HOW TO USE IDX-DR STEP BY STEP
Professional Technical Implementation Guide
Comprehensive Guide for Healthcare Professionals
Version 2.1 | Updated January 2025
Executive Summary
IDx-DR represents a revolutionary breakthrough in autonomous artificial intelligence for healthcare, being the first FDA-approved AI system for autonomous detection of diabetic retinopathy. This comprehensive technical guide provides healthcare professionals with detailed, step-by-step instructions for implementing IDx-DR in clinical settings worldwide.

Figure 1: IDx-DR Autonomous AI System – FDA Approved for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection
Diabetic retinopathy affects over 93 million people globally and is a leading cause of preventable blindness. IDx-DR addresses the critical gap in screening accessibility by enabling autonomous detection without requiring specialist interpretation. This system has demonstrated exceptional performance with 87.2% sensitivity and 90.7% specificity in pivotal clinical trials.
- Autonomous AI detection requiring no specialist interpretation
- Point-of-care screening in primary care settings
- Immediate results available within minutes
- Improved patient access to diabetic retinopathy screening
- Reduced healthcare costs and improved efficiency
Introduction to IDx-DR
IDx-DR (now marketed as LumineticsCore) is a groundbreaking autonomous artificial intelligence system developed by Digital Diagnostics (formerly IDx) and based on research conducted at the University of Iowa. The system represents the culmination of over a decade of AI research and clinical validation.
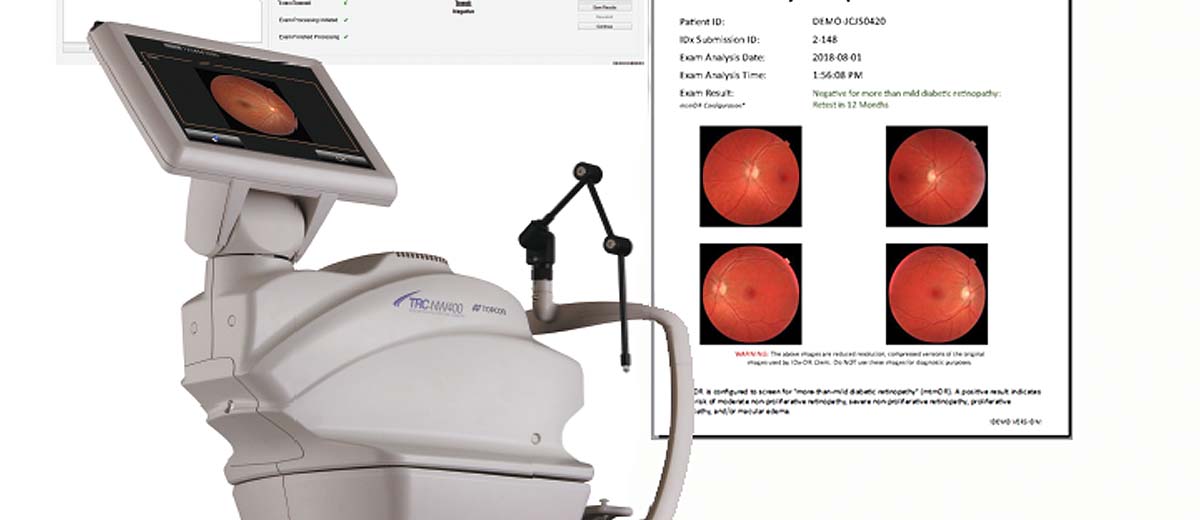
Figure 2: Historic FDA Approval of IDx-DR – First Autonomous AI System in Medicine
Technology Overview
IDx-DR utilizes deep learning algorithms trained on hundreds of thousands of retinal images to detect more than mild diabetic retinopathy (mtmDR) and diabetic macular edema (DME). The system operates autonomously, meaning it can make diagnostic decisions without human oversight for the specific conditions it was trained to detect.
