MEDICAL DEVICE AI BUILT-IN VS MEDICAL DEVICE AI THROUGH THE CLOUD: A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF DEPLOYMENT ARCHITECTURES
The healthcare industry stands at the precipice of a technological revolution, where artificial intelligence (AI) has become the cornerstone of modern medical innovation. As healthcare providers and medical device manufacturers navigate the complex landscape of AI implementation, a critical decision emerges: should AI capabilities be embedded directly within medical devices (edge AI) or delivered through cloud-based platforms? This comprehensive analysis explores the fundamental differences, advantages, limitations, and strategic considerations of both approaches, providing healthcare professionals and technology decision-makers with the insights necessary to make informed choices about AI deployment in medical environments.

Understanding the Fundamental Architectures
Built-In Medical Device AI: Edge Computing Paradigm
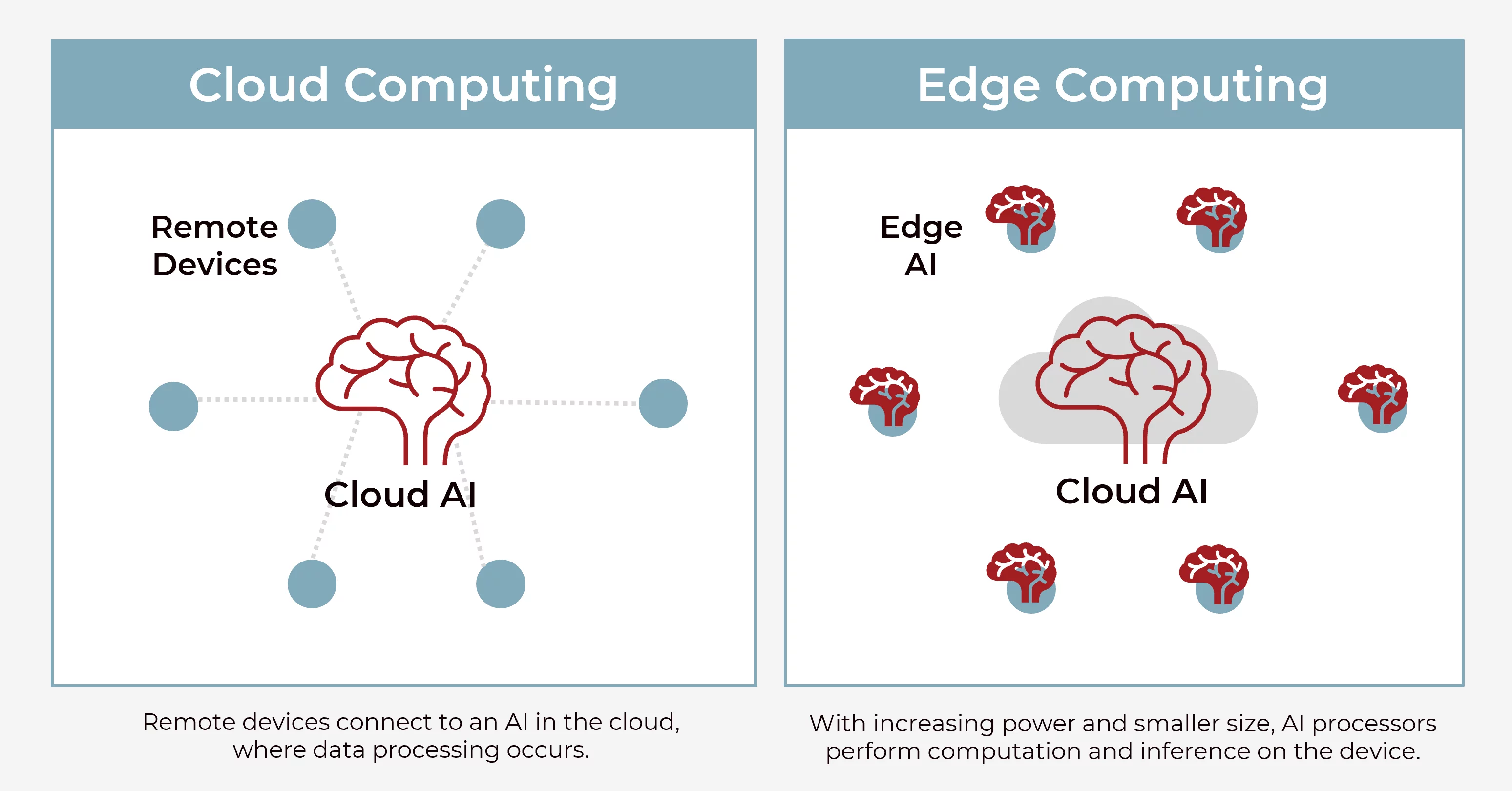
Built-in AI represents the edge computing approach to medical device intelligence, where artificial intelligence algorithms, machine learning models, and processing capabilities are embedded directly within the physical hardware of medical devices. This architecture creates self-contained intelligent systems capable of performing complex analytical tasks without requiring external connectivity or cloud infrastructure dependencies.
