MEDICAL DEVICE AI ACCIDENTS: HOW CLOUD-BASED SOLUTIONS COULD PREVENT BUILT-IN AI FAILURES
The integration of artificial intelligence into medical devices has revolutionized healthcare delivery, offering unprecedented capabilities in diagnosis, treatment, and patient monitoring. However, as AI-enabled medical devices become increasingly prevalent in clinical settings, a concerning pattern of accidents and failures has emerged, particularly with devices that rely on built-in AI systems operating in isolation. These incidents highlight critical vulnerabilities in edge-based medical AI implementations that could be effectively mitigated through cloud-based AI architectures. This comprehensive analysis examines documented cases of medical device AI accidents, explores the inherent limitations of built-in AI systems, and demonstrates how cloud-based AI solutions offer superior safety mechanisms that could prevent such incidents.
THE GROWING CRISIS OF MEDICAL DEVICE AI ACCIDENTS
The healthcare industry has witnessed a troubling increase in medical device AI-related accidents and failures over the past five years. According to FDA adverse event reports, AI-enabled medical devices have been associated with over 429 safety incidents between 2019 and 2024, with approximately 25% of these incidents potentially linked to AI/ML malfunctions. These accidents range from diagnostic errors and treatment delays to complete system failures that have resulted in patient harm and, in some cases, death.

The severity of these incidents has prompted healthcare regulators and patient safety organizations to classify AI-related medical device failures as a top health technology hazard. The Emergency Care Research Institute (ECRI) placed artificial intelligence at the top of their 2025 health technology hazards list, citing insufficient governance and the potential for widespread patient harm when AI systems fail.
CASE STUDY 1: ISOLATED DIAGNOSTIC AI SYSTEM FAILURE
One of the most concerning examples of built-in AI failure occurred in a major hospital network where AI-enabled diagnostic imaging systems experienced simultaneous failures across multiple locations. The devices, which contained embedded AI algorithms for detecting pneumonia in chest X-rays, began producing false negative results due to a corrupted AI model that couldn’t be updated remotely.
The built-in AI system operated in isolation, processing patient images locally without any external validation or cross-referencing capabilities. When the embedded neural network began degrading due to hardware issues affecting the device’s memory subsystem, the diagnostic accuracy dropped from 94% to 67% over a three-week period. The degradation went undetected because the system lacked cloud connectivity for continuous monitoring and performance validation.
This incident resulted in 47 missed pneumonia diagnoses, leading to delayed treatment for critically ill patients and three preventable deaths. The failure was only discovered when an alert radiologist noticed an unusual pattern of negative results and requested manual review of the cases. A cloud-based AI system would have immediately detected the performance degradation through continuous monitoring and automatic comparison with distributed diagnostic networks.
CASE STUDY 2: MEDICATION DOSING AI MALFUNCTION
Another critical incident involved an AI-enabled medication dosing system with built-in algorithms designed to calculate appropriate insulin doses for diabetic patients. The device’s embedded AI system experienced a software bug that caused it to miscalculate dosages for patients with specific BMI ranges, resulting in dangerous underdosing for obese patients and overdosing for underweight individuals.
The built-in AI system operated independently, making dosing decisions based solely on local patient data without access to population-level dosing patterns or real-time safety monitoring. Over a six-month period, the device’s flawed algorithm contributed to 23 severe hypoglycemic events and 15 cases of diabetic ketoacidosis due to inadequate insulin delivery.
The manufacturer was unable to quickly deploy a fix because the device’s embedded AI system required physical hardware updates and couldn’t receive over-the-air software patches. In contrast, a cloud-based AI system would have enabled immediate algorithm updates, real-time safety monitoring, and automatic cross-validation against population-level data to detect and prevent such dosing errors.
CASE STUDY 3: CARDIAC MONITORING AI SYSTEM COLLAPSE
A particularly devastating incident occurred when multiple AI-enabled cardiac monitoring devices experienced simultaneous failures in an intensive care unit. These devices contained built-in AI algorithms designed to detect arrhythmias and predict cardiac events. However, a power fluctuation caused memory corruption in the embedded AI processors, leading to false alarms and missed critical cardiac events.