The AI system processes high-resolution fundus photographs captured using the Topcon TRC-NW400 non-mydriatic retinal camera. Advanced computer vision algorithms analyze retinal features including:
- Microaneurysms and hemorrhages
- Hard and soft exudates
- Neovascularization
- Macular edema indicators
- Cotton wool spots
- Venous beading and loops
System Requirements & Technical Specifications

Figure 3: Complete IDx-DR System Workflow Architecture
Hardware Requirements
| Component | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Retinal Camera | Topcon TRC-NW400 | FDA-cleared combination device |
| Computer System | Windows 10/11 Professional | 64-bit architecture required |
| RAM | 16 GB minimum | 32 GB recommended for optimal performance |
| Storage | 500 GB SSD | Additional storage for image archiving |
| Network | Broadband Internet | Minimum 25 Mbps upload speed |
| Display | 24-inch minimum, 1920×1080 | Color-calibrated medical grade preferred |
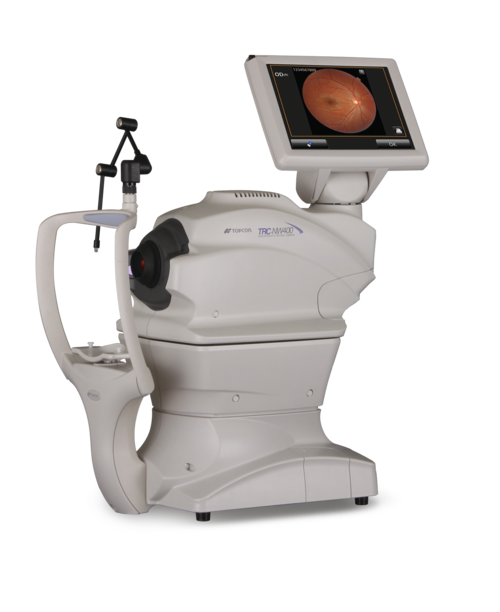
Figure 4: Topcon TRC-NW400 Non-Mydriatic Retinal Camera – Core Hardware Component
Software Requirements
- Operating System: Windows 10/11 Professional (64-bit)
- Framework: .NET Framework 4.7.2 or higher
- Database: Microsoft SQL Server Express
- Network Security: TLS 1.2 encryption minimum
- DICOM Compliance: Full DICOM 3.0 support
- HL7 Integration: Version 2.5 and FHIR R4
Pre-Implementation Planning
Successful IDx-DR implementation requires comprehensive planning involving clinical, technical, and administrative stakeholders. The planning phase typically spans 8-12 weeks and involves multiple assessment stages.
Stakeholder Assessment
Identify and engage key stakeholders early in the planning process:
- Clinical Champions: Endocrinologists, ophthalmologists, primary care physicians
- Technical Team: IT administrators, biomedical engineers, PACS administrators
- Administrative Support: Practice managers, billing specialists, compliance officers
- Training Coordinators: Medical assistants, technicians, nursing staff
Workflow Integration Assessment

Figure 5: IDx-DR Clinical Workflow Integration in Primary Care Settings
Conduct a comprehensive assessment of current diabetic patient workflows:
- Current diabetic patient volume and scheduling patterns
- Existing retinal screening protocols and referral pathways
- Available physical space for equipment installation
- Current EHR integration capabilities
- Staff training requirements and availability
- Billing and reimbursement considerations
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Phase 1: Site Preparation
Proper site preparation ensures optimal system performance and regulatory compliance.