The edge AI approach involves integrating specialized processors, neural processing units (NPUs), and dedicated AI chips directly into medical equipment. These embedded systems run optimized AI models that have been specifically trained and compressed to operate within the computational and memory constraints of the device hardware. The result is a medical device that can perform real-time AI-powered analysis, decision-making, and automated responses independently of external networks.
Modern embedded AI medical devices utilize advanced semiconductor technologies, including ARM-based processors with integrated AI accelerators, NVIDIA edge computing platforms, and specialized medical-grade chips designed to meet stringent regulatory requirements while delivering high-performance AI capabilities. These systems often incorporate multiple layers of AI functionality, from basic sensor data processing to complex diagnostic algorithms and predictive analytics.
Cloud-Based Medical AI: Centralized Intelligence Platform
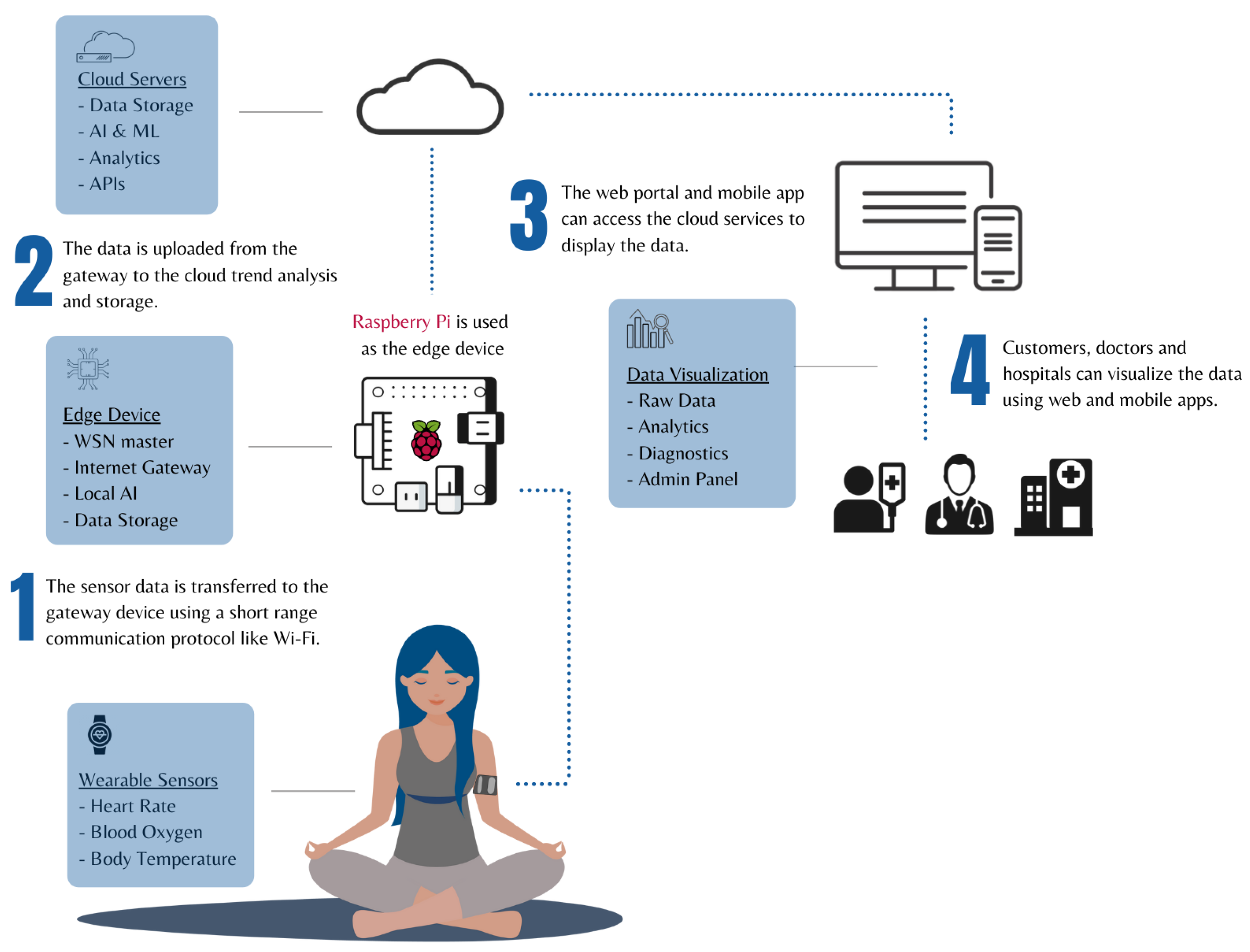
Cloud-based medical AI represents a fundamentally different architectural approach, where the intelligence and computational power reside in remote cloud infrastructure rather than within the medical devices themselves. In this model, medical devices function primarily as data collection and transmission endpoints, capturing patient information, sensor readings, and diagnostic data, then transmitting this information to cloud-based AI platforms for processing and analysis.
