IBM CLOUD FOR HEALTHCARE: STEP BY STEP IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE
Executive Summary
The healthcare industry stands at a critical juncture where digital transformation is no longer optional but essential for delivering quality patient care, ensuring operational efficiency, and maintaining competitive advantage. IBM Cloud for Healthcare emerges as a comprehensive, enterprise-grade platform specifically designed to address the unique challenges facing healthcare organizations worldwide.
This comprehensive guide provides healthcare IT executives, Chief Information Officers, and implementation teams with a detailed roadmap for successfully deploying IBM Cloud for Healthcare solutions. Drawing from real-world implementations across Japan, Finland, Canada, and India, this document presents proven strategies, best practices, and lessons learned from organizations that have successfully transformed their healthcare IT infrastructure.
IBM Cloud for Healthcare offers a robust foundation combining Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) capabilities, enhanced with industry-specific tools for clinical data management, AI-powered analytics, and regulatory compliance. The platform addresses critical healthcare challenges including data interoperability, security compliance, scalability demands, and the integration of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning into clinical workflows.
The implementation methodology outlined in this guide follows an eight-step process that has been validated across multiple healthcare organizations globally. From initial assessment and planning through data migration, security configuration, and go-live procedures, each phase is detailed with specific deliverables, timelines, and success metrics. Real-world case studies demonstrate measurable outcomes including 70% reduction in on-premises servers, 24/7 system availability, improved disaster recovery capabilities, and enhanced clinical decision-making through AI-powered insights.

Figure 1: IBM Cloud for Healthcare Platform Architecture Overview
IBM Cloud for Healthcare Platform Overview
IBM Cloud for Healthcare represents a paradigm shift in how healthcare organizations approach IT infrastructure and data management. Built on IBM’s enterprise-grade cloud foundation, the platform provides a secure, scalable, and compliant environment specifically tailored for healthcare workloads. The platform integrates seamlessly with existing healthcare systems while providing pathways for modernization and innovation.
The core architecture encompasses multiple layers of services and capabilities. At the infrastructure level, IBM Cloud provides bare metal servers, virtual servers, and containerized environments optimized for healthcare workloads. The platform layer includes specialized healthcare services such as IBM Watson Health capabilities, FHIR-compliant data stores, and clinical decision support systems. Security and compliance are embedded throughout the stack, with HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulatory frameworks built into the foundation.
Key platform components include IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service for containerized applications, IBM Cloudant for NoSQL database requirements, IBM Cloud Object Storage for unstructured data management, and IBM Watson for AI and machine learning capabilities. The platform supports both hybrid and multi-cloud deployments, enabling organizations to maintain on-premises systems while leveraging cloud capabilities for specific use cases such as analytics, backup, and disaster recovery.
IBM Cloud for Healthcare addresses critical industry challenges through specialized solutions. Clinical data integration is facilitated through FHIR-compliant APIs and data transformation services. Patient engagement is enhanced through secure portals and mobile applications. Population health management is supported through advanced analytics and predictive modeling capabilities. Research and development activities benefit from high-performance computing resources and collaborative research platforms.
The platform’s scalability enables organizations to start with specific use cases and expand their cloud footprint over time. This incremental approach reduces implementation risk while allowing organizations to realize value quickly. Built-in monitoring and management tools provide visibility into system performance, security posture, and compliance status, enabling proactive management of the healthcare IT environment.

Figure 2: IBM Cloud for Healthcare Implementation Process Flow
Step-by-Step Implementation Process
Step 1: Healthcare IT Assessment and Strategic Planning
Duration: 4-6 weeks | Key Stakeholders: CIO, IT Director, Clinical Leadership
The implementation journey begins with a comprehensive assessment of the current healthcare IT landscape. This phase involves cataloging existing systems, identifying integration points, and evaluating current infrastructure capacity and performance. Clinical workflow analysis is conducted to understand how technology supports patient care delivery and identify opportunities for improvement.
Strategic planning activities include defining cloud adoption objectives, establishing success metrics, and creating a multi-year roadmap for digital transformation. Risk assessment covers technical, operational, and regulatory considerations. Budget planning encompasses not only technology costs but also training, change management, and ongoing operational expenses.