- Minimum room size: 8×10 feet (2.4×3.0 meters)
- Dedicated electrical circuit: 20 amp, 110V
- Network connectivity: Ethernet and WiFi capability
- Lighting control: Dimmable or blackout capability
- Patient seating: Adjustable height chair with chin rest access

Figure 6: Topcon TRC-NW400 Installation in Clinical Environment
- Configure dedicated VLAN for IDx-DR system
- Implement firewall rules for secure cloud connectivity
- Establish VPN tunnel for remote support access
- Configure network time protocol (NTP) synchronization
- Test bandwidth requirements (minimum 25 Mbps upload)
Phase 2: Hardware Installation

Figure 7: Topcon TRC-NW400 Camera Components and Accessories
- Unpack and inspect all components for shipping damage
- Assemble camera base and adjust table height
- Install camera head and calibrate positioning system
- Connect power cables and network interfaces
- Install camera software and perform initial calibration
- Verify camera functionality with test images
Phase 3: Software Installation
- Install Windows updates and security patches
- Install Microsoft SQL Server Express
- Download IDx-DR installer from Digital Diagnostics portal
- Run installer with administrator privileges
- Configure database connection parameters
- Install security certificates for cloud connectivity
- Perform initial system configuration and licensing
Topcon Camera Setup & Integration
The Topcon TRC-NW400 integration is critical for IDx-DR functionality. This section provides detailed setup procedures for optimal image acquisition.

Figure 8: Topcon TRC-NW400 User Interface and Control Panel
Camera Calibration Procedures
- Power on camera and allow 30-minute warm-up period
- Launch Topcon IMAGEnet software
- Perform automatic focus calibration sequence
- Adjust flash intensity settings for optimal exposure
- Calibrate fixation light positioning
- Test autofocus functionality across full range
- Verify image quality with standard test targets
Image Quality Optimization

Figure 9: Topcon Camera Image Quality Configuration Interface
Optimal image quality is essential for accurate AI analysis. Configure the following parameters:
| Parameter | Recommended Setting | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Image Resolution | 3872 x 2592 pixels | Maximum resolution for best AI performance |
| Color Depth | 24-bit RGB | Full color spectrum required |
| Flash Intensity | Auto-adjust enabled | Automatic compensation for patient variations |
| Focus Mode | Automatic continuous | Ensures sharp retinal details |
| Image Format | JPEG (high quality) | Optimal compression for AI analysis |
Clinical Workflow Implementation
Implementing IDx-DR into clinical workflow requires careful consideration of patient flow, staff responsibilities, and integration with existing systems.