The cloud AI infrastructure typically consists of powerful server clusters, specialized AI processing units (GPUs, TPUs), and vast storage systems capable of handling enormous datasets and complex machine learning operations. These platforms offer virtually unlimited computational resources, enabling the deployment of sophisticated AI models that would be impossible to run on edge devices due to hardware constraints.
Cloud-based medical AI systems leverage major cloud platforms such as AWS HealthLake, Google Cloud Healthcare AI, Microsoft Azure Health Data Services, and IBM Watson Health, each offering specialized tools and services designed specifically for healthcare applications. These platforms provide comprehensive AI development environments, pre-trained medical models, and regulatory compliance frameworks that accelerate the deployment of AI-powered healthcare solutions.
Performance and Latency Considerations
Real-Time Processing Advantages of Built-In AI
One of the most compelling advantages of built-in medical device AI lies in its ability to deliver real-time processing capabilities with minimal latency. When AI algorithms are embedded directly within medical devices, data processing occurs instantaneously at the point of data generation, eliminating the delays associated with network transmission, cloud processing queues, and data return pathways.

In critical medical applications such as cardiac monitoring, emergency diagnostics, surgical robotics, and intensive care unit monitoring, millisecond delays can have profound implications for patient outcomes. Built-in AI systems can analyze electrocardiogram readings, detect arrhythmias, identify emergency conditions, and trigger automated responses within microseconds of data collection. This real-time capability is particularly crucial in scenarios where immediate medical intervention is required, such as automated defibrillator activation, emergency alert systems, or real-time surgical guidance applications.
The deterministic nature of edge processing also provides consistent performance characteristics, as built-in AI systems are not subject to network congestion, cloud server load variations, or internet connectivity fluctuations that can introduce unpredictable latencies in cloud-based systems. This predictability is essential for medical devices that must meet strict regulatory requirements for response times and reliability.
Cloud AI Processing Power and Computational Capabilities
While built-in AI excels in real-time processing, cloud-based medical AI platforms offer unprecedented computational capabilities that far exceed what individual medical devices can achieve. Cloud infrastructure can accommodate the most advanced AI models, including large language models, complex neural networks, and sophisticated machine learning algorithms that require enormous computational resources.
Cloud-based systems can process multiple data streams simultaneously, correlate information from hundreds or thousands of patients, identify population-level patterns, and perform complex analytics that would be impossible on individual edge devices. This capability is particularly valuable for applications such as epidemiological analysis, drug discovery research, population health management, and large-scale diagnostic pattern recognition.
The scalability of cloud computing allows medical AI systems to dynamically allocate computational resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak usage periods while maintaining cost efficiency during lower-demand periods. This flexibility enables healthcare organizations to deploy sophisticated AI capabilities without the substantial upfront hardware investments required for equivalent edge computing power.
Data Privacy and Security Implications
Edge AI Privacy Advantages
Built-in medical device AI offers inherent privacy advantages by processing sensitive patient data locally without transmitting information to external systems. This local processing approach aligns perfectly with healthcare privacy requirements, including HIPAA compliance, GDPR regulations, and other data protection frameworks that emphasize minimizing data exposure and maintaining patient confidentiality.

When medical data remains within the confines of the medical device and the immediate clinical environment, the attack surface for potential security breaches is significantly reduced. Edge AI systems eliminate many of the vulnerabilities associated with data transmission, cloud storage, and network-based attacks. Patient information never leaves the device, reducing exposure to potential interception, unauthorized access, or data breaches that could compromise patient privacy.
This local processing capability is particularly important for sensitive medical applications such as mental health monitoring, genetic analysis, reproductive health tracking, and other areas where patient privacy concerns are paramount. Healthcare providers can deploy AI-powered diagnostic and monitoring capabilities while maintaining complete control over patient data and ensuring compliance with the strictest privacy regulations.