Key Deliverables: Current state assessment report, cloud readiness evaluation, strategic roadmap, business case documentation, risk mitigation plan
Step 2: Compliance and Regulatory Framework Design
Duration: 3-4 weeks | Key Stakeholders: Compliance Officer, Legal Counsel, IT Security
Healthcare organizations must navigate complex regulatory requirements including HIPAA, HITECH, GDPR, and industry-specific regulations. This phase involves mapping regulatory requirements to IBM Cloud capabilities and designing governance frameworks to ensure ongoing compliance. Data classification schemes are established to identify protected health information and determine appropriate security controls.
Compliance architecture design includes access control frameworks, audit logging requirements, and data encryption standards. Business Associate Agreements are reviewed and updated to reflect cloud service relationships. Incident response procedures are developed specifically for cloud environments, including breach notification requirements and forensic capabilities.
Key Deliverables: Compliance framework document, data governance policies, security control matrix, updated Business Associate Agreements
Step 3: Infrastructure Architecture and Service Selection
Duration: 2-3 weeks | Key Stakeholders: Solution Architect, Infrastructure Team
Infrastructure design focuses on selecting appropriate IBM Cloud services to support healthcare workloads. Compute requirements are analyzed to determine the optimal mix of bare metal servers, virtual servers, and containerized environments. Storage architecture is designed to accommodate structured clinical data, medical imaging, and unstructured content while meeting performance and availability requirements.
Network architecture design includes connectivity options such as IBM Cloud Direct Link for secure, high-bandwidth connections to on-premises systems. Disaster recovery and business continuity requirements are translated into specific service configurations including geographic distribution and replication strategies.
Key Deliverables: Infrastructure architecture diagrams, service selection matrix, capacity planning documentation, network topology design
Step 4: Security Configuration and Identity Management
Duration: 3-4 weeks | Key Stakeholders: Security Team, Identity Management Team
Security implementation begins with establishing identity and access management frameworks that integrate with existing healthcare identity systems. Role-based access controls are configured to ensure clinical staff have appropriate access to patient information while maintaining security boundaries. Multi-factor authentication is implemented for administrative access and sensitive clinical applications.
Encryption configuration covers data at rest, data in transit, and data in use scenarios. Key management systems are established to maintain cryptographic keys according to healthcare security standards. Security monitoring and alerting systems are configured to detect potential threats and compliance violations.
Key Deliverables: Security configuration documentation, identity integration procedures, encryption key management policies, security monitoring dashboard
Step 5: Data Migration Strategy and Execution
Duration: 6-12 weeks | Key Stakeholders: Data Management Team, Clinical Informatics
Data migration represents one of the most critical and complex aspects of healthcare cloud implementation. The process begins with comprehensive data discovery and classification to understand the volume, variety, and sensitivity of information to be migrated. Data quality assessment identifies cleansing and transformation requirements to ensure information integrity during the migration process.
Migration execution follows a phased approach, typically starting with non-production environments and progressing to critical clinical systems. Data validation procedures ensure accuracy and completeness throughout the migration process. Rollback procedures are established to address potential issues during migration windows.
Key Deliverables: Data migration plan, transformation specifications, validation procedures, rollback protocols, migration success report
Step 6: Application Deployment and Integration
Duration: 8-16 weeks | Key Stakeholders: Application Teams, Integration Specialists
Application deployment encompasses both migration of existing healthcare applications and implementation of new cloud-native solutions. Containerization strategies are employed where appropriate to improve portability and scalability. Integration patterns are implemented to ensure seamless data flow between cloud and on-premises systems.
Clinical application deployment requires careful attention to workflow impacts and user experience considerations. Performance testing validates that applications meet clinical requirements for response time and availability. Integration testing ensures that clinical data flows correctly between systems and that clinical decision-making is not disrupted.
Key Deliverables: Application deployment procedures, integration configuration documentation, performance test results, user acceptance testing reports
Step 7: Testing, Validation, and User Training
Duration: 4-6 weeks | Key Stakeholders: Quality Assurance, Training Team, Clinical Staff
Comprehensive testing validates all aspects of the IBM Cloud healthcare implementation including functional testing, performance testing, security testing, and disaster recovery testing. Clinical workflow testing ensures that patient care processes function correctly in the new environment. Regulatory compliance testing validates that all security and privacy controls function as designed.