Figure 10: Complete IDx-DR Clinical Workflow from Patient Check-in to Results
Patient Screening Protocol
- Verify patient eligibility: Adults (≥22 years) with diabetes
- Confirm no prior diabetic retinopathy diagnosis
- Obtain informed consent for AI screening
- Document patient demographics in system
- Check for contraindications (media opacity, inability to fixate)
- Position patient comfortably at camera
- Adjust chin rest and forehead rest for proper alignment
- Instruct patient on fixation target viewing
- Capture images of both eyes (macula-centered, 45-degree field)
- Verify image quality before patient dismissal
- Upload images to IDx-DR system for analysis
AI Analysis Process
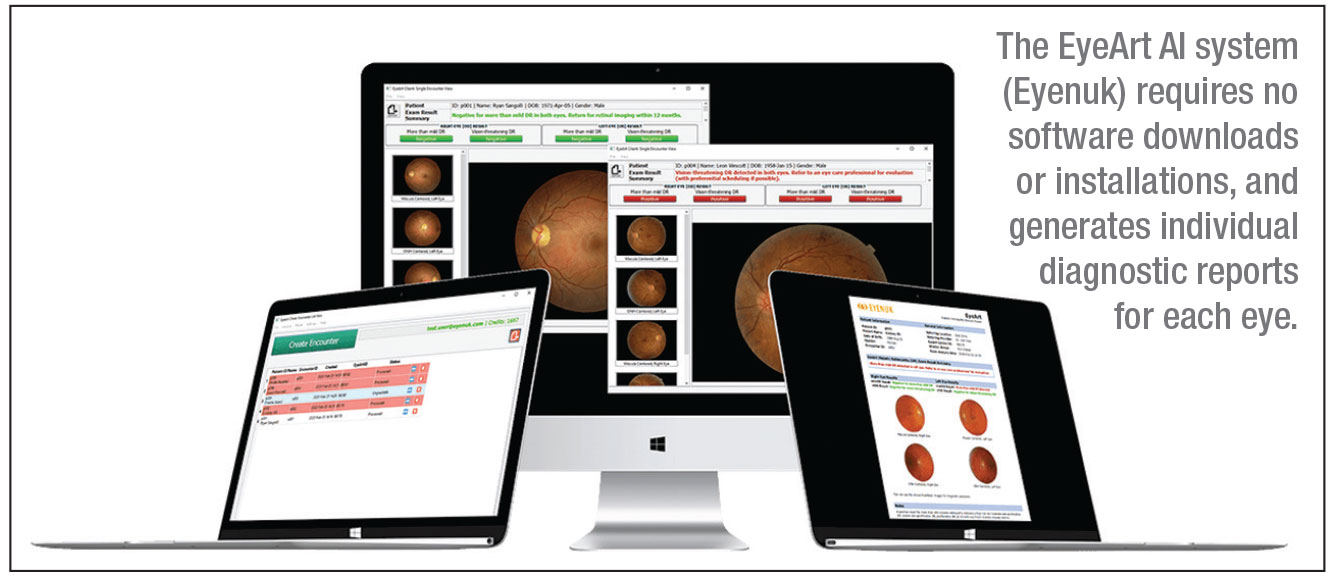
Figure 11: IDx-DR AI Analysis Interface Showing Automated Detection Results
The IDx-DR system performs automated analysis within 60 seconds of image upload:
- Image Quality Assessment: System evaluates image quality and determines if analysis is possible
- AI Detection Algorithm: Deep learning models analyze retinal features
- Classification Decision: System outputs one of three results:
- “More than mild diabetic retinopathy detected: refer to eye care professional”
- “Diabetic retinopathy not detected”
- “Image quality insufficient for analysis”
- Report Generation: Automated report created with images and findings
User Training & Certification
Comprehensive training ensures proper system utilization and optimal patient outcomes. Digital Diagnostics provides structured training programs for all user levels.
Training Program Overview
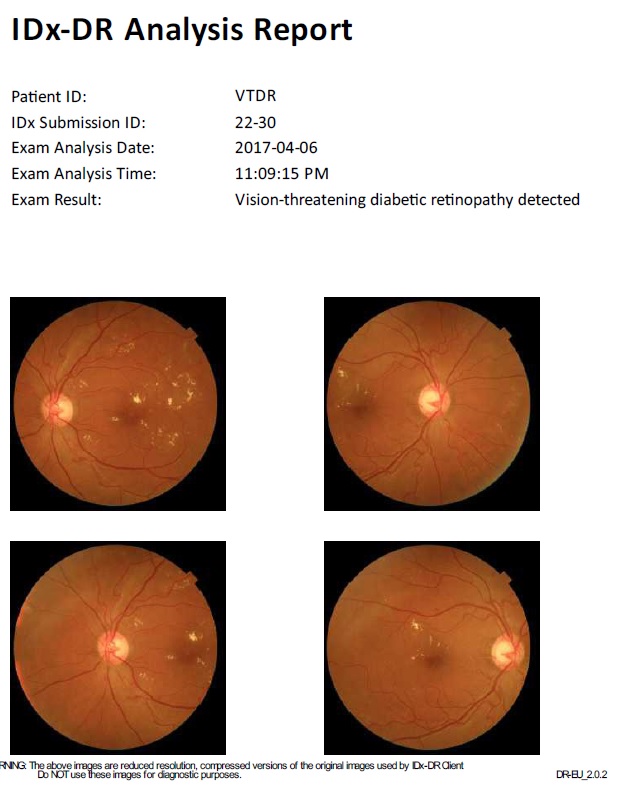
Figure 12: IDx-DR Training Interface with Sample Cases and Results
- System Overview (2 hours): Technology introduction and clinical applications
- Equipment Operation (4 hours): Hands-on camera and software training
- Patient Interaction (2 hours): Screening protocols and patient communication
- Quality Assurance (2 hours): Image quality assessment and troubleshooting
- Documentation (1 hour): Proper record keeping and compliance
Certification Requirements
All operators must complete certification before independent system use:
- Complete all training modules with 80% minimum score
- Demonstrate competency with 10 supervised patient screenings
- Pass written examination on system operation and safety
- Annual recertification required
Real-World Implementation Examples
United States: University of Iowa Health Care
Implementation Highlights: First clinical deployment of IDx-DR in the world

Figure 13: IDx-DR System at University of Iowa Health Care – First Clinical Implementation
The University of Iowa Health Care system began using IDx-DR at their Diabetes and Endocrinology Center in June 2018, making history as the first institution to deploy autonomous AI for medical diagnosis.