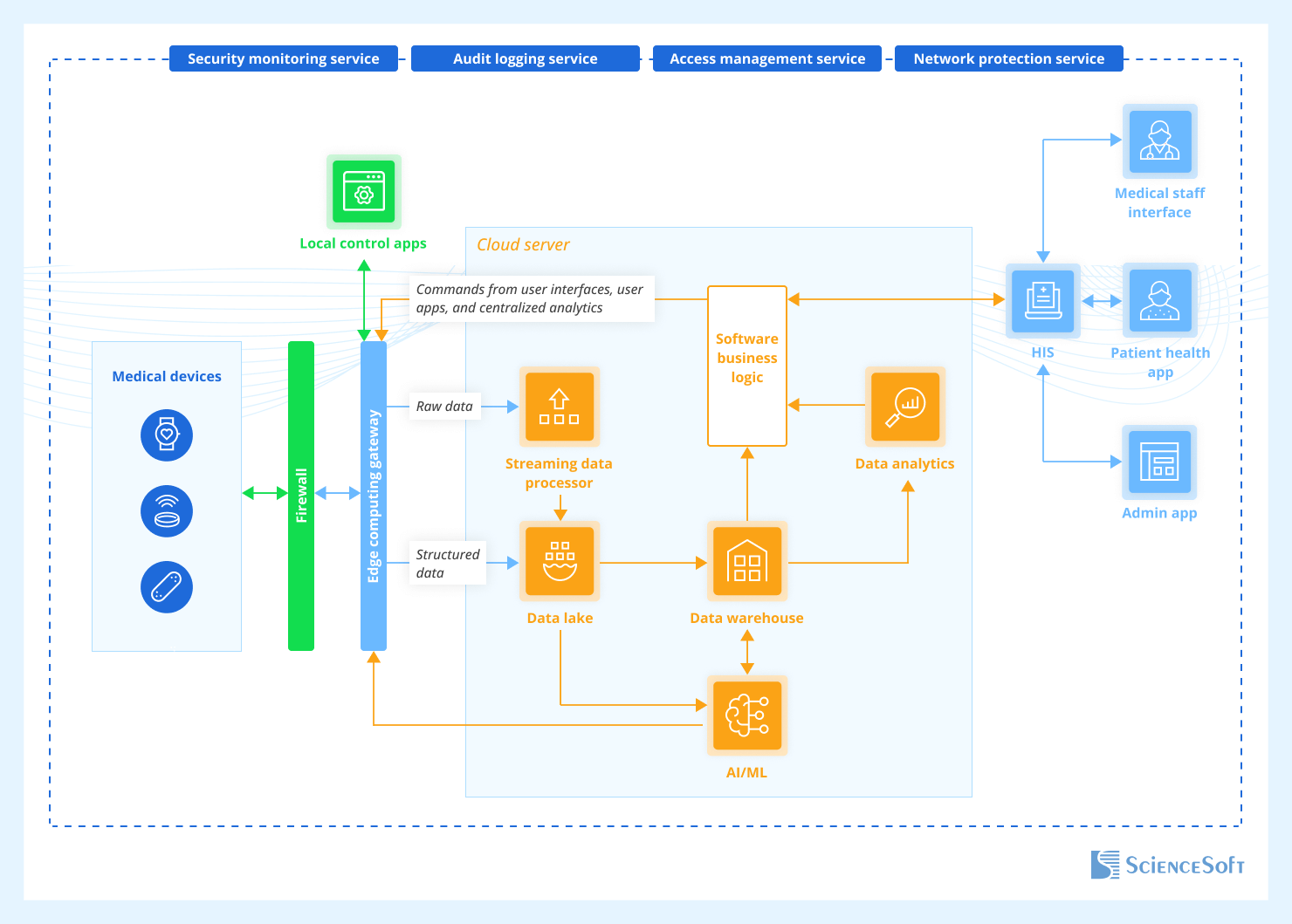
Cloud AI Security Infrastructure and Compliance
Cloud-based medical AI platforms, while requiring careful security implementation, offer comprehensive security infrastructures that individual healthcare organizations might find difficult or expensive to replicate independently. Major cloud providers invest billions of dollars annually in cybersecurity measures, employing dedicated security teams, advanced threat detection systems, and cutting-edge encryption technologies.
These platforms typically provide enterprise-grade security features including multi-factor authentication, end-to-end encryption, advanced access controls, comprehensive audit logging, and compliance certifications for healthcare-specific regulations. Cloud providers also offer specialized healthcare security services such as HIPAA-compliant infrastructure, medical-grade data encryption, and regulatory compliance monitoring tools.
However, cloud-based systems do introduce additional complexity in terms of data governance, security management, and regulatory compliance. Healthcare organizations must carefully evaluate cloud providers’ security practices, implement proper data governance policies, and ensure that all data handling practices meet applicable regulatory requirements. The shared responsibility model of cloud security means that while cloud providers secure the infrastructure, healthcare organizations remain responsible for properly configuring security settings and managing access controls.
Scalability and Update Management
Cloud AI Scalability and Model Updates
One of the most significant advantages of cloud-based medical AI lies in its inherent scalability and ability to continuously update and improve AI models. Cloud platforms can instantly deploy updated algorithms, incorporate new training data, and enhance AI capabilities across all connected devices simultaneously without requiring physical hardware modifications or manual device updates.

This scalability extends beyond computational resources to encompass data integration capabilities, multi-institutional collaboration, and global knowledge sharing. Cloud-based AI systems can aggregate data from thousands of medical devices, multiple healthcare institutions, and diverse patient populations, creating comprehensive datasets that enable more robust and generalizable AI models.
The continuous learning capabilities of cloud AI systems allow for real-time model improvement based on new data, emerging medical knowledge, and evolving clinical practices. As new medical research becomes available, treatment protocols evolve, or disease patterns change, cloud-based AI systems can be updated immediately to reflect the latest medical knowledge and best practices.
Cloud platforms also facilitate the rapid deployment of new AI applications and features. Healthcare organizations can access cutting-edge AI capabilities as soon as they become available, without waiting for hardware replacement cycles or complex device update procedures. This agility enables healthcare providers to stay current with the latest AI advances and continuously improve patient care delivery.
