Using QR Codes for Device Authentication: A Comprehensive Security Guide
Introduction
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, secure and convenient authentication methods have become paramount for organizations worldwide. As traditional password-based systems prove increasingly inadequate against sophisticated cyber threats, Quick Response (QR) codes have emerged as a compelling solution for device authentication. This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted world of QR code authentication, examining its implementation strategies, security considerations, and best practices for modern enterprise environments.
The proliferation of QR codes during the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated their adoption across various industries, from contactless payments to digital menus. This widespread acceptance has naturally extended to authentication systems, where QR codes offer a bridge between the physical and digital worlds. Organizations are increasingly leveraging QR code authentication to streamline user experiences while maintaining robust security standards.
Understanding QR Code Authentication
QR code authentication represents a paradigm shift from traditional login mechanisms, utilizing two-dimensional barcodes to facilitate secure device access. Originally developed by Denso Wave in 1994 for automotive part tracking, QR codes have evolved into versatile tools capable of storing substantial amounts of data in compact, scannable formats. The technology’s inherent characteristics make it particularly suitable for authentication applications.
The fundamental principle underlying QR code authentication involves the generation of unique, time-sensitive codes that serve as temporary credentials for device access. These codes typically contain encrypted information that, when scanned by an authorized device, initiates a secure communication channel between the authenticating device and the target system. This process eliminates the need for manual credential entry while maintaining high security standards through cryptographic verification.
Core Components of QR Code Authentication Systems
Effective QR code authentication systems comprise several critical components working in concert to deliver secure access control. The authentication server generates unique QR codes containing encrypted session tokens, while mobile applications or dedicated scanning devices capture and process these codes. The verification process involves real-time communication between devices to validate credentials and establish authenticated sessions.
Types of QR Code Authentication Methods
Native App-Based Authentication
Native app-based QR code authentication leverages dedicated mobile applications to facilitate secure login processes. This method involves displaying a QR code on the target device or login interface, which users scan using their smartphone’s native app. The app processes the embedded URL or data, triggering an authentication workflow that validates the user’s identity through existing app credentials.

Popular implementations of native app authentication include services like WhatsApp Web, where users scan a QR code to link their mobile device with a web browser session. This approach offers excellent user experience for organizations with established mobile app ecosystems, as users can authenticate using familiar interfaces and existing credential stores. However, it requires users to have the specific app installed and properly configured on their mobile devices.
Passkey-Based Cross-Device Authentication
Passkey-based QR code authentication represents the cutting edge of secure authentication technology, implementing WebAuthn standards to enable cross-device authentication without requiring specialized applications. This method utilizes platform-level authenticators built into iOS and Android devices, leveraging biometric verification and cryptographic keys stored in secure hardware elements.