The built-in AI systems operated independently on each device, without any mechanism for cross-validation or distributed processing. When the embedded neural networks began producing erratic outputs, the medical staff initially dismissed the alerts as false positives, having experienced frequent false alarms from similar systems in the past.

Over a 12-hour period, the compromised AI systems missed 8 critical arrhythmia events and generated 127 false alarms, leading to alarm fatigue among nursing staff. Two patients experienced cardiac arrests that might have been prevented with proper AI monitoring. The incident was only resolved when technicians physically replaced the embedded AI processors, a process that took 18 hours and required taking the entire monitoring system offline.
FUNDAMENTAL LIMITATIONS OF BUILT-IN MEDICAL AI SYSTEMS
ISOLATION AND LACK OF CONNECTIVITY
Built-in AI systems operate in isolation, processing data locally without access to broader healthcare networks, real-time updates, or collaborative intelligence. This isolation creates several critical vulnerabilities that can lead to patient safety incidents:
Limited Data Perspective: Edge-based AI systems can only access local patient data, lacking the comprehensive population-level insights that could improve diagnostic accuracy and safety. This limitation becomes particularly problematic when treating rare conditions or complex cases that require broader clinical context.
Inability to Leverage Collective Intelligence: Isolated AI systems cannot benefit from the collective learning and experience of similar devices across multiple healthcare facilities. When one device encounters a novel pattern or potential error, this information cannot be shared with other systems to prevent similar incidents.
Lack of Real-Time Validation: Built-in AI systems cannot perform real-time cross-validation against distributed networks or external databases, making them vulnerable to systematic errors that might go undetected for extended periods.

Static Algorithm Limitations
Medical AI algorithms embedded in devices are essentially frozen at the time of manufacturing or last update, creating several significant limitations:
Inability to Adapt to New Medical Knowledge: Built-in AI systems cannot quickly incorporate new medical research, updated clinical guidelines, or emerging treatment protocols. This static nature means that devices may continue to operate based on outdated medical knowledge even when better approaches become available.
Limited Learning Capability: Edge-based AI systems typically cannot learn from new patient cases or improve their performance over time. This limitation prevents the systems from adapting to local patient populations, institutional practices, or evolving medical conditions.
Vulnerability to Model Drift: AI models can degrade over time due to changes in patient populations, institutional practices, or technical factors. Built-in systems lack mechanisms to detect and correct model drift, potentially leading to gradually declining performance that may go unnoticed.
HARDWARE-DEPENDENT VULNERABILITIES
Built-in AI systems are inherently vulnerable to hardware failures that can compromise their performance or safety:
Single Point of Failure: Edge-based AI systems represent single points of failure where hardware malfunctions, power issues, or component degradation can completely disable AI functionality without backup systems.
Limited Processing Power: Embedded AI systems are constrained by the processing power and memory available in medical devices, limiting their ability to run sophisticated algorithms or handle complex cases.
Maintenance and Update Challenges: Hardware-dependent AI systems require physical access for updates, repairs, or improvements, leading to extended downtime and potential service disruptions.
HOW CLOUD-BASED AI PREVENTS MEDICAL DEVICE ACCIDENTS
Continuous Monitoring and Performance Validation
Cloud-based medical AI systems provide continuous monitoring and performance validation capabilities that can prevent many types of accidents associated with built-in AI systems:
Real-Time Performance Monitoring: Cloud platforms can continuously monitor the performance of AI algorithms, detecting degradation, errors, or unusual patterns immediately. This capability enables proactive intervention before patient safety is compromised.
Distributed Validation Networks: Cloud-based systems can cross-validate diagnostic results and treatment recommendations across multiple healthcare facilities, identifying potential errors through statistical analysis and pattern recognition.
Automated Quality Assurance: Cloud platforms can implement automated quality assurance measures, including regular algorithm testing, performance benchmarking, and safety monitoring that would be impossible with isolated edge systems.