User training programs are developed and delivered to ensure clinical and administrative staff can effectively use the new cloud-based systems. Training materials are customized for different user roles and include both technical training and clinical workflow training. Change management activities help organizations adapt to new processes and technologies.
Key Deliverables: Test execution reports, user training materials, change management plan, readiness assessment
Step 8: Go-Live Support and Optimization
Duration: 2-4 weeks intensive, ongoing optimization | Key Stakeholders: All Teams
Go-live activities include final system checks, cutover procedures, and intensive monitoring during the initial production period. Command center operations provide real-time support during the transition to ensure any issues are quickly identified and resolved. Performance monitoring validates that systems meet clinical requirements under production workloads.
Post-implementation optimization focuses on fine-tuning system performance, adjusting capacity based on actual usage patterns, and implementing additional automation to reduce operational overhead. Lessons learned documentation captures insights for future implementations and ongoing system management.
Key Deliverables: Go-live checklist, cutover procedures, performance optimization recommendations, lessons learned report
Figure 3: Global IBM Cloud for Healthcare Implementation Examples
Real-World Case Studies from Different Countries
Japan: University of Fukui Hospital – Digital Transformation Excellence
Implementation Overview
University of Fukui Hospital in Japan exemplifies successful healthcare digital transformation through IBM Cloud implementation. Founded in 1983 with 600 beds and 1,600 employees, the hospital embarked on a multi-phase journey beginning in 2006 to modernize its IT infrastructure and improve patient care delivery.
Technical Implementation
The hospital implemented a comprehensive hybrid cloud solution utilizing IBM Cloud Bare Metal Servers, IBM Cloud Object Storage, IBM Power Systems Virtual Server, and IBM Spectrum Protect. The infrastructure provides 24/7 availability with robust disaster recovery capabilities. Electronic health records were successfully migrated to the cloud platform, enabling access from any location while maintaining security and compliance.
Quantifiable Results
| Metric | Before Implementation | After Implementation | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-premises Servers | 100+ physical servers | 30 physical servers | 70% reduction |
| System Availability | Business hours only | 24/7/365 | Continuous availability |
| Operational Staff Load | High maintenance burden | Significantly reduced | 60% reduction in admin tasks |
| Data Access | On-site only | Anywhere, anytime | Complete mobility |
Strategic Outcomes
According to Associate Professor Yoshinori Yamashita from the Department of Medical Informatics, “The purpose for digitalization is not managing the machines. It is most important to provide the environment to use the data.” The implementation enabled the hospital to optimize data management without over-extending on-premises capacity, eliminate machine room requirements, and establish robust business continuity planning.
Finland: Watson Health Center of Excellence
National Healthcare Innovation Initiative
Finland’s partnership with IBM represents a national-level commitment to healthcare innovation through cognitive computing. Established in 2016, the Watson Health Center of Excellence in Helsinki serves as the first Nordic Healthcare Competence Center, focusing on personalized medicine and population health management.
Implementation Scope
The Finnish implementation encompasses Watson Health Cloud capabilities designed to restructure and digitize the national healthcare system. The platform integrates with Finland’s existing healthcare infrastructure while providing advanced analytics, clinical decision support, and research capabilities. The center focuses on utilizing Finland’s comprehensive health data to improve patient outcomes and advance medical research.
Key Capabilities Deployed
- Watson Health Cloud for national health data integration
- Cognitive computing for clinical decision support
- Population health analytics and monitoring
- Personalized medicine research platforms
- Healthcare innovation development environment
Strategic Impact
The Finnish implementation demonstrates how national healthcare systems can leverage IBM Cloud for Healthcare to drive innovation while maintaining patient privacy and data security. The center serves as a model for other Nordic countries and provides insights into large-scale healthcare transformation initiatives.
Canada: NexJ Health – Senior Care Innovation
Addressing Social Isolation Through Technology
NexJ Health’s implementation of IBM Cloud demonstrates innovative approaches to addressing healthcare challenges beyond traditional clinical care. The organization developed a digital platform specifically designed to combat loneliness among seniors, utilizing IBM Cloud infrastructure to provide scalable, secure services.