The passkey approach offers significant advantages in terms of phishing resistance and cross-platform compatibility. When a user scans a QR code for passkey authentication, their device establishes a Bluetooth connection with the target device to verify proximity, preventing remote attacks. The authentication process involves cryptographic challenge-response protocols that ensure the user’s private keys never leave their device, maintaining optimal security standards.
Time-Based One-Time Password (TOTP) Integration
QR codes frequently serve as the initial setup mechanism for TOTP authentication systems, where users scan a code to configure their authenticator applications. This integration combines the convenience of QR code deployment with the security benefits of rotating authentication tokens. Organizations can generate QR codes containing TOTP secret keys, allowing users to quickly establish secure authentication relationships with minimal manual configuration.
- Rapid deployment of two-factor authentication systems
- Standardized setup process across different authenticator applications
- Reduced user error in manual key entry
- Compatible with popular authenticator apps like Google Authenticator and Authy
Security Considerations and Risk Assessment
Common Security Vulnerabilities
While QR code authentication offers numerous advantages, organizations must carefully address potential security vulnerabilities to maintain system integrity. QR code replacement attacks represent a primary concern, where malicious actors physically replace legitimate codes with compromised versions that redirect users to phishing sites or malware distribution platforms.
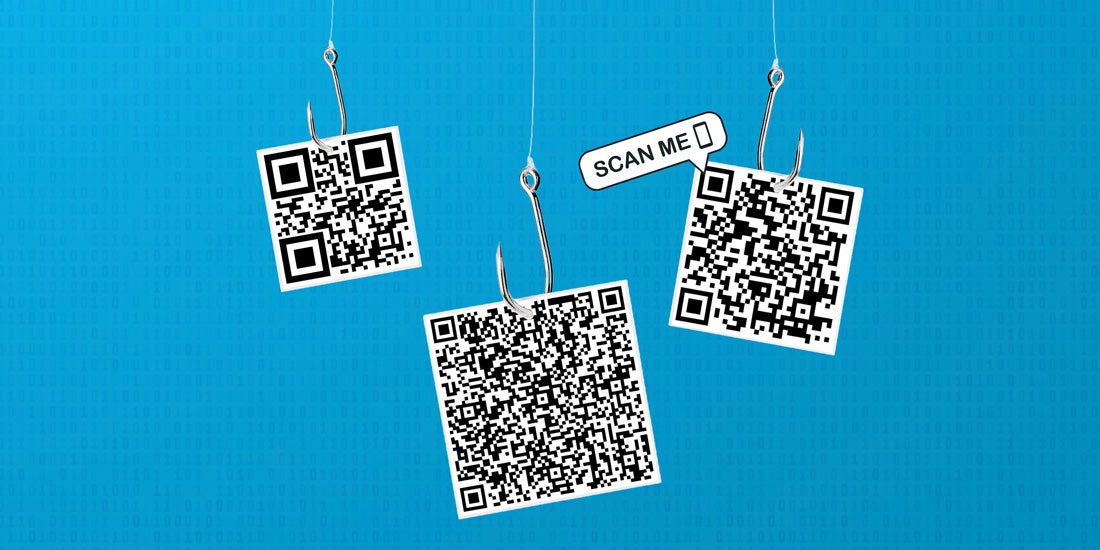

Network-based attacks pose another significant threat, particularly in environments where QR codes facilitate Wi-Fi network configuration or access control. Attackers may deploy rogue access points or manipulate QR codes to direct devices toward compromised networks, enabling data interception and unauthorized access to sensitive information. Organizations must implement comprehensive monitoring and validation systems to detect and prevent such attacks.
Implementation Security Best Practices
Establishing robust security foundations for QR code authentication requires implementing multiple layers of protection and validation mechanisms. Organizations should prioritize the use of reputable QR code generation platforms that incorporate security features such as encryption, expiration timers, and usage tracking. These platforms typically offer enhanced protection against common attack vectors while providing administrative oversight capabilities.

Time-based restrictions represent a critical security component, limiting QR code validity to short time windows that minimize exposure to unauthorized access attempts. Industry best practices recommend maximum validity periods of 120 seconds or less, with automatic refresh mechanisms that generate new codes before expiration. This approach significantly reduces the risk of man-in-the-middle attacks and unauthorized code reuse.
Implementation Strategies for Enterprise Environments
Infrastructure Requirements and Planning
Successful QR code authentication deployment requires careful infrastructure planning and system integration considerations. Organizations must evaluate their existing authentication systems, mobile device management policies, and network security frameworks to ensure seamless integration. The implementation process typically involves establishing secure code generation services, configuring mobile device policies, and training end users on proper authentication procedures.