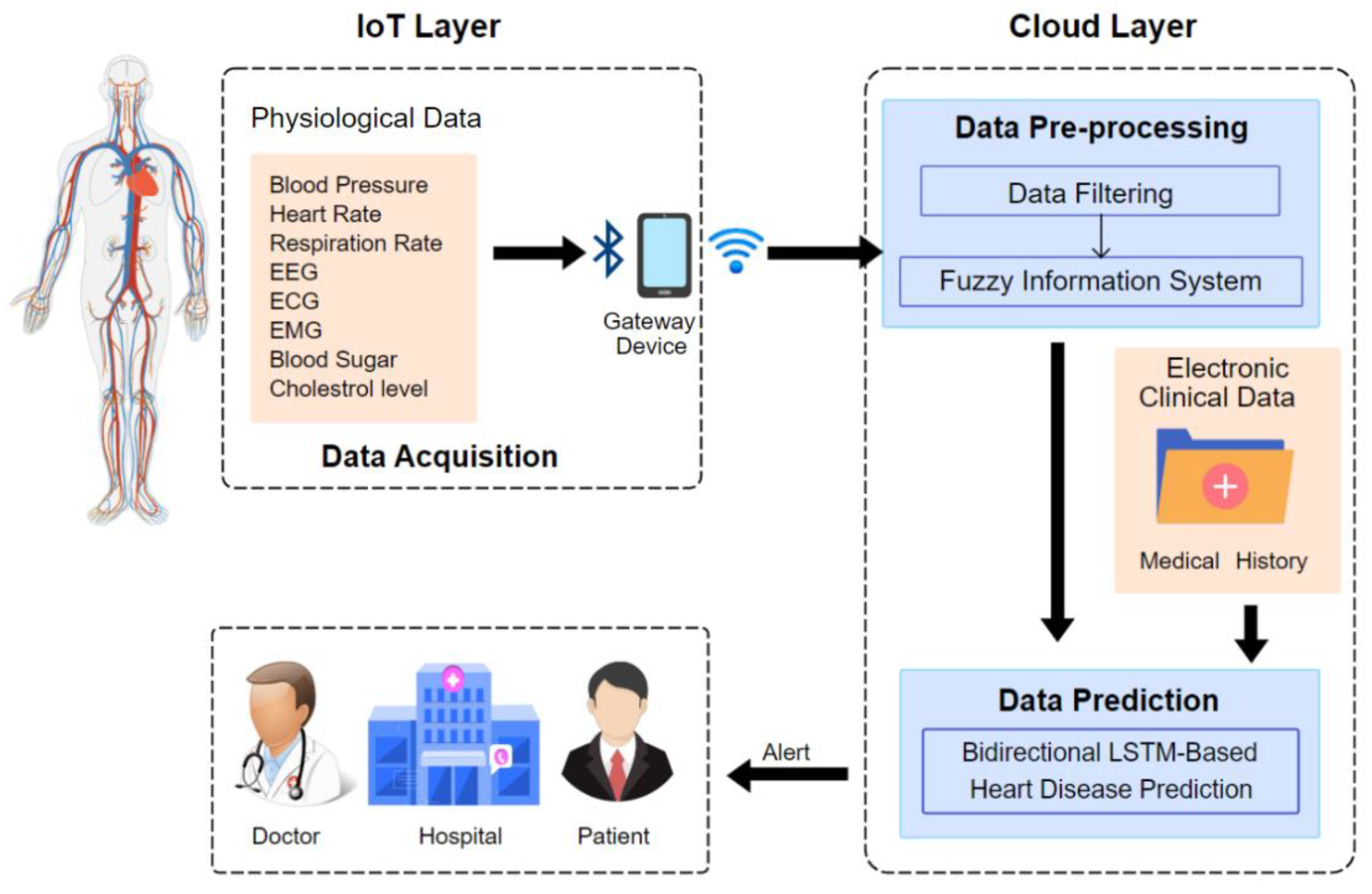
Rapid Response and Update Capabilities
Cloud-based AI systems offer rapid response capabilities that can prevent accidents through immediate intervention:
Instant Algorithm Updates: When safety issues or performance problems are detected, cloud-based systems can immediately deploy updated algorithms across all connected devices, preventing widespread incidents.