Technical Solution
The platform leverages IBM Cloud’s PaaS capabilities to deliver virtual social interactions, health monitoring, and care coordination services. The solution integrates with existing healthcare systems while providing new capabilities for remote patient engagement and social wellness monitoring.
Implementation Benefits
- Scalable infrastructure supporting thousands of senior users
- Secure patient data management and privacy protection
- Integration with existing healthcare provider systems
- Real-time monitoring and alert capabilities
- Cost-effective delivery of innovative social care services
Healthcare Innovation Impact
The NexJ Health implementation illustrates how IBM Cloud for Healthcare enables innovative service delivery models that address broader determinants of health. The platform’s success demonstrates the potential for cloud technology to support holistic approaches to patient care and wellness.
India: iKure and Apollo Hospitals – AI-Powered Cardiac Care
Predictive Analytics for Clinical Decision Making
The collaboration between iKure and IBM Cloud represents advancement in AI-powered healthcare delivery in India. iKure deployed IBM Cloud Pak and Watson AI capabilities to develop and deploy predictive models for cardiac care, demonstrating the potential for artificial intelligence to improve clinical outcomes in resource-constrained environments.
Technical Implementation
The solution utilizes IBM Watson AI integrated with IBM Cloud Pak for Data to analyze patient information and predict cardiac risk factors. The platform processes multiple data streams including vital signs, laboratory results, and medical history to provide real-time clinical decision support to healthcare providers.
Apollo Hospitals Integration
Apollo Hospitals, one of India’s leading healthcare providers, has integrated IBM Watson capabilities across multiple facilities. The implementation includes clinical decision support systems, medical imaging analysis, and patient care optimization tools that enhance the quality of care delivery across the hospital network.
Measurable Clinical Outcomes
| Outcome Metric | Improvement | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac Risk Prediction Accuracy | 85% accuracy rate | Earlier intervention and prevention |
| Clinical Decision Time | 40% reduction | Faster patient care delivery |
| Treatment Plan Optimization | 25% improvement | Better patient outcomes |
Scalability and Accessibility
The IBM Cloud implementation enables these AI-powered capabilities to be deployed across multiple healthcare facilities, extending advanced clinical decision support to underserved areas. The cloud-based delivery model reduces infrastructure requirements while providing access to sophisticated healthcare analytics.
Figure 4: IBM Cloud for Healthcare Security and Compliance Framework
Security and Compliance Framework
Comprehensive Security Architecture
IBM Cloud for Healthcare implements a multi-layered security framework designed specifically for healthcare organizations’ stringent requirements. The platform provides built-in security controls that address HIPAA, HITECH, GDPR, and other regulatory frameworks while maintaining the flexibility needed for healthcare innovation.
The security architecture encompasses multiple domains including identity and access management, data protection, network security, and compliance monitoring. Identity management integrates with existing healthcare directory services while providing enhanced authentication capabilities including multi-factor authentication and risk-based access controls. Role-based access controls ensure that clinical staff have appropriate access to patient information based on their clinical responsibilities and patient assignments.
Data protection measures include encryption at rest and in transit using industry-standard algorithms and key management systems. IBM Key Protect provides hardware security module-backed key management that meets healthcare encryption requirements. Data loss prevention capabilities monitor and control data movement to prevent unauthorized disclosure of protected health information.
Network security includes virtual private cloud configurations, network segmentation, and dedicated connectivity options through IBM Cloud Direct Link. Security groups and network access control lists provide granular control over network traffic. Distributed denial of service protection and web application firewalls protect against external threats.
Compliance monitoring provides continuous assessment of security posture and regulatory compliance status. IBM Cloud Security and Compliance Center provides centralized visibility into security configurations and compliance violations. Automated remediation capabilities can address certain compliance issues without manual intervention.
Regulatory Compliance Capabilities
HIPAA compliance is built into the IBM Cloud for Healthcare platform through comprehensive Business Associate Agreements, administrative safeguards, physical safeguards, and technical safeguards. Audit logging captures all access to protected health information with immutable log storage to support compliance investigations and reporting requirements.