Network infrastructure considerations include ensuring adequate bandwidth for real-time authentication verification, implementing secure communication channels between authentication servers and client devices, and establishing redundancy mechanisms to maintain service availability. Organizations should also consider the geographic distribution of their user base and implement content delivery networks or regional authentication servers to optimize performance and reduce latency.
User Experience Optimization
Creating intuitive user experiences while maintaining security standards requires balancing convenience with protection mechanisms. Organizations should provide clear guidance on QR code scanning procedures, implement progressive authentication flows that adapt to user behavior patterns, and offer alternative authentication methods for users who may not have compatible devices or scanning capabilities.
Training and support programs play crucial roles in successful deployment, particularly in organizations with diverse user populations or varying levels of technical expertise. Comprehensive training materials should cover proper scanning techniques, troubleshooting common issues, and security awareness topics such as recognizing potentially malicious QR codes. Regular refresher training ensures users maintain awareness of security best practices and emerging threats.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Industry Standards and Frameworks
Organizations implementing QR code authentication must navigate various regulatory frameworks and industry standards that govern authentication systems and data protection. The WebAuthn standard, developed by the World Wide Web Consortium and FIDO Alliance, provides comprehensive guidelines for implementing secure authentication systems that include QR code-based cross-device authentication mechanisms.
Compliance requirements vary significantly across industries and geographic regions, with healthcare organizations subject to HIPAA regulations, financial institutions governed by PCI DSS standards, and companies operating in Europe required to comply with GDPR data protection requirements. QR code authentication systems must incorporate appropriate data handling, encryption, and audit logging capabilities to meet these diverse regulatory obligations.
Privacy Considerations
Privacy protection represents a fundamental consideration in QR code authentication system design, particularly regarding the collection, storage, and processing of user authentication data. Organizations must implement privacy-by-design principles that minimize data collection, provide transparent disclosure of data usage practices, and offer users appropriate control over their authentication information.
- Minimize collection of personally identifiable information
- Implement data retention policies with automatic deletion
- Provide transparent privacy notices and user consent mechanisms
- Enable user control over authentication data and device linking
- Establish secure data transmission and storage protocols
Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies promises to enhance QR code authentication systems through improved fraud detection, behavioral analysis, and adaptive security measures. Machine learning algorithms can analyze authentication patterns to identify anomalous behavior, detect potential security threats, and automatically adjust security policies based on risk assessments.
Predictive analytics capabilities enable organizations to anticipate security threats and implement proactive protection measures. These systems can analyze historical authentication data to identify trends, predict potential attack vectors, and recommend security policy adjustments. As AI technology continues to advance, QR code authentication systems will likely incorporate more sophisticated intelligence capabilities to provide enhanced protection against evolving threats.
Blockchain and Distributed Authentication
Blockchain technology offers potential advantages for QR code authentication systems, particularly in environments requiring decentralized authentication verification and immutable audit trails. Distributed ledger systems can provide tamper-evident logging of authentication events, enable cross-organizational authentication federation, and support self-sovereign identity models where users maintain control over their authentication credentials.
The convergence of QR code authentication with blockchain technology may enable new use cases such as verifiable credential systems, decentralized identity networks, and smart contract-based access control mechanisms. These developments could significantly enhance security and user privacy while reducing dependence on centralized authentication infrastructure.
Best Practices and Recommendations
Operational Excellence
Achieving operational excellence in QR code authentication requires establishing comprehensive monitoring, maintenance, and incident response procedures. Organizations should implement real-time monitoring systems that track authentication success rates, identify potential security incidents, and provide visibility into system performance metrics. Regular security assessments and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities and validate security controls.
Change management processes ensure that system updates and modifications maintain security standards while improving functionality. Organizations should establish testing procedures for new features, maintain backup and recovery capabilities, and develop incident response plans that address potential security breaches or system failures. Regular review and updating of security policies ensure continued alignment with evolving threats and regulatory requirements.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement processes enable organizations to adapt their QR code authentication systems to changing requirements and emerging threats. Regular user feedback collection helps identify usability issues and opportunities for enhancement, while security monitoring data provides insights into attack patterns and system vulnerabilities.
Technology evolution requires ongoing evaluation of new authentication methods, security standards, and implementation approaches. Organizations should maintain awareness of industry developments, participate in security communities and working groups, and regularly assess their authentication systems against current best practices and emerging threats.
Conclusion
QR code authentication represents a significant advancement in secure access control technology, offering organizations the opportunity to enhance security while improving user experience. The successful implementation of QR code authentication systems requires careful consideration of security requirements, user needs, and operational constraints. Organizations that adopt comprehensive security practices, maintain awareness of emerging threats, and implement robust monitoring and response capabilities will be best positioned to realize the benefits of this innovative authentication approach.
As the technology continues to evolve, QR code authentication will likely become increasingly sophisticated, incorporating advanced security features and intelligence capabilities. Organizations should prepare for this evolution by establishing flexible authentication architectures that can adapt to new requirements and technologies. The investment in QR code authentication infrastructure today positions organizations for future success in an increasingly complex and demanding security landscape.
The journey toward secure, convenient authentication continues to evolve, with QR codes playing an increasingly important role in bridging traditional security requirements with modern user expectations. Organizations that embrace these technologies while maintaining focus on security fundamentals will create authentication systems that serve their users effectively while protecting valuable digital assets.