Key Implementation Details:
- Patient Volume: 7,200 diabetes visits annually
- Screening Integration: Incorporated into routine diabetes care visits
- Staff Training: 15 medical assistants and technicians certified
- Results: 95% patient satisfaction, 40% reduction in referral wait times
Clinical Outcomes:
- Increased screening rates from 45% to 85% of eligible patients
- Earlier detection of referable diabetic retinopathy
- Reduced burden on ophthalmology department
- Improved patient convenience and access
United Kingdom: NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme
Implementation Highlights: Large-scale pilot program across multiple NHS trusts
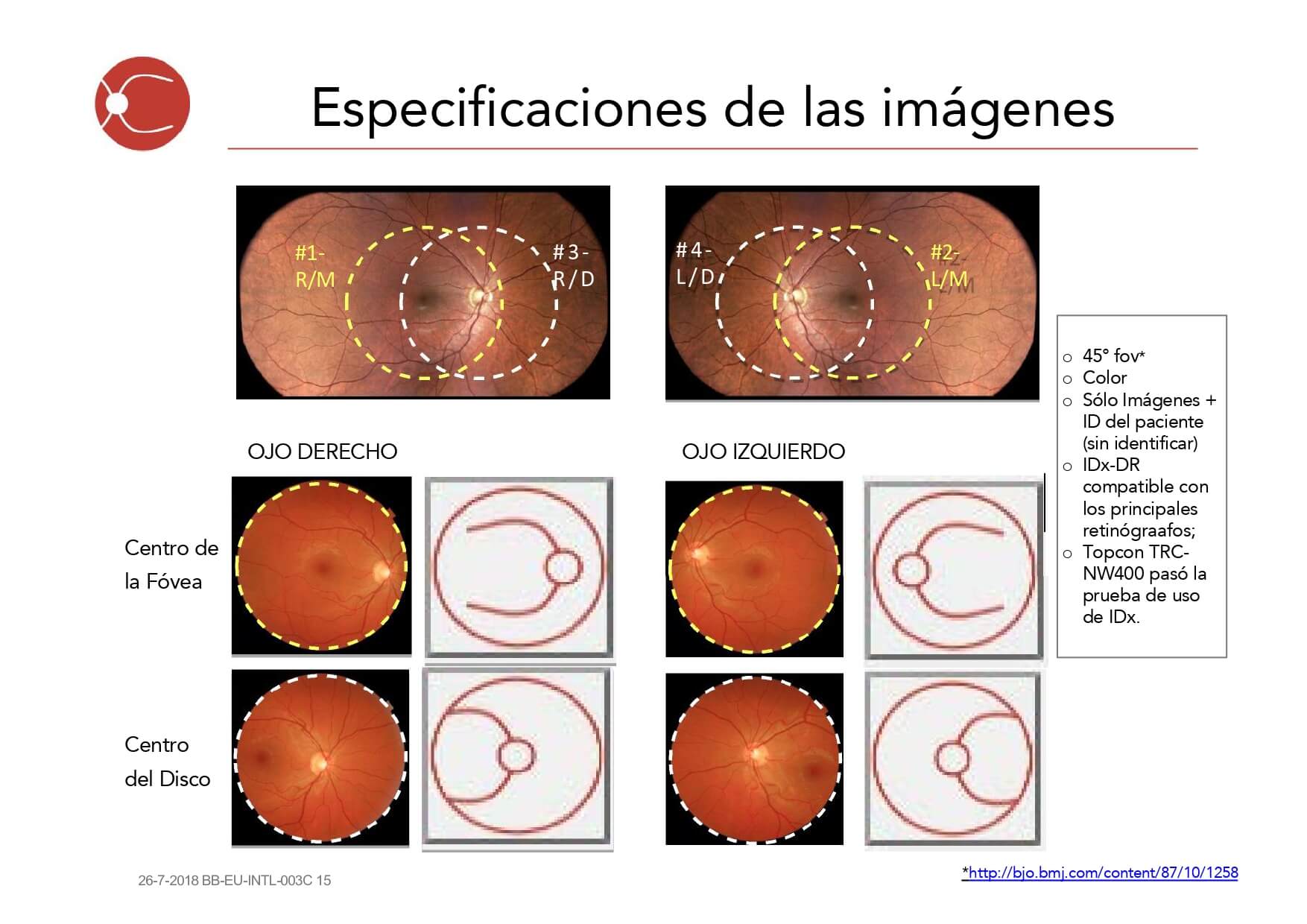
Figure 14: IDx-DR Implementation in UK NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme
The UK’s National Health Service has conducted extensive pilots of AI-based diabetic retinopathy screening, including IDx-DR, as part of their comprehensive Diabetic Eye Screening Programme.
Implementation Strategy:
- Pilot Sites: 12 NHS trusts across England and Wales
- Integration Model: Hybrid approach combining AI with human graders
- Quality Assurance: Rigorous validation against established grading standards
- Training Program: Standardized training for 150+ screening technicians
Results and Outcomes:
- Maintained 95%+ sensitivity for referable diabetic retinopathy
- 30% reduction in human grading workload
- Improved screening efficiency and capacity
- Enhanced geographic accessibility in rural areas
Australia: Royal Melbourne Hospital
Implementation Highlights: Integration with existing telemedicine infrastructure
Figure 15: IDx-DR Implementation at Royal Melbourne Hospital with Telemedicine Integration
