diagnostic equipment safely and effectively. Assessment methods must evaluate both knowledge acquisition and skill development, providing objective measures of training effectiveness. Regular competency evaluation helps identify areas for improvement and ensures ongoing compliance with regulatory requirements.
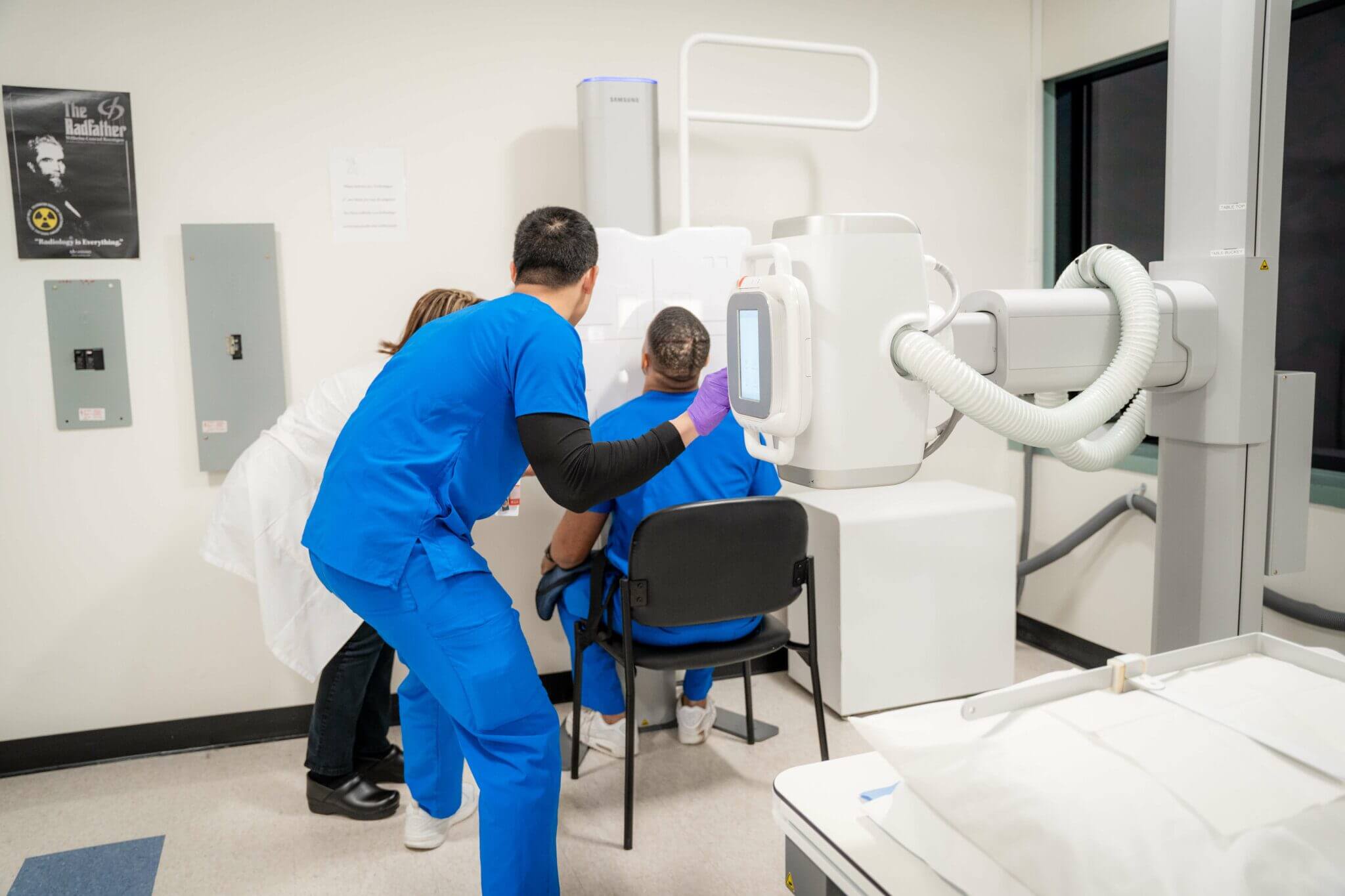
Figure 7: Professional radiologic technology training program with comprehensive assessment protocols
Initial competency assessment establishes baseline performance levels and identifies individual learning needs. Pre-training evaluations help instructors tailor content delivery to participant needs and ensure that foundational knowledge requirements are met before advanced training begins. These assessments should evaluate both theoretical knowledge and practical skills relevant to specific equipment types and job responsibilities.