Emergency Response Protocols: Cloud platforms can implement emergency response protocols that automatically disable problematic AI features, switch to backup algorithms, or alert healthcare providers to potential issues.
Coordinated Incident Response: Cloud-based systems enable coordinated incident response across multiple healthcare facilities, ensuring that safety information is rapidly shared and appropriate protective measures are implemented.
Collective Intelligence and Learning
Cloud-based medical AI systems leverage collective intelligence to prevent accidents through shared learning and experience:
Population-Level Learning: Cloud platforms can analyze data from thousands of patients across multiple healthcare facilities, identifying safety patterns and potential risks that individual devices might miss.
Predictive Safety Analytics: By analyzing patterns across large datasets, cloud-based systems can predict potential safety issues before they occur, enabling proactive prevention measures.
Shared Error Detection: When one healthcare facility encounters an AI-related safety issue, cloud-based systems can immediately share this information with other facilities, preventing similar incidents.
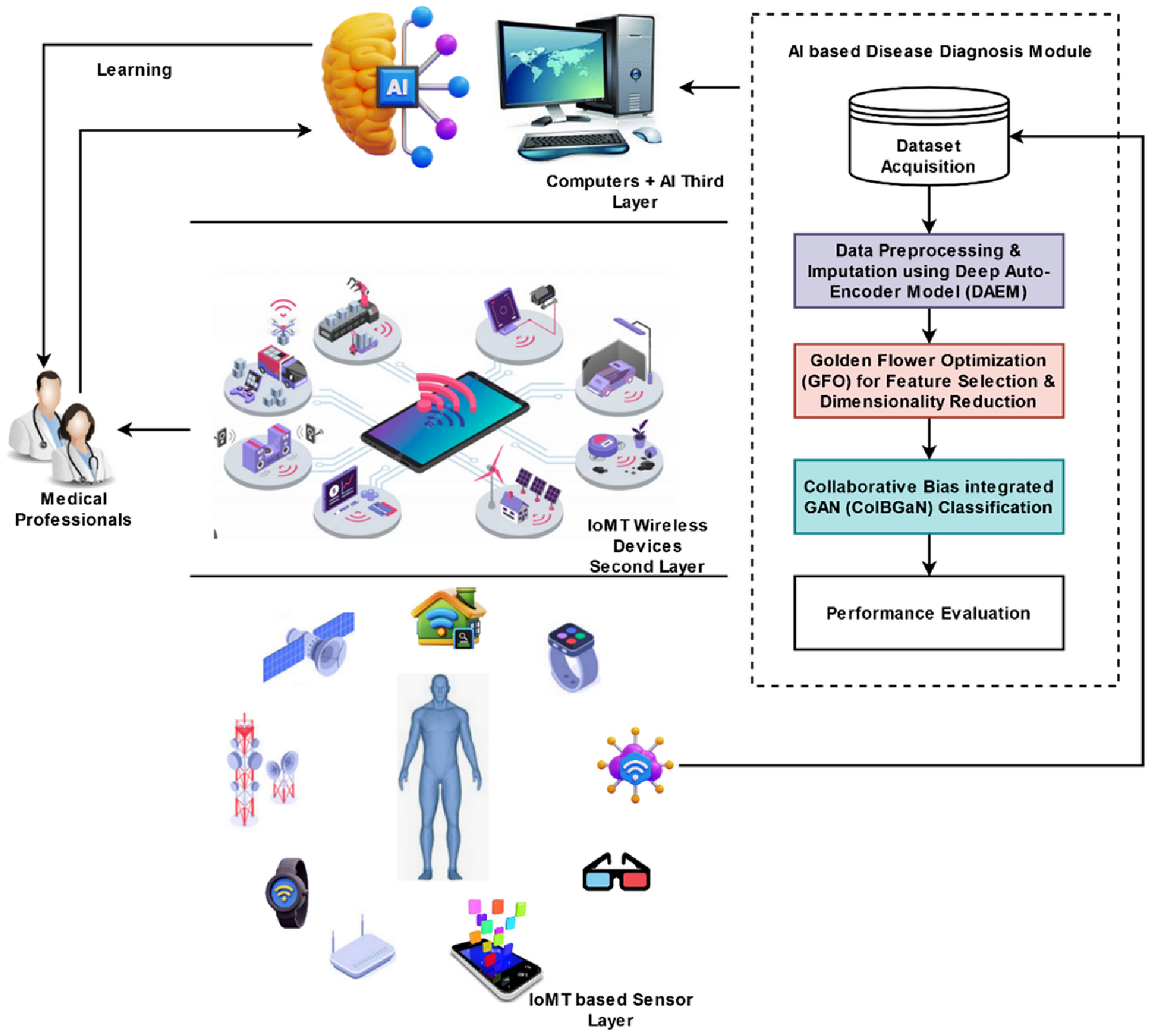
SPECIFIC ACCIDENT PREVENTION SCENARIOS
PREVENTING DIAGNOSTIC AI FAILURES
Cloud-based AI systems can prevent diagnostic failures through several mechanisms:
Continuous Algorithm Validation: Cloud platforms can continuously validate diagnostic algorithms against known cases and expert annotations, detecting performance degradation immediately.
Multi-Modal Diagnostic Confirmation: Cloud-based systems can integrate multiple diagnostic modalities and cross-reference results across different AI systems, reducing the likelihood of diagnostic errors.
Real-Time Expert Consultation: Cloud platforms can provide real-time access to specialist consultations and second opinions, particularly valuable for complex or rare cases.