Built-In AI Update Limitations and Advantages
While built-in AI systems face certain limitations in terms of update frequency and model complexity, they offer important advantages in terms of system stability, regulatory compliance, and deployment predictability. Embedded AI systems typically undergo rigorous testing and validation procedures before deployment, ensuring that all AI models meet strict medical device regulatory requirements and performance standards.
The update process for built-in AI systems often involves comprehensive validation procedures, regulatory approvals, and careful change management processes that prioritize patient safety and system reliability over rapid deployment. While this approach may result in slower update cycles compared to cloud-based systems, it provides greater assurance of system stability and regulatory compliance.
Built-in AI systems also offer the advantage of version control and predictable performance characteristics. Healthcare providers know exactly which AI model version is running on each device, can predict system behavior with certainty, and maintain detailed documentation for regulatory compliance and quality assurance purposes.
Cost Considerations and Economic Impact
Initial Investment and Total Cost of Ownership
The economic implications of choosing between built-in and cloud-based medical AI extend far beyond initial purchase prices to encompass total cost of ownership, operational expenses, and long-term value considerations. Built-in AI medical devices typically require higher upfront investments due to the sophisticated hardware components, specialized processors, and embedded AI capabilities integrated into each device.
The initial cost premium for embedded AI capabilities can range from 20% to 100% above comparable non-AI devices, depending on the complexity of AI features and the sophistication of embedded processors. However, these higher upfront costs may be offset by lower ongoing operational expenses, reduced networking requirements, and elimination of cloud service subscription fees.
Cloud-based medical AI systems often have lower initial device costs since the intelligence resides in the cloud rather than embedded hardware. However, organizations must account for ongoing cloud service fees, data transmission costs, network infrastructure requirements, and potential scaling expenses as usage grows. Cloud pricing models typically involve subscription fees based on data volume, processing time, number of users, or API calls, which can result in significant ongoing operational expenses.
Long-Term Financial Implications
The long-term financial implications of each approach depend heavily on usage patterns, scaling requirements, and organizational priorities. For healthcare organizations with high-volume, continuous AI processing needs, built-in AI systems may provide better long-term value by eliminating recurring cloud service fees and reducing dependency on external providers.
Conversely, organizations with variable AI usage patterns, limited upfront capital budgets, or requirements for diverse AI capabilities may find cloud-based solutions more economically attractive. Cloud platforms offer the flexibility to scale services up or down based on actual usage, avoiding over-investment in hardware that may not be fully utilized.
The economic analysis must also consider indirect costs such as IT support requirements, system maintenance, security management, and regulatory compliance overhead. Built-in AI systems may require specialized technical expertise for maintenance and updates, while cloud-based systems may involve ongoing vendor management and data governance costs.
REGULATORY COMPLIANCE AND FDA CONSIDERATIONS
FDA APPROVAL PROCESSES FOR DIFFERENT AI ARCHITECTURES
The regulatory landscape for AI-enabled medical devices varies significantly depending on whether AI capabilities are embedded within devices or delivered through cloud services. The FDA has established specific guidelines and approval pathways for different types of AI medical devices, with distinct requirements for Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) that operates on edge devices versus cloud-based AI platforms.
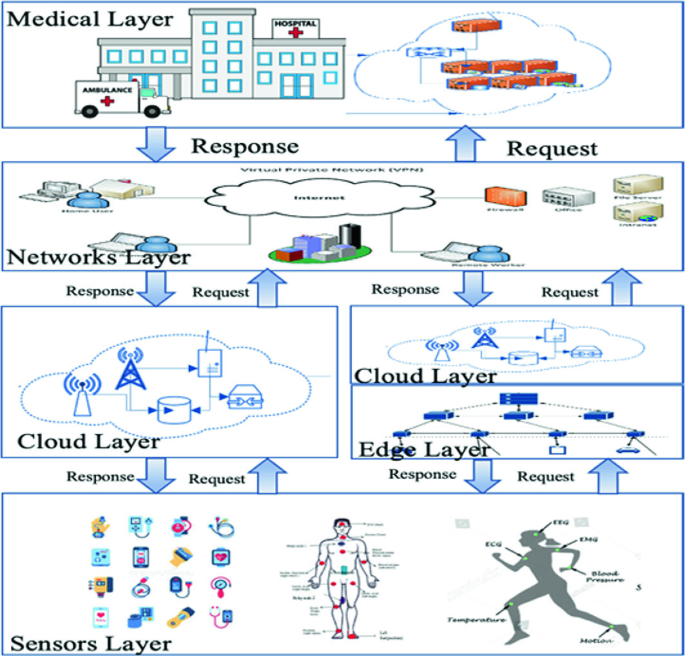
Built-in AI medical devices typically undergo traditional FDA medical device approval processes, including 510(k) premarket notification or Premarket Approval (PMA) procedures. These devices are evaluated as complete systems where the AI algorithms, hardware components, and clinical applications are assessed together as integrated medical devices. The FDA evaluates the safety and effectiveness of the entire system, including AI model performance, hardware reliability, and clinical outcomes.