Ongoing competency monitoring ensures that staff members maintain required skill levels and stay current with evolving technology and procedures. Regular assessments should be conducted at predetermined intervals based on regulatory requirements, equipment complexity, and risk factors. These evaluations may include written examinations, practical demonstrations, and direct observation of routine work performance. Competency monitoring helps identify performance trends and training needs across the organization.
Remedial training programs address competency deficits identified through assessment activities. These programs should provide targeted instruction to help individuals improve specific areas of weakness while maintaining focus on critical safety and quality requirements. Remedial training must be documented thoroughly and include reassessment to verify improvement. Organizations should establish clear policies regarding competency requirements and consequences for failure to meet standards.
Technology Integration and Digital Learning Platforms
Modern training programs increasingly rely on digital technologies to enhance learning effectiveness, improve accessibility, and reduce costs. Learning management systems (LMS), virtual reality simulators, and mobile applications provide innovative approaches to diagnostic equipment training that complement traditional instructional methods. Technology integration requires careful planning to ensure that digital tools enhance rather than replace essential hands-on practice.
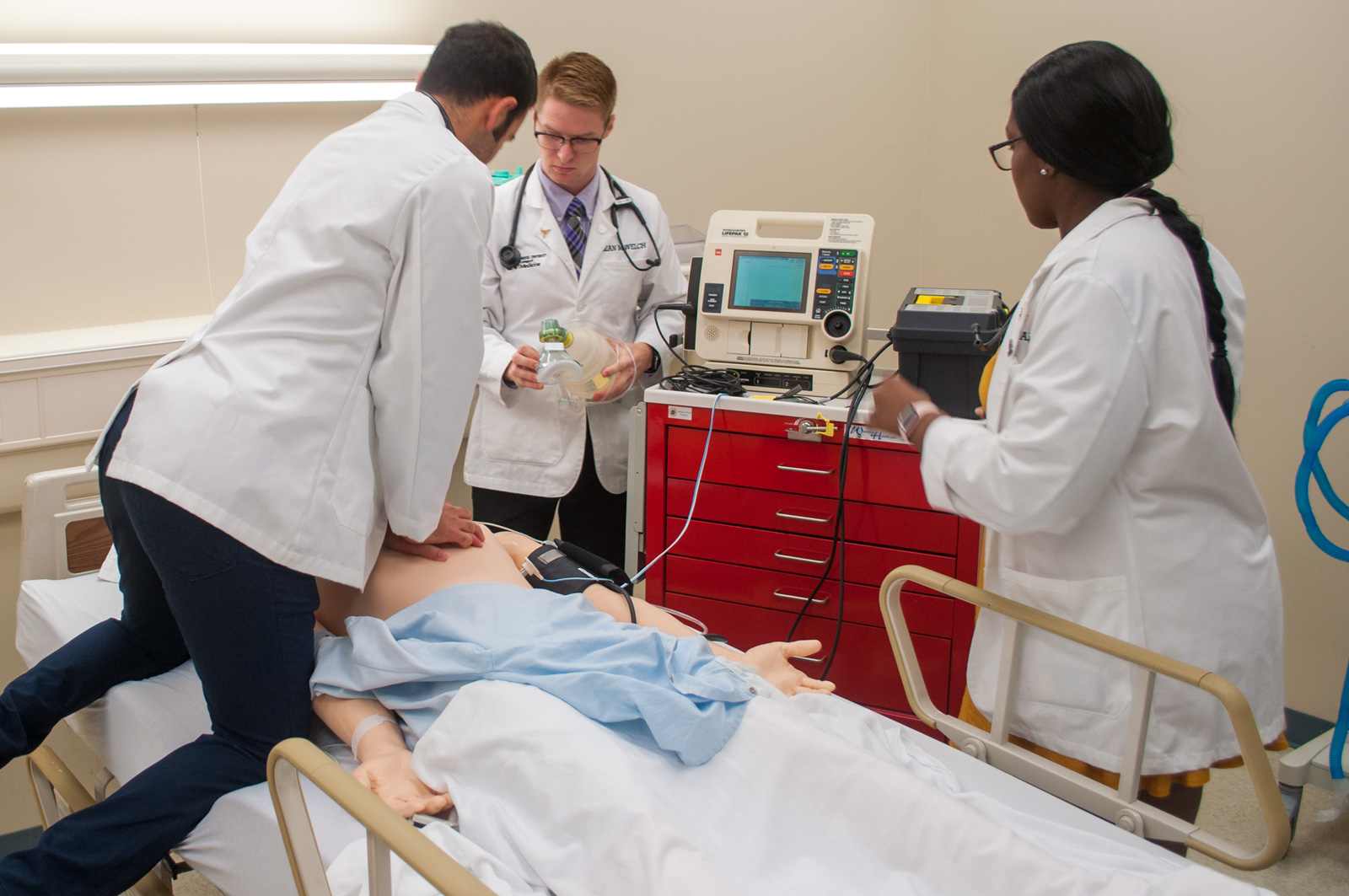
Figure 8: Contemporary hands-on learning environment incorporating digital technology and traditional training methods
Learning management systems provide centralized platforms for delivering training content, tracking progress, and managing competency records. These systems can deliver interactive modules, video demonstrations, and virtual simulations that supplement hands-on training. LMS platforms also facilitate communication between instructors and participants, provide access to reference materials, and generate reports for compliance documentation. Integration with human resources information systems can streamline training administration and ensure that all required personnel complete mandatory training.