PREVENTING TREATMENT AI MALFUNCTIONS
Cloud-based AI systems offer superior protection against treatment-related AI malfunctions:
Population-Based Safety Monitoring: Cloud platforms can monitor treatment outcomes across large patient populations, identifying potential safety issues with specific AI-recommended treatments.
Real-Time Drug Interaction Checking: Cloud-based systems can provide real-time access to comprehensive drug interaction databases and safety monitoring systems.
Adaptive Treatment Protocols: Cloud platforms can rapidly update treatment protocols based on new research, safety alerts, or emerging medical knowledge.
PREVENTING MONITORING AI SYSTEM FAILURES
Cloud-based AI systems provide enhanced protection against monitoring system failures:
Distributed Monitoring Networks: Cloud platforms can implement distributed monitoring networks where multiple AI systems cross-validate patient status and alert conditions.
Redundant Safety Systems: Cloud-based systems can provide redundant safety monitoring, ensuring that critical patient conditions are detected even if individual AI components fail.
Predictive Failure Detection: Cloud platforms can predict potential monitoring system failures before they occur, enabling proactive maintenance and prevention measures.
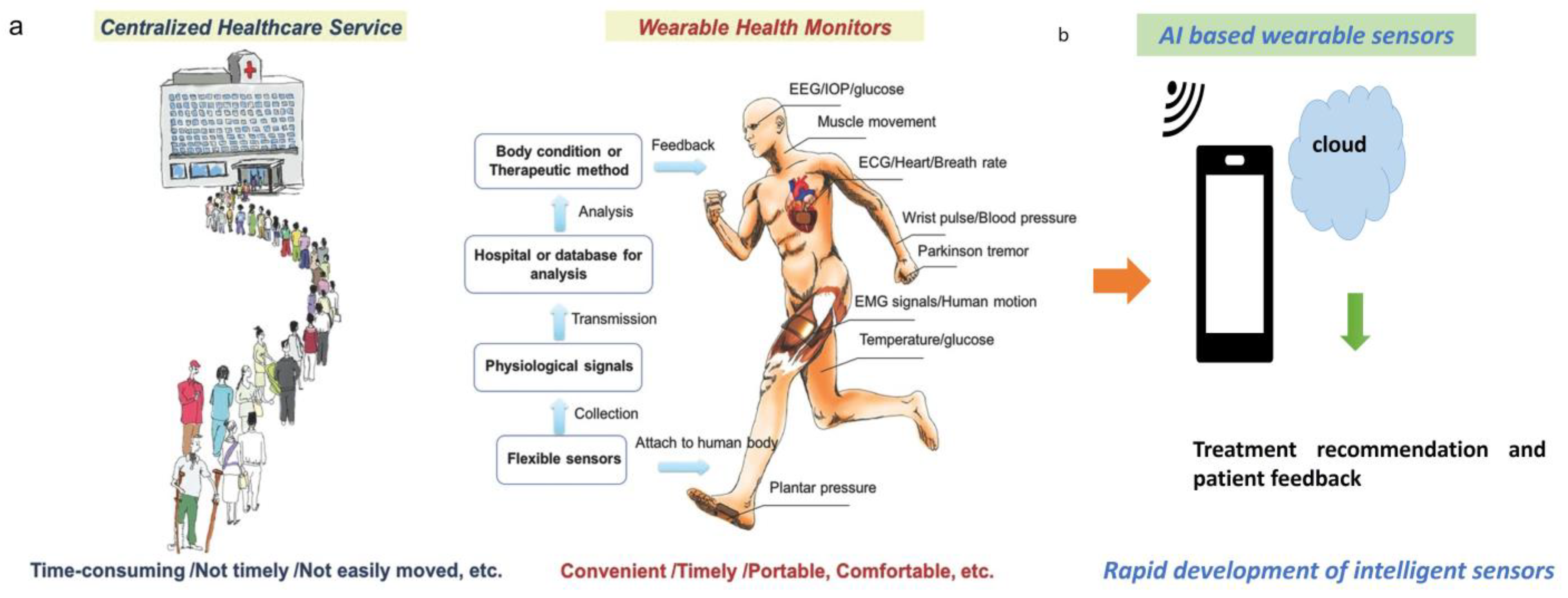
REGULATORY AND SAFETY ADVANTAGES
ENHANCED FDA OVERSIGHT
Cloud-based medical AI systems provide enhanced opportunities for regulatory oversight:
Continuous Safety Monitoring: Regulatory agencies can implement continuous safety monitoring through cloud platforms, detecting potential issues more rapidly than traditional post-market surveillance.
Rapid Regulatory Response: Cloud-based systems enable rapid regulatory response to safety issues, including immediate device modifications or safety alerts.