GDPR compliance capabilities include data subject rights management, privacy impact assessment tools, and data processing agreement templates. Data residency controls ensure that European patient data remains within appropriate geographic boundaries when required by local regulations.
Industry-specific certifications include SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, and FedRAMP authorizations that provide third-party validation of security controls. These certifications reduce the compliance burden on healthcare organizations by providing pre-validated security frameworks.
Incident Response and Forensics
Incident response capabilities include automated threat detection, security incident management workflows, and forensic investigation tools. Security information and event management integration provides real-time security monitoring and alerting. Incident response playbooks are customized for healthcare environments and include breach notification procedures that comply with regulatory requirements.
Digital forensics capabilities enable detailed investigation of security incidents while maintaining chain of custody requirements. Forensic imaging and analysis tools are available through IBM Cloud services, reducing the need for specialized on-premises forensic infrastructure.
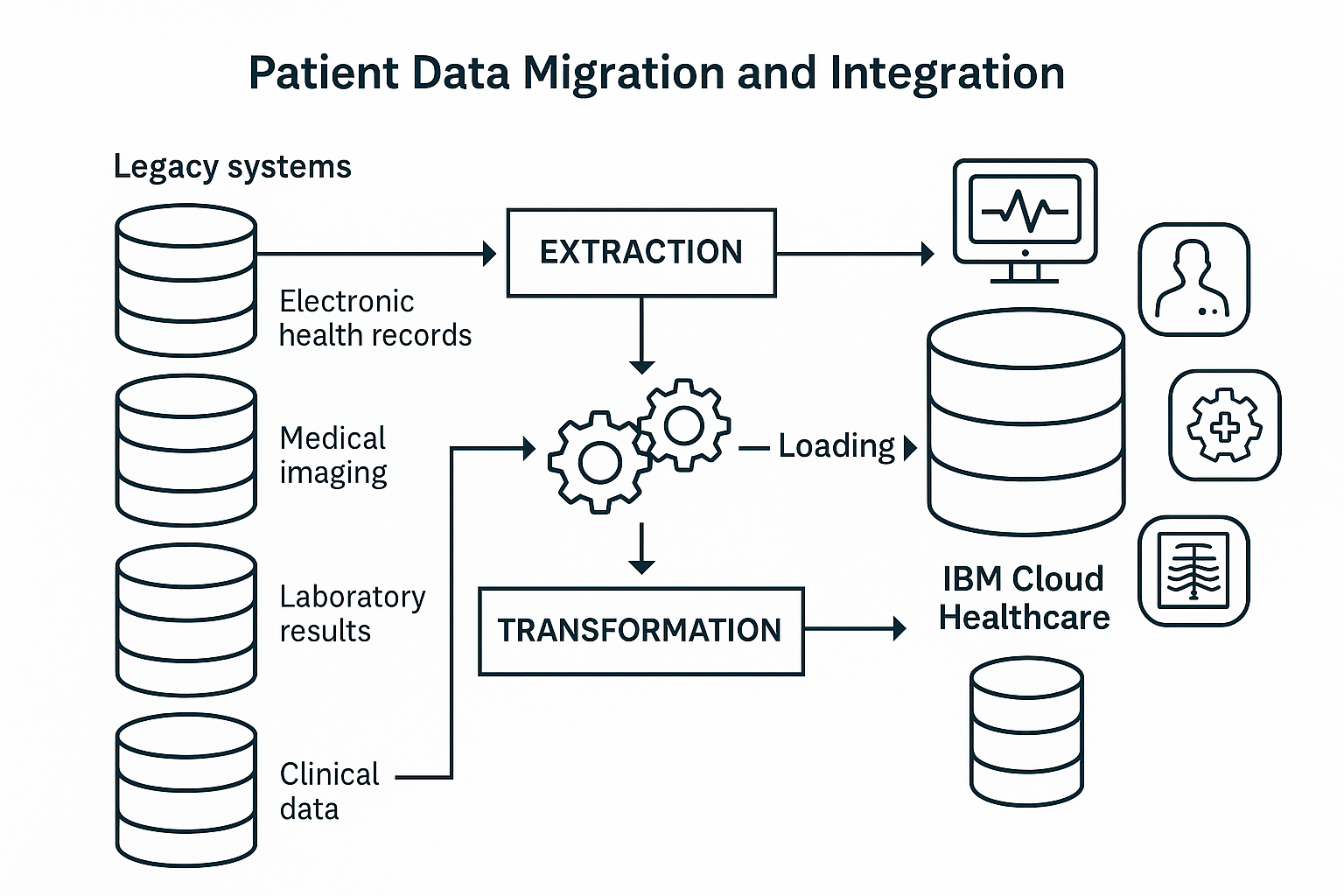
Figure 5: Healthcare Data Migration and Integration Workflow
Data Migration and Integration Strategies
Healthcare data migration requires specialized approaches that address the unique characteristics of clinical information including structured data from electronic health records, unstructured clinical notes, medical images, and real-time monitoring data. The migration strategy must ensure data integrity, maintain patient safety, and minimize disruption to clinical operations.