Virtual and augmented reality technologies offer immersive training experiences that can replicate equipment operation and clinical scenarios with high fidelity. These technologies are particularly valuable for training on expensive or limited-availability equipment, allowing multiple participants to practice simultaneously without scheduling conflicts. Virtual reality simulators can present various clinical scenarios and equipment malfunctions that may be difficult to recreate in traditional training settings. However, virtual training must be carefully balanced with hands-on practice to ensure that participants develop real-world competency.
Mobile learning applications provide just-in-time access to training materials, reference guides, and troubleshooting resources. These tools can support performance during actual equipment operation, providing quick access to operational procedures, safety protocols, and quality control requirements. Mobile applications can also deliver microlearning modules that reinforce key concepts and provide ongoing education between formal training sessions. However, mobile tools should supplement rather than replace comprehensive training programs.
Quality Improvement and Continuous Enhancement
Training programs must incorporate quality improvement methodologies to ensure continuous enhancement of effectiveness and efficiency. Regular evaluation of training outcomes, participant feedback, and performance indicators helps identify opportunities for improvement and ensures that programs remain current with evolving technology and practices. Quality improvement activities should be systematic, data-driven, and focused on achieving measurable improvements in training effectiveness.
Program evaluation should assess multiple dimensions of training effectiveness, including learning outcomes, participant satisfaction, behavior change, and organizational impact. Kirkpatrick’s four-level evaluation model provides a comprehensive framework for assessing training effectiveness at reaction, learning, behavior, and results levels. Regular evaluation helps identify successful practices that should be maintained and areas requiring improvement or modification.
Participant feedback provides valuable insights into training quality, relevance, and effectiveness from the learner perspective. Feedback collection should include both quantitative ratings and qualitative comments about specific program components. Anonymous feedback mechanisms encourage honest responses and help identify improvement opportunities that may not be apparent to instructors or administrators. Feedback should be collected immediately after training and at follow-up intervals to assess long-term impact and retention.
Performance indicators should be established to monitor training program outcomes and organizational impact. These indicators may include error rates, equipment downtime, regulatory compliance scores, and staff confidence levels. Regular monitoring of performance indicators helps demonstrate training value and identify areas where additional education may be needed. Trending analysis can reveal patterns and help predict future training needs.
Challenges and Solutions in Diagnostic Equipment Training
Healthcare organizations face numerous challenges in developing and maintaining effective diagnostic equipment training programs. Resource constraints, scheduling difficulties, technology complexity, and regulatory requirements create obstacles that must be addressed through creative solutions and strategic planning. Understanding common challenges and proven solutions helps organizations develop more effective training strategies.
Figure 9: Comparison of advanced diagnostic medical imaging training approaches and technologies
Resource limitations represent one of the most significant challenges facing training programs, particularly in smaller healthcare organizations with limited budgets and staff. Solutions include partnerships with equipment vendors for training support, shared training programs among multiple organizations, and creative use of existing resources. Grant funding may be available for training initiatives that address workforce development or quality improvement goals. Organizations should also consider return on investment calculations that demonstrate the financial benefits of comprehensive training programs.
Scheduling conflicts arise when training requirements compete with patient care responsibilities and operational demands. Solutions include flexible training schedules, just-in-time learning opportunities, and integration of training with routine work activities. Some organizations have successfully implemented mandatory training during less busy periods or have developed rotating schedules that ensure coverage while allowing participation. Technology-based solutions can provide training accessibility outside of regular work hours.