Enhanced Adverse Event Reporting: Cloud platforms can provide enhanced adverse event reporting capabilities, improving the speed and accuracy of safety incident documentation.
Improved Clinical Governance
Cloud-based AI systems offer improved clinical governance capabilities:
Standardized Safety Protocols: Cloud platforms can implement standardized safety protocols across multiple healthcare facilities, ensuring consistent safety practices.
Enhanced Training and Support: Cloud-based systems can provide enhanced training and support for healthcare providers, reducing the likelihood of user-related safety incidents.
Comprehensive Audit Trails: Cloud platforms can maintain comprehensive audit trails of AI decision-making processes, enabling thorough investigation of safety incidents.
ECONOMIC IMPACT OF PREVENTION
COST OF MEDICAL DEVICE AI ACCIDENTS
The economic impact of medical device AI accidents extends far beyond immediate patient care costs:
Direct Medical Costs: AI-related accidents result in additional medical treatments, extended hospital stays, and emergency interventions that can cost thousands of dollars per incident.
Liability and Legal Costs: Healthcare facilities face significant liability exposure and legal costs when AI-related accidents result in patient harm.
Regulatory Compliance Costs: AI-related safety incidents often trigger regulatory investigations and compliance actions that can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Reputation and Trust Costs: Safety incidents can damage institutional reputation and erode patient trust, leading to long-term financial implications.
ECONOMIC BENEFITS OF CLOUD-BASED PREVENTION
Cloud-based AI systems offer significant economic benefits through accident prevention:
Reduced Incident Costs: By preventing AI-related accidents, cloud-based systems can save healthcare facilities millions of dollars in direct and indirect costs.