The regulatory process for built-in AI devices often involves comprehensive clinical validation studies, performance benchmarking against existing diagnostic methods, and detailed documentation of AI algorithm training, validation, and testing procedures. Once approved, these devices can operate independently without requiring additional regulatory approvals for routine operation.
Cloud-based medical AI systems face more complex regulatory considerations due to the separation between data collection devices and cloud-based AI processing platforms. The FDA has developed specific guidance for Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) that operates in cloud environments, addressing issues such as algorithm updates, data security, and change control procedures.
CHANGE CONTROL AND CONTINUOUS LEARNING REGULATIONS
One of the most significant regulatory challenges facing cloud-based AI systems involves change control and continuous learning capabilities. While cloud platforms offer the technical ability to continuously update AI models based on new data and improved algorithms, FDA regulations require careful oversight of any changes that could affect device safety or effectiveness.
The FDA has introduced Pre-Cert programs and Digital Health Software Precertification (Pre-Cert) pilot programs specifically designed to address the unique challenges of regulating continuously updating AI systems. These programs aim to provide regulatory frameworks that allow for responsible innovation while maintaining patient safety standards.
Built-in AI systems offer regulatory advantages in terms of change control since updates typically require formal regulatory review and approval processes. This approach provides greater regulatory certainty but may limit the ability to rapidly incorporate new medical knowledge or respond to emerging clinical needs.
CLINICAL INTEGRATION AND WORKFLOW IMPACT
SEAMLESS INTEGRATION WITH EXISTING CLINICAL WORKFLOWS
The choice between built-in and cloud-based medical AI significantly impacts clinical workflow integration and user experience. Built-in AI systems often provide more seamless integration with existing clinical workflows since they operate as self-contained units that don’t require additional network connectivity, user authentication, or external system dependencies.
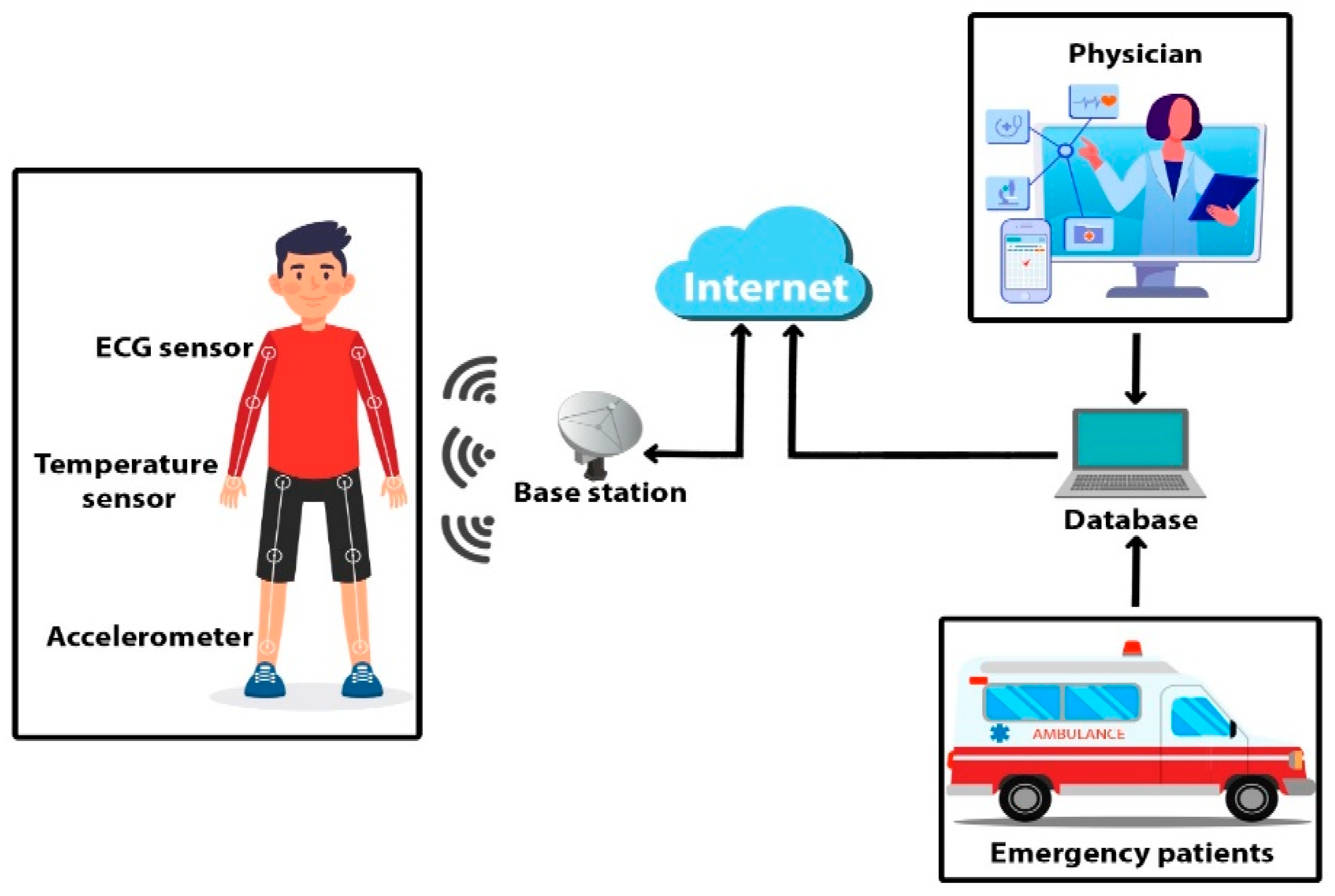
Healthcare professionals can interact with embedded AI capabilities through familiar device interfaces without needing to learn new cloud-based applications or manage additional system logins. This integration simplicity can improve clinical adoption rates and reduce training requirements for healthcare staff.