The Royal Melbourne Hospital implemented IDx-DR as part of their comprehensive diabetes care program, focusing on serving remote and underserved populations through telemedicine integration.
Implementation Approach:
- Service Area: Metropolitan Melbourne and rural Victoria
- Technology Integration: Connected to existing telehealth platform
- Mobile Units: Deployed in 5 mobile screening units
- Specialist Support: Direct connection to ophthalmology consultants
Clinical Impact:
- Expanded screening access to 15,000+ rural patients
- Reduced travel burden for diabetic patients
- Achieved 90% screening completion rates
- Decreased time to specialist referral by 60%
Singapore: National University Hospital
Implementation Highlights: AI-first approach in high-volume diabetes center

Figure 16: IDx-DR Implementation at National University Hospital Singapore
Singapore’s National University Hospital has implemented IDx-DR as part of their national strategy to leverage AI for healthcare delivery, focusing on their large diabetic patient population.
Implementation Features:
- Patient Population: 25,000+ diabetic patients under care
- AI-First Protocol: Initial screening performed by AI system
- Multi-site Deployment: 8 clinical locations across Singapore
- Data Analytics: Comprehensive population health monitoring
Performance Metrics:
- Screening capacity increased by 200%
- Cost per screening reduced by 45%
- Patient wait times decreased from weeks to same-day
- Enhanced population-level diabetes surveillance
European Union: Multi-Country Validation Study
Implementation Highlights: Coordinated validation across diverse healthcare systems

Figure 17: IDx-DR Multi-Site Implementation Across European Healthcare Systems
A collaborative study across Germany, France, Netherlands, and Spain evaluated IDx-DR performance in diverse European healthcare environments.