Pre-migration activities include comprehensive data discovery to catalog all healthcare information assets, data quality assessment to identify cleansing requirements, and dependency mapping to understand relationships between different data elements. Data classification identifies protected health information and determines appropriate security controls during migration.
Migration execution follows a phased approach that typically begins with non-production environments and historical data before progressing to active clinical systems. Real-time data synchronization ensures that clinical operations can continue during migration windows. Validation procedures include automated data quality checks and clinical review of migrated information to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Clinical System Integration
Integration architecture focuses on maintaining interoperability between cloud-based systems and existing healthcare applications. FHIR-compliant APIs provide standardized interfaces for clinical data exchange. HL7 message processing ensures compatibility with existing healthcare information systems.
Real-time integration patterns support clinical workflows that require immediate data availability including laboratory results, vital signs monitoring, and clinical decision support. Batch integration processes handle bulk data transfers such as medical imaging and historical record synchronization.
Master data management ensures consistent patient identification and data quality across integrated systems. Patient matching algorithms address the challenge of maintaining accurate patient records across multiple systems and data sources.
Performance Optimization
Performance optimization focuses on ensuring that cloud-based systems meet clinical requirements for response time and availability. Caching strategies reduce latency for frequently accessed clinical information. Content delivery networks improve performance for medical imaging and other large data files.
Database optimization includes indexing strategies specific to healthcare queries, query optimization for clinical reporting, and capacity planning based on clinical usage patterns. Monitoring and alerting provide visibility into system performance and enable proactive management of potential issues.
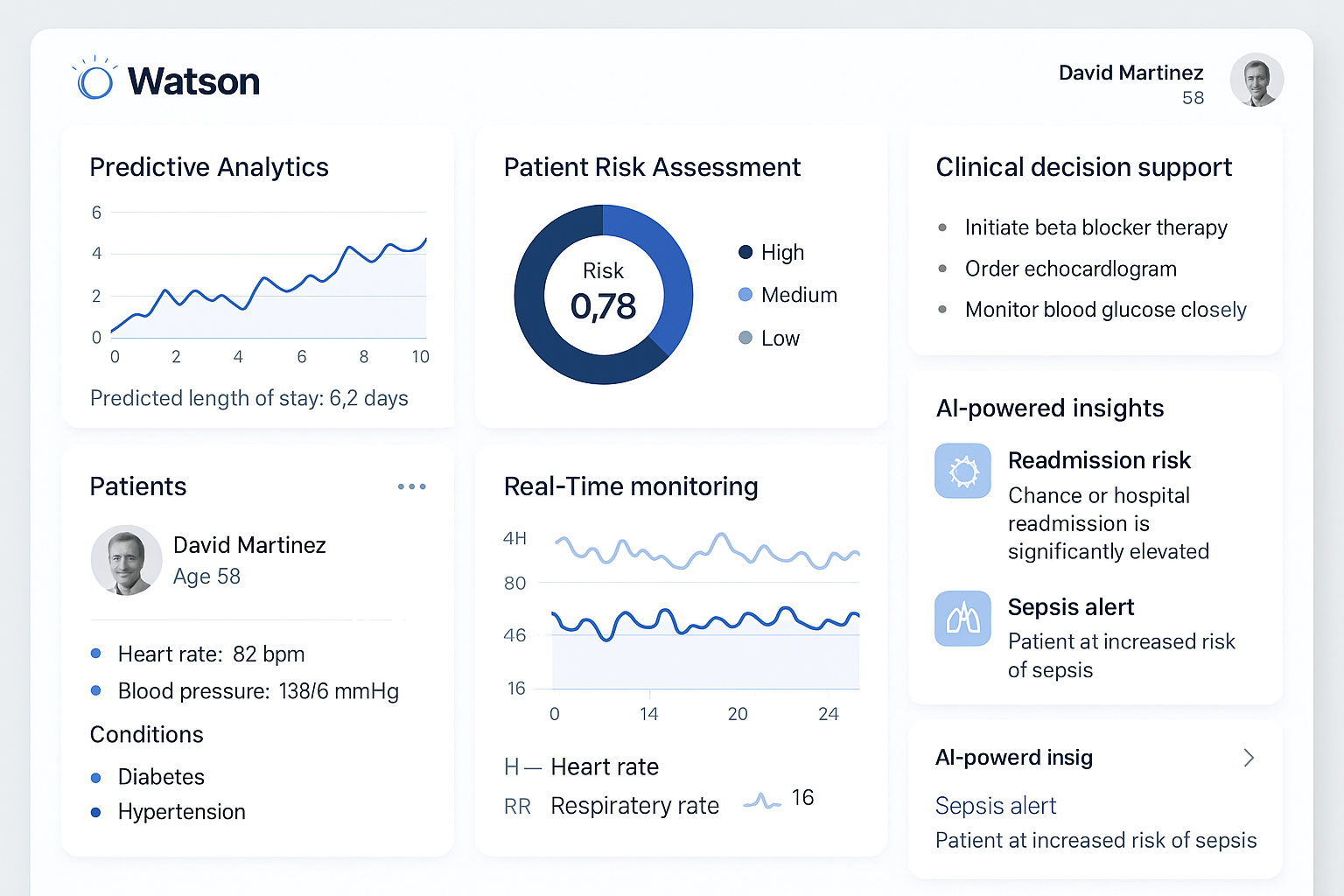
Figure 6: IBM Watson Health Analytics Dashboard for Clinical Decision Support
Future Outlook and Recommendations