Built-in AI systems also offer greater reliability in clinical environments where network connectivity may be intermittent or restricted. Emergency departments, operating rooms, and remote clinical locations can benefit from AI capabilities that don’t depend on external network access or cloud service availability.
Multi-Device Integration and Data Aggregation
Cloud-based medical AI systems excel in scenarios requiring integration across multiple devices, healthcare systems, and clinical locations. These platforms can aggregate data from diverse medical devices, electronic health records, laboratory systems, and imaging equipment to provide comprehensive clinical insights that wouldn’t be possible with individual embedded AI systems.
The ability to correlate information across multiple data sources enables cloud-based AI to provide more comprehensive diagnostic insights, identify complex patterns spanning multiple clinical domains, and support population health management initiatives. This integration capability is particularly valuable for chronic disease management, preventive care programs, and clinical research applications.
Cloud platforms also facilitate collaboration between healthcare providers, specialists, and research institutions by providing shared access to AI capabilities and clinical insights. This collaborative approach can improve care coordination and enable more comprehensive treatment planning.
TECHNOLOGY EVOLUTION AND FUTURE CONSIDERATIONS
EMERGING HYBRID ARCHITECTURES
The future of medical AI deployment is likely to involve hybrid architectures that combine the benefits of both edge and cloud computing approaches. These hybrid systems might incorporate basic AI capabilities embedded within medical devices for real-time processing and emergency response, while utilizing cloud-based platforms for complex analytics, model training, and population-level insights.
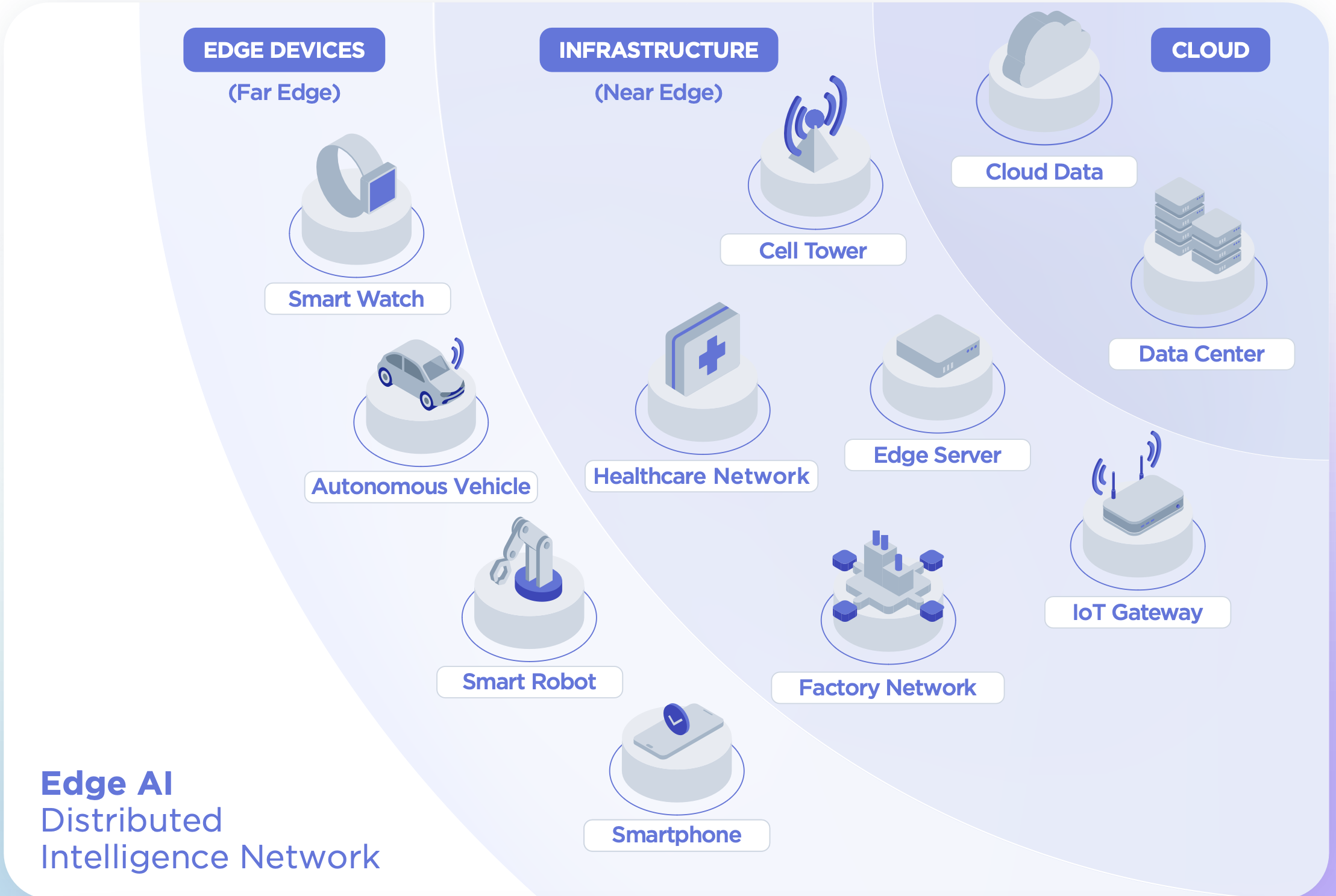
Emerging technologies such as 5G networks, edge cloud computing, and federated learning are enabling new deployment models that bridge the gap between pure edge and cloud approaches. These technologies allow for low-latency cloud connectivity, distributed AI processing, and collaborative learning while maintaining data privacy and local processing capabilities.
The development of more powerful embedded processors, specialized AI chips, and efficient neural network architectures is also expanding the capabilities of built-in AI systems. Future medical devices may be able to run increasingly sophisticated AI models locally while maintaining real-time performance and low power consumption.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE MODEL COMPLEXITY AND ADVANCEMENT
As AI models become more sophisticated and capable, the computational requirements for advanced medical AI applications continue to grow. Large language models, multi-modal AI systems, and complex neural networks that can process medical imaging, natural language, and sensor data simultaneously may require computational resources that exceed what individual medical devices can reasonably accommodate.
This trend toward AI model complexity suggests that cloud-based platforms will continue to play important roles in delivering cutting-edge AI capabilities to healthcare applications. However, advances in chip technology, compression algorithms, and model optimization techniques may enable more sophisticated AI capabilities to be deployed on edge devices in the future.