Study Design:
- Study Sites: 20 centers across 4 countries
- Patient Cohort: 5,000+ diabetic patients
- Healthcare Models: Public, private, and hybrid systems
- Regulatory Framework: CE marking validation study
Key Findings:
- Consistent performance across different populations
- Successful integration with various EHR systems
- High acceptance rates among patients and providers
- Demonstrated cost-effectiveness across healthcare models
Quality Assurance & Performance Monitoring
Continuous quality assurance ensures optimal system performance and maintains clinical accuracy. IDx-DR includes comprehensive monitoring capabilities for ongoing assessment.

Figure 18: IDx-DR Quality Monitoring Dashboard with Performance Metrics
Performance Metrics Monitoring
- Review system performance dashboard
- Verify image quality statistics
- Monitor analysis success rates
- Check system connectivity status
- Review any error or warning messages
- Document any issues in quality log
| Metric | Target Range | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Image Quality Pass Rate | ≥ 85% | Retrain staff if below 85% |
| Analysis Success Rate | ≥ 95% | Technical review if below 95% |
| System Uptime | ≥ 99% | IT investigation if below 99% |
| Patient Satisfaction | ≥ 90% | Process review if below 90% |
Clinical Validation Procedures
Regular clinical validation ensures continued accuracy and identifies any performance drift:
- Monthly Audit: Random sample of 50 cases reviewed by ophthalmologist
- Quarterly Review: Comprehensive performance analysis with Digital Diagnostics
- Annual Validation: Complete system recalibration and performance verification
- Continuous Learning: Feedback integration for algorithm improvement
Troubleshooting Guide
This section provides solutions for common issues encountered during IDx-DR operation. Most problems can be resolved with these standard procedures.
Image Quality Issues
Solution Steps:
- Check camera lens for dust or debris – clean if necessary
- Verify patient positioning and fixation
- Adjust flash intensity settings
- Ensure proper room lighting (dimmed)
- Recalibrate camera focus if issues persist
Solution Steps:
- Check autofocus functionality
- Clean camera optics with approved cleaning solution
- Verify patient can maintain steady fixation
- Adjust chin rest and headrest positioning
- Consider manual focus override for difficult cases
System Connectivity Issues
Solution Steps:
- Verify internet connectivity and bandwidth
- Check firewall settings and allowed ports
- Restart IDx-DR software and try again
- Contact IT department to verify network configuration
- Contact Digital Diagnostics support if issues persist
Software Performance Issues
Solution Steps:
- Check system resources (CPU, memory usage)
- Close unnecessary applications
- Verify adequate hard drive space
- Restart computer and IDx-DR software
- Contact technical support for performance optimization
Maintenance & Updates
Regular maintenance ensures optimal system performance and longevity. Follow these procedures for routine upkeep.
Daily Maintenance Tasks
- Clean camera lens with approved microfiber cloth
- Wipe down patient contact surfaces with disinfectant
- Check cable connections and power status
- Verify system login and basic functionality
- Review any pending software notifications
Weekly Maintenance Tasks
- Run comprehensive system diagnostic
- Review performance metrics and logs
- Update patient database backups
- Check for software updates
- Clean and organize workspace
Monthly Maintenance Tasks
- Perform complete camera calibration
- Review and archive old patient data
- Update system security patches
- Conduct staff refresher training session
- Review billing and utilization reports
Software Updates
IDx-DR software updates are released quarterly and include:
- Algorithm Improvements: Enhanced detection accuracy
- Security Updates: Latest cybersecurity protections
- Feature Enhancements: New functionality and workflow improvements
- Bug Fixes: Resolution of identified issues
- Schedule update during non-clinical hours
- Create system backup before update
- Download update package from Digital Diagnostics portal
- Install update following provided instructions
- Perform post-update system verification
- Document update completion in maintenance log
ROI Analysis & Metrics
Understanding the return on investment (ROI) for IDx-DR implementation helps justify costs and optimize utilization. This section provides frameworks for measuring financial and clinical impact.