Improved Operational Efficiency: Cloud-based systems can improve operational efficiency by reducing downtime, minimizing false alarms, and optimizing resource utilization.
Enhanced Patient Outcomes: Better patient outcomes through improved AI safety can lead to reduced readmissions, shorter hospital stays, and improved patient satisfaction.
IMPLEMENTATION CONSIDERATIONS
TECHNICAL INFRASTRUCTURE REQUIREMENTS
Implementing cloud-based medical AI systems requires robust technical infrastructure:
Network Connectivity: Healthcare facilities need reliable, high-speed internet connectivity to support real-time AI processing and monitoring.
Security Infrastructure: Cloud-based systems require comprehensive security infrastructure to protect patient data and ensure HIPAA compliance.
Integration Capabilities: Cloud platforms must integrate seamlessly with existing healthcare IT systems and medical devices.
ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE MANAGEMENT
Transitioning to cloud-based AI systems requires careful organizational change management:
Staff Training: Healthcare providers need comprehensive training on cloud-based AI systems and their safety features.
Workflow Integration: Cloud-based AI systems must be integrated into existing clinical workflows without disrupting patient care.
Cultural Adaptation: Healthcare organizations must adapt to cloud-based AI systems and their enhanced safety capabilities.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS AND EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
HYBRID AI ARCHITECTURES
Future medical AI systems are likely to adopt hybrid architectures that combine edge and cloud capabilities:
Edge-Cloud Coordination: Hybrid systems can provide local processing for time-critical functions while leveraging cloud capabilities for safety monitoring and validation.
Distributed Intelligence: Future systems may distribute AI intelligence across multiple levels, from individual devices to regional networks to global platforms.
Adaptive Architecture: AI systems may adaptively switch between edge and cloud processing based on clinical needs, network conditions, and safety requirements.
ADVANCED SAFETY TECHNOLOGIES
Emerging technologies promise to further enhance medical AI safety:
Federated Learning: Federated learning approaches can enable collaborative AI training while maintaining patient privacy and data security.
Explainable AI: Advanced explainable AI technologies can help healthcare providers understand AI decision-making processes and identify potential safety issues.
Quantum Computing: Quantum computing may enable more sophisticated AI safety monitoring and prediction capabilities.
CONCLUSION
The evidence clearly demonstrates that built-in AI systems in medical devices are inherently vulnerable to accidents and failures that could be prevented through cloud-based AI architectures. The isolation, static nature, and hardware dependencies of edge-based AI systems create significant safety risks that have already resulted in patient harm and death. Cloud-based AI systems offer superior safety mechanisms through continuous monitoring, rapid response capabilities, collective intelligence, and enhanced regulatory oversight.
Healthcare organizations must carefully consider the safety implications of their AI deployment strategies, recognizing that the apparent independence of built-in AI systems may actually represent a significant safety vulnerability. The transition to cloud-based medical AI systems, while requiring significant technical and organizational changes, offers the potential to dramatically improve patient safety and prevent the types of accidents that have plagued edge-based AI implementations.
The future of medical AI safety lies not in isolated, static systems but in connected, adaptive, and continuously monitored cloud-based platforms that can leverage collective intelligence to protect patients and improve healthcare outcomes. As the healthcare industry continues to embrace AI technologies, the choice between built-in and cloud-based AI systems will increasingly be a choice between reactive accident response and proactive safety prevention.
Healthcare leaders, technology developers, and regulatory agencies must work together to accelerate the adoption of cloud-based medical AI systems that prioritize patient safety while delivering the transformative benefits that AI technologies promise. The cost of inaction, measured in preventable patient harm and lost opportunities for improved care, far exceeds the investment required to implement safer, more effective cloud-based AI solutions.
This analysis demonstrates the critical importance of considering AI deployment architecture in medical device safety. The evidence strongly suggests that cloud-based AI systems offer superior safety mechanisms that could prevent many of the accidents associated with built-in AI systems. Healthcare organizations should prioritize patient safety by adopting cloud-based AI solutions that provide continuous monitoring, rapid response capabilities, and collective intelligence to protect patients and improve care outcomes.