STRATEGIC DECISION FRAMEWORK
EVALUATING USE CASE REQUIREMENTS
Healthcare organizations and medical device manufacturers must carefully evaluate their specific use cases, clinical requirements, and operational constraints when choosing between built-in and cloud-based AI approaches. Critical considerations include latency requirements, data privacy needs, regulatory constraints, scalability requirements, and integration complexity.
Applications requiring real-time response, operating in network-constrained environments, or handling highly sensitive data may benefit from built-in AI approaches. Conversely, applications requiring complex analytics, multi-device integration, or frequent model updates may be better suited for cloud-based platforms.
IMPLEMENTATION BEST PRACTICES
Successful implementation of either approach requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and ongoing management. Organizations should develop comprehensive AI governance frameworks, establish clear data management policies, and implement robust security measures regardless of the deployment model chosen.
Healthcare providers should also consider the importance of vendor relationships, long-term support capabilities, and technology roadmap alignment when selecting AI deployment strategies. The chosen approach should align with organizational strategic objectives, technical capabilities, and long-term growth plans.
CONCLUSION
The choice between built-in and cloud-based medical AI represents one of the most important strategic decisions facing healthcare organizations today. Both approaches offer distinct advantages and limitations that must be carefully evaluated in the context of specific clinical applications, organizational requirements, and regulatory constraints.
Built-in AI excels in applications requiring real-time processing, maximum data privacy, and independence from network connectivity. These systems provide predictable performance, enhanced security, and seamless clinical workflow integration, making them ideal for critical care applications, emergency medicine, and point-of-care diagnostics.
Cloud-based AI platforms offer superior scalability, continuous learning capabilities, and access to cutting-edge AI technologies that would be impossible to deploy on individual devices. These systems enable comprehensive data integration, collaborative care delivery, and rapid deployment of new AI capabilities, making them valuable for population health management, clinical research, and complex analytical applications.
The future of medical AI deployment will likely involve thoughtful combinations of both approaches, leveraging the strengths of each model to create comprehensive AI ecosystems that optimize patient care, clinical efficiency, and healthcare outcomes. Healthcare organizations that carefully evaluate their specific needs, develop comprehensive AI strategies, and implement appropriate deployment models will be best positioned to realize the transformative potential of artificial intelligence in healthcare.
As AI technology continues to evolve, the distinctions between edge and cloud computing may blur, with hybrid architectures and new deployment models emerging to address the diverse needs of healthcare applications. The key to success lies in maintaining focus on patient outcomes, clinical effectiveness, and healthcare value while leveraging the most appropriate AI deployment strategies for each specific application and environment.