Strategic Recommendations for Healthcare Organizations
Healthcare organizations should approach IBM Cloud for Healthcare implementation as a strategic transformation initiative rather than a tactical technology deployment. Success requires strong executive sponsorship, comprehensive change management, and a phased approach that demonstrates value while building organizational capabilities.
Future developments in IBM Cloud for Healthcare will likely focus on enhanced artificial intelligence capabilities, expanded interoperability standards, and advanced analytics for population health management. Organizations should plan for these capabilities by establishing data governance frameworks and building analytics competencies within their teams.
The continued evolution of healthcare regulations will require ongoing attention to compliance and security capabilities. Organizations should establish processes for monitoring regulatory changes and updating their cloud configurations accordingly. Partnership with IBM and other technology providers will be essential for staying current with regulatory requirements and best practices.
Investment in training and change management will continue to be critical success factors for healthcare cloud implementations. Organizations should develop comprehensive training programs that address both technical skills and clinical workflow changes. Change management activities should focus on demonstrating the clinical value of cloud-based systems and addressing concerns about technology adoption.
The healthcare industry’s increasing focus on value-based care and population health management will drive demand for advanced analytics and predictive modeling capabilities. Organizations should plan their IBM Cloud for Healthcare implementations to support these future requirements through scalable data architectures and analytics platforms.
Recommended Implementation Timeline
Months 1-3: Assessment, planning, and design phases
Months 4-9: Infrastructure deployment and security configuration
Months 10-15: Data migration and application deployment
Months 16-18: Testing, training, and go-live preparation
Months 19-24: Production deployment and optimization
This comprehensive guide provides healthcare organizations with the knowledge and strategies needed to successfully implement IBM Cloud for Healthcare solutions, drawing from proven methodologies and real-world success stories from leading healthcare institutions worldwide.