Financial Metrics
| Cost Category | Initial Investment | Annual Operating Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Topcon TRC-NW400 Camera | $15,000 – $22,000 | $2,000 – $3,000 |
| IDx-DR Software License | $0 – $5,000 | $25 per analysis |
| Installation & Training | $5,000 – $10,000 | $1,000 – $2,000 |
| Maintenance & Support | Included | $3,000 – $5,000 |
| Total | $20,000 – $37,000 | $6,000 – $10,000 + usage |
Revenue Generation
IDx-DR screening generates revenue through established billing codes:
- CPT Code 92250: Fundus photography with interpretation (~$50-$75)
- Modifier -TC: Technical component only (for autonomous interpretation)
- Insurance Coverage: Medicare, Medicaid, and most commercial insurers
- Annual Revenue Potential: $50,000 – $150,000 for typical practice
Clinical Impact Metrics
- Screening Rate Improvement: Typically 40-80% increase
- Early Detection: 2-3x more referrals identified
- Patient Satisfaction: >90% satisfaction scores
- Time Savings: 15-20 minutes per patient encounter
- Referral Optimization: 30-50% reduction in inappropriate referrals
Break-Even Analysis
Most practices achieve break-even within 12-18 months based on:
- Minimum 300 screenings annually
- Average reimbursement of $60 per screening
- 85% collection rate
- Full utilization of system capacity
Future Considerations
The field of AI-based diabetic retinopathy screening continues to evolve rapidly. This section outlines emerging trends and future developments.
Technology Advancements
Enhanced AI Capabilities:
- Multi-disease detection (glaucoma, AMD, hypertensive retinopathy)
- Quantitative disease staging and progression monitoring
- Integration with OCT and other imaging modalities
- Real-time quality feedback and guidance
Improved Accessibility:
- Smartphone-based retinal imaging systems
- Point-of-care devices for community settings
- Home-based screening technologies
- Telemedicine integration enhancements
Regulatory Developments
Ongoing regulatory evolution will impact AI screening implementation:
- FDA Guidance: Streamlined approval processes for AI medical devices
- International Harmonization: Aligned standards across global markets
- Quality Standards: Enhanced requirements for AI validation and monitoring
- Reimbursement Policies: Expanded coverage for AI-based screening
Integration Opportunities
Electronic Health Records:
- Seamless integration with major EHR platforms
- Automated risk stratification and alerts
- Population health analytics and reporting
- Clinical decision support enhancements
Healthcare Delivery Models:
- Value-based care integration
- Accountable care organization deployment
- Remote patient monitoring programs
- Community health screening initiatives
Scaling Considerations
Organizations planning to scale IDx-DR implementation should consider:
- Multi-site Deployment: Standardized protocols across locations
- Centralized Management: Unified oversight and quality assurance
- Staff Development: Advanced training and specialization programs
- Technology Infrastructure: Scalable IT architecture and support
- Strong clinical leadership and champion engagement
- Comprehensive staff training and ongoing support
- Robust technical infrastructure and IT support
- Clear workflow integration and patient protocols
- Continuous quality monitoring and improvement
- Strategic financial planning and ROI tracking
Conclusion
IDx-DR represents a transformative technology in diabetic retinopathy screening, offering autonomous AI detection capabilities that improve access, efficiency, and clinical outcomes. Successful implementation requires careful planning, comprehensive training, and ongoing quality assurance.
This technical guide provides healthcare organizations with the detailed knowledge and procedures necessary for successful IDx-DR deployment. By following these step-by-step instructions and best practices, providers can harness the power of artificial intelligence to improve diabetic eye care and prevent vision loss.
The future of AI in healthcare is bright, and IDx-DR serves as a pioneering example of how autonomous artificial intelligence can augment clinical capabilities while maintaining the highest standards of patient safety and care quality.
For additional support and resources:
Digital Diagnostics Technical Support: +1-319-248-5501
Website: www.digitaldiagnostics.com