Technology complexity continues to increase as diagnostic equipment becomes more sophisticated and automated. Training programs must evolve to address these challenges while maintaining focus on fundamental principles and safety requirements. Manufacturer partnerships can provide access to specialized training resources and expertise. Collaborative relationships with academic institutions may provide access to simulation facilities and educational resources that would be prohibitively expensive for individual organizations.
Staff turnover creates ongoing challenges for maintaining competency levels and training consistency. Solutions include mentorship programs, competency-based orientation processes, and comprehensive documentation of training requirements. Cross-training initiatives can provide backup coverage and reduce the impact of staff departures. Organizations should also focus on retention strategies that reduce turnover and preserve training investments.
Best Practices and Recommendations
Successful diagnostic equipment training programs share common characteristics that contribute to their effectiveness and sustainability. These best practices provide guidance for organizations developing new training initiatives or seeking to improve existing programs. Implementation of proven practices can accelerate program development and improve training outcomes.
Leadership commitment represents the foundation of successful training programs, providing necessary resources, policy support, and cultural emphasis on continuous learning. Senior leadership must champion training initiatives and demonstrate their commitment through resource allocation and active participation. Middle management support is equally important for ensuring that training requirements are integrated into daily operations and that staff members are encouraged to participate actively.
Stakeholder engagement ensures that training programs address the needs and perspectives of all relevant parties, including clinical staff, administrators, patients, and regulatory bodies. Regular communication with stakeholders helps maintain support and identifies emerging needs or concerns. Advisory committees can provide ongoing guidance and feedback for program development and improvement activities.
Evidence-based approaches ensure that training programs incorporate proven educational methodologies and assessment techniques. Regular review of educational research and industry best practices helps identify innovative approaches and emerging trends. Collaboration with academic institutions and professional organizations can provide access to cutting-edge research and development activities.
Documentation and record-keeping systems must support regulatory compliance requirements while providing useful information for program management and improvement. Comprehensive documentation includes training curricula, competency standards, assessment results, and improvement activities. Electronic systems can streamline documentation processes and provide better access to training records for auditing and reporting purposes.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of diagnostic equipment training will be shaped by technological innovations, changing regulatory requirements, and evolving healthcare delivery models. Understanding emerging trends helps organizations prepare for future challenges and opportunities while ensuring that current training programs remain relevant and effective.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are beginning to transform both diagnostic equipment capabilities and training approaches. AI-powered training systems can provide personalized learning experiences, adaptive assessment methods, and predictive analytics for performance improvement. These technologies may also enable more sophisticated simulation environments and real-time performance feedback during equipment operation.
Telemedicine and remote diagnostics are expanding the scope of diagnostic equipment training to include home-based and community settings. Training programs must address the unique challenges of remote equipment operation, including technical support, quality assurance, and patient safety considerations. Distance learning technologies will become increasingly important for reaching distributed staff members and maintaining competency in remote locations.
Regulatory evolution continues to shape training requirements as healthcare quality initiatives and patient safety concerns drive policy changes. Organizations must stay informed about regulatory developments and ensure that training programs adapt to new requirements. Collaboration with regulatory agencies and professional organizations can provide early insight into emerging requirements and implementation strategies.
Conclusion
Training healthcare staff on new diagnostic equipment represents a critical investment in patient safety, quality care, and organizational success. The complexity of modern diagnostic technology demands comprehensive training programs that address technical competency, regulatory compliance, and clinical application. Successful training initiatives require systematic planning, evidence-based methodologies, and ongoing evaluation to ensure effectiveness and sustainability.
Healthcare organizations must recognize that training is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that evolves with technology, regulations, and clinical practice. Investment in robust training programs yields significant returns through improved patient outcomes, reduced errors, enhanced compliance, and increased staff satisfaction. Organizations that prioritize training excellence position themselves for success in an increasingly complex and competitive healthcare environment.
The future of diagnostic equipment training will continue to evolve with technological innovations and changing healthcare needs. Organizations that embrace best practices, leverage emerging technologies, and maintain focus on continuous improvement will be best positioned to meet these challenges. By following the strategies and recommendations outlined in this guide, healthcare organizations can develop training programs that support their mission of providing excellent patient care while meeting regulatory requirements and operational objectives.
Ultimately, the success of diagnostic equipment training programs depends on organizational commitment, stakeholder engagement, and dedication to excellence. When healthcare organizations invest in comprehensive training initiatives, they invest in their most valuable asset—their people—and create the foundation for sustained success in delivering high-quality diagnostic services that improve patient lives and advance the practice of medicine.


